Biology Chapter 12 Notes Paleontologists use fossils to reconstruct
advertisement

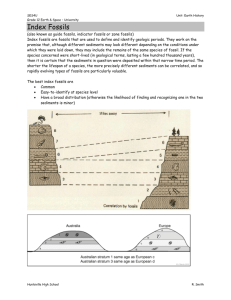
Biology Chapter 12 Notes Paleontologists use fossils to reconstruct the history of life and what happened in the past. ____Fossils__ – a record of life that existed in the past Most fossils form in ___sedimentary___ rock. The best environments for any type of fossilization include wetlands, bogs, and areas where sediment is continuously deposited, such as _____mouth______ of ______rivers______, ____lakebeds______, and _____floodplains____. Processes that produce fossils: 1.____Permineralization___ - occurs when minerals carried away by water are deposited around a hard structure (may replace the hard structure itself) 2. __Natural casts___ - form when flowing water removes all of the original bone or tissue, leaving just an impression in sediment – minerals fill in the mold recreating the original shape of the organism 3. __Trace fossils__ - record the activity of an organism – include nests, burrows, imprints of leaves, and footprints. 4. ___Amber__-__preserved fossils____ - are organisms that becomes trapped in tree resin that hardens into amber after the trees gets buried underground 5. ___Preserved remains __ - form when an entire organism becomes encased in material such as ice or volcanic ash or immersed in bogs *Scientists use one of two methods to determine how old fossils are: Relative dating – determining whether an event or object, such as a fossil, is older or younger than other events or objects Radiometric dating – determining the age of an object or event in years by looking at the _isotopes___ that are found in materials * Isotopes are atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons __Half-life__– the time it takes for half of the __isotope__ in a sample to break down into its different form Radiometric dating results suggest that the Earth is __4.5 billion__ years old. __Index fossils _ are another tool for determining the ages of fossils and rock layers. These are fossils of organisms that existed only during _specific__ spans of time and lived in large _geographic areas_. They would be found in rock. Geologic Time Scale – calendar scientists use to outline the history of life on Earth After a fossil has been dated using relative or radiometric dating techniques, a paleontologist can place the fossil in chronological order with other fossils – this helps form a picture of the past *The time scale is made of __3_ basic units of time: 1. __Era__ - last tens to hundreds of ___millions___ of years and have 2 or more periods. 2. __Periods___ - are the most __commonly___ used units of time, they last tens of __millions__ of years. 3. _Epochs_ - are the _smallest_ unit of geologic time, they last several _million_ years. The names for the 3 eras came from early ideas about fossils. Paleozoic means __ancient life______ Mesozoic means _middle life_____ Cenozoic means ___recent life____ *Scientists hypothesize that life developed from nonliving matter – it started from the chemicals that already existed in the environment Energy present in the early Earth caused these chemicals to react with one another, forming the complex molecules that made life possible *These small complex molecules are thought to have joined together to form larger molecules and these larger molecules combined to form more complicated structures – these eventually became the first true cells, prokaryotes - lack a nucleus – these cells were anaerobic (they didn’t require oxygen) * The earliest fossils of photosynthetic life are _3.5 billion__ years old. These fossils are of __cyanobacteria___. *These organism produced oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis – this was released into the _atmosphere___and into the _ocean__ which allowed for the evolution of organisms that use oxygen. __eukaryotic__ cells evolved by _1.5 billion_ years ago. Most scientists agree that the evolution of eukaryotes involved _endosymbiosis__. (a relationship in which one organism lives within the body of another, and both benefit) The theory of endosymbiosis is based on several characteristics of both __mitochondria___ and __chloroplasts___. The first prokaryotes and the first eukaryotes reproduced _asexually____. __Sexual reproduction_ requires more time and energy, but increases ___genetic variation_. *Multicellular organisms first appeared during the _Paleozoic__ era, which began __544 million___ years ago. Early during this time period a huge diversity of _animal species_ __ evolved. (Cambrian explosion) Early Paleozoic era- all life was _in the ocean___. Mid Paleozoic era – life _moved onto land__. Near the end of the Paleozoic era – the remains of millions of organisms were buried in sediment. (became coal and petroleum) The _Mesozoic___ era began _248__ million years ago and ended 65 million years ago. It is often called the __Age of Reptiles___, because dinosaurs lived during this time. Divided into 3 periods: _the _Triassic__, __the Jurassic__, __the Cretaceous___ The first mammals evolved during the Triassic_. A __mass extinction_ ended the Triassic and was followed by the radiation of the dinosaurs in the __Jurassic period__. In the __Cretaceous period__, __dinosaur___ diversity was at its greatest. A _meteorite_ struck Earth near the end of the Cretaceous period, leading to another mass extinction and the end of the _Cretaceous period__. The _Cenozoic__ era began 65 million years ago and continues _today___. It is sometimes called the _Age of Mammals__, because many kinds of mammals evolved during this time. It is divided into 2 periods: __Tertiary____ and _Quaternary__. * Humans are one of the __primates__, a category of mammals that share particular traits which include: 1. Flexible hands and feet 2. Forward-looking eyes, allow for excellent 3-D vision 3. Large brain relative to body size 4. Arms that can rotate in a circle 5. Thumbs that can move against their fingers 6. Similar to each other at the molecular level There are 2 main groups of primates that share a common ancestor: prosimians, which are the oldest living primate group Anthropoids, which are the humanlike primates Humans are classified as _hominids_. * The evolutionary histories of organisms can be represented by a branching tree. Each place a branch splits represents a _evolution_ event. * Animals that can walk on 2 legs are called _bipedal____. * Most hominid species are classified into 2 groups: the genus Australopithecus and the genus Homo. * Australopithecus atarensis lived 3 to 4 million years ago. Its brain was smaller than modern humans, but it had humanlike __limbs__. * Homo habilis is the earliest know member of the genus Homo, and lived ___2.4 – 1.5 million_ years ago. This was the earliest known hominid to make stone tools. *Homo neanderthalensis, commonly called _Neanderthals_, lived from 200 – 300 thousand years ago, possibly at the same time as Homo sapiens * The first Homo sapiens lived around __100,000__ years ago.