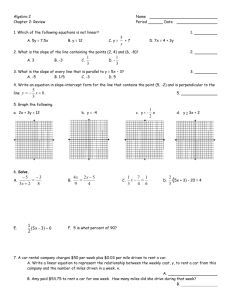
Module 2: Psychology & Science Research Methods Each provides

1
Module 2: Psychology & Science
Each provides a different kind of information
Research Methods
_______________
way to obtain information by asking many individuals
answer a fixed set of questions about particular subjects
Disadvantages
information can contain errors
results can be biased
Advantage
efficient way to obtain much information from a large number of people
Case study
– an in-depth analysis of the thoughts, feelings, beliefs, experiences, behaviors, or problems of a
_______________ individual
– Disadvantage
– detailed information about a particular person may not apply to others
• Advantage
– detailed information allows greater understanding of a _______________ person’s life
• Example:
_______________: statement in support of a particular viewpoint based on detailed observations of a person’s own experience.
• Problems that make testimonials susceptible to error:
– personal beliefs
– self-_______________ prophecy.
Experiment
– a method for identifying cause-and-effect relationships by following a set of rules and guidelines that
_______________ the possibility of error, bias, and _______________ occurrences.
• Disadvantage
– information obtained in one experimental situation or laboratory setting may not apply to other situations
• Advantage
– has the greatest potential for identifying cause-and-effect relationships with less error and bias than either
_______________ or case studies
_______________
– intervention, such as taking a pill, that resembles medical therapy but which in fact, has no _______________ effects
• Placebo effect
– change in the patient’s illness that is attributable to an _______________ treatment rather than to a medical treatment
– researchers believe that placebos work by reducing tension and distress and by creating powerful selffulfilling prophecies
– individuals think and behave as if the drug, actually a placebo, is effective
Correlation
– an association or _______________ between the occurrence of two or more events
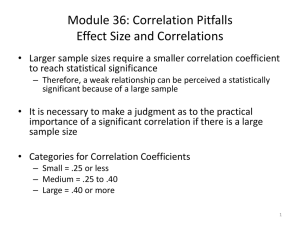
• Correlation _______________
– a number that indicates the strength of a relationship between two or more events: the closer the number is to –1.00 or +1.00, the _______________ is the strength of the relationship
• Perfect positive correlation coefficient
– +1.00 means that an increase in one event is always matched by an equal increase in a second event
• Positive correlation coefficient
– indicates that as one event tends to increase, the second event tends to, but does not always,
_______________
2
– increases from +0.01 to +0.99 indicate a strengthening of the relationship between the occurrence of two events
• _______________ correlation
– indicates that there is no relationship between the occurrence of one _______________ and the occurrence of a second event
• _______________ correlation coefficient
– indicates that as one event tends to increase, the second event tends to, but does not always, decrease
– -0.01 to -0.99 indicates a strengthening in the relationship of one event increasing and the other decreasing
• Perfect negative correlation coefficient
– -1.00 means that an increase in one event is always matched by an equal decrease in a second event
– correlations such as –1.00 are virtually never found in applied psychological research
– r= +0.37
_____=correlation coefficient, + indicates the direction of relationship & number indicates the strength (0.00 to 1.00)
Correlation vs. Causation
Correlations cannot indicate cause-and –effect relationships; however, correlations:
help ______________ behavior
point where to look for possible causes
Decisions About Doing Research
_______________: technique for obtaining information by asking questions, ranging from _______________-ended to highly structured, about a subject’s behaviors and attitudes, usually in a one-on-one situation
Questionnaire: technique for obtaining information by asking subjects to read a _______________ of written questions and check off specific answers
• Laboratory experiments: techniques to gather information about the brain, genes, or behavior with the least error and bias by using a_______________environment that allows careful observation and measurement
• _______________ tests: technique to obtain information by administering a psychological test that has been given to
_____________ of people and shown to reliably measure thought patterns, personality traits, emotions, or behaviors
• _______________ Models: involves examining or manipulating some behavioral, genetic, or physiological factor that closely approximates some human problem, disease, or condition
Choosing research settings
• _______________ setting: relatively normal environment in which researchers gather information by observing individuals’ behaviors without attempting to change or control the situation
• Laboratory setting: involves studying individuals under systematic and controlled conditions, with many of the realworld influences eliminated
Scientific Method: Experiment
– approach of gathering information and answering questions so that errors and biases are minimized
• Rule 1: Ask
– ______________: educated guess about some phenomenon stated in precise, _______________ language to rule out any confusion or error in the meaning of its terms
• Rule 2: Identify
– _______________ variable
• a treatment or something that the researcher controls or manipulates
– _______________ variable
• one or more of the subjects’ behaviors that are used to measure the potential effects of the treatment or independent variable
• Rule 3: Choose
– _______________ selection
• each participant in a sample population has an _______________ chance of being selected for the experiment
• Rule 4: _______________
– experimental group
• those who receive the treatment
• _______________ group-participants who undergo all the same procedures as the experimental participants except that the control participants do not receive the treatment
• Rule 5: Manipulate
– double _______________ procedure
• neither participants nor researchers know which group is receiving which treatment
• Rule 6: Measure
– by manipulating the treatment so that the experimental group receives a different treatment than the control group, researchers are able to measure how the independent variable (treatment) affects those behaviors that have been selected as the dependent variables
• Rule 7: _______________
– statistical procedures
• used to determine whether differences observed in dependent variables (behaviors) are due to independent variables (treatment) or to error or chance occurrence
Application: Research Concerns
• Concerns about being a subject
– human and animal
• Code of _______________
– the American Psychological Association publishes a code of ethics and conduct for psychologists to follow when doing research, counseling, teaching, and related activities
• Role of _______________
– one way that researchers control for participants’ expectations is to use bogus procedures or instructions that _______________ participants from learning the experiment’s true purpose
– Researchers must debrief study subjects-explain the purpose & method
• Ethics of animal research
– How many animals are used in research?
• _______________ to 22 million animals are used each year in biomedical research
– Are research animals mistreated?
• Of the millions of animals used in research, only a_______________ cases of animal mistreatment have been confirmed.
• Ethics of animal research
– Is the use of animals justified?
• researchers are currently using animals to study epilepsy, _______________ disease, fetal alcohol syndrome, schizophrenia, AIDS, and transplantation of brain tissue, none of which is possible with human subjects
– Who checks on the use of animals in research?
• U. S. Department of _______________
• universities hire veterinarians
• universities have animal subject committees
• Ethics of animal research
– How do we strike a balance?
• many experts in the scientific, medical, and mental health communities believe that the conscientious and responsible use of animals in research is justified and should continue
Research Focus: ADHD
• Attention-deficit/_______________ disorder
• Diagnosed by occurrence of behavioral problems
• Must have six or more symptoms of _______________, such as careless mistakes on schoolwork
&
• _______________ or more symptoms of hyperactivity, talking excessively
• Controversial because
– accuracy & reliability diagnosis, based on reported behavioral symptoms, not medical tests
– treatment for: nondrug, behavioral or drug & behavioral treatment
– Long-term effects
3