Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction
advertisement

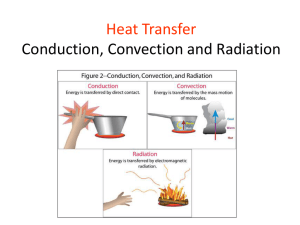
Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation Notes • Heat always moves from a ________________ place to a _____________ place. • Hot objects in a cooler room will _____________ to room temperature. • Cold objects in a warmer room will __________ __________ to room temperature. • Heat transfers in three ways: • ____________________ • ____________________ • ____________________ Conduction As you heat the metal, the particles vibrate, these vibrations make the adjacent particles vibrate, and so on and so on, the vibrations are passed along the metal and so is the heat. We call this? _______________________ The outer e_____________ of metal atoms drift, and are free to move. When the metal is heated, this ‘sea of electrons’ gain k_________ energy and transfer it throughout the metal. Insulators, such as w_________ and p_______________, do not have this ‘sea of electrons’ which is why they do not conduct heat as well as metals. Convection Air and Water Movement What happens to the particles in a liquid or a gas when you heat them? The particles __________out and become ___________dense. Cooler, more d__________, fluids sink through w___________, less dense fluids. In effect, warmer liquids and gases r______ up. Cooler liquids and gases s______. Convection currents are formed as water warms; warm water rises and cool water sinks. Air works the same way; the cold air form the sea moves in to take the warm air that has risen. Where is the freezer compartment put in a fridge? It is put at the ___________, because cool air __________, so it cools the food on the way down. It is ____________at the bottom, so this warmer air ____________ and convection current is set up. Radiation How does heat energy get from the Sun to the Earth? There are __________ __________ between the Sun and the Earth so it CANNOT travel by _____________________or by ______________________. Radiation is energy leaving in the form of an electromagnetic ___________ (such as light). Radiation is the _______________form, but it is impossible to stop. Radiation travels in __________ ___________and can travel through a ________ (for example, air). Emitting (Releasing) Heat Four containers were filled with warm water. Which container would have the warmest water after ten minutes? The _______________ _______________ container would be the warmest after ten minutes because its shiny surface reflects heat _____________ back into the container so less is lost. The ________ ___________ container would be the coolest because it is the best at _______________ heat radiation. Absorbing Heat Four containers were placed equidistant from a heater. Which container would have the warmest water after ten minutes? The ____________ ____________ container would be the warmest after ten minutes because its surface absorbs heat _______ the best. The _________ ________container would be the coolest because it is the poorest at __________ heat radiation. Questions Why does hot air rise and cold air sink? Why are boilers placed beneath hot water tanks in people’s homes? Why are houses painted white in hot countries? Why are shiny foil blankets wrapped around marathon runners at the end of a race? In which of the following are the particles closest together? How does heat energy reach the Earth from the Sun? Which is the best surface for reflecting heat radiation? Which is the best surface for absorbing heat radiation?