K Unit of Study
advertisement

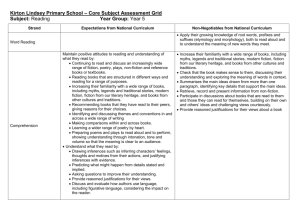
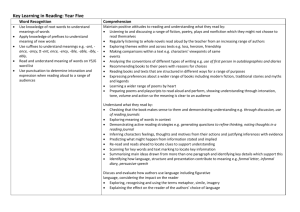
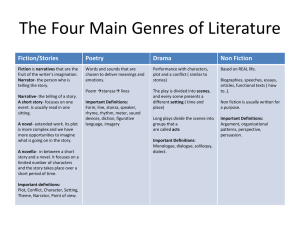
Backwards Design for Unit of Study: Kindergarten Big Ideas: Enduring Understanding Throughout the unit, students will learn about the roles and responsibilities of community members inside and outside of the school setting. Students will learn how to be a successful friend and student at school by recognizing appropriate behaviors and interactions. Students will learn about how text is organized for narrative and informational and how that structure helps communicate meaning. Essential Question How is a fiction text organized? How is the story and/or information presented through words and pictures? How can we communicate our ideas using consistent concepts of print? What roles and responsibilities do community members have inside and outside of a school setting? Guiding Questions How do the pictures help you know the characters and the setting? What are the characters problems and events in the story? How are the beginning, middle, and end different? What makes you think that this text is fiction/non fiction? How do the illustrations and words tell the story? What does an author do? What does an illustrator do? How do you get information from a text? How do I make sense of my reading? Possible Misconception(s) Different genres: Fiction/Non fiction and their features (Fiction= story/ Non fiction= teaches and provides information) Relationship between words and illustrations and how they connect to tell a story and provide information What is a community? How does this connect to me? Learning Target: KNOW? o Fiction structural elements: character, setting, beginning, middle, end, problem, solution o Varying genres: Fiction- Non Fiction o Authors and illustrators purpose o Relationship between text and illustrations and Learning Target: DO? o Describe structural elements o Identify different types of texts (fiction vs. non fiction) o Explain what the author and illustrator do o Use the pictures in the story to figure out what is happening in the story 1 how they work together to tell a story or present information o What is a community? o Identify a community and determine the roles and responsibilities of its members. Culminating Activity: Students are able to communicate their understanding of how text is organized by using visual art and speaking to represent their thinking. They will create a visual representation of their classroom community in a story that includes character(s), settings, roles, and responsibilities. They will present and describe the characters, setting, and what the people in the community did. Students will identify that they were illustrators by creating the visual and an author when they are describing their work. What will mastery/success look like? Visual is made with various art supplies: drawing, painting, collage, etc. Setting and Characters are identifiable Student orally explaining his/her work or label pictures Indicators? Student name Multiple colors Character(s) Setting When prompted, students can identify when they were the author and illustrator 2 Standards Student Outcomes English Language Arts RL.K.1 With prompting and support, ask and answer questions about key details in a RL.K.3, RL.K.5, RL.K.7, RI.K.6 Structure of text. Text RL.K.3 With prompting and support, identify characters, settings, and major events Identify structural elements: character, in a story. setting, and major events RL.K.4 Ask and answer questions about unknown words in a text. (problem/solution) RL.K.5 Recognize common types of texts (e.g., storybooks, poems). Identify different types of texts (fiction RL.K.7 With prompting and support, describe the relationship between illustrations vs. non fiction) and the story in which they appear (e.g., what moment in a story an illustration Explain what the author and illustrator depicts). do RI.K.1 With prompting and support, ask and answer questions about key details in a text. RI.K.2 With prompting and support, identify the main topic and retell key details of a text. RI.K.4 With prompting and support, ask and answer questions about unknown words in a text. RI.K.5 Identify the front cover, back cover, and title page of a book. RI.K.6 Name the author and illustrator of a text and define the role of each in presenting the ideas or information in a text. RF.K.1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print. a. Follow words from left to right, top to bottom, and page by page. b. Recognize that spoken words are represented in written language by specific sequences of letters. c. Understand that words are separated by spaces in print. d. Recognize and name all upper- and lowercase letters of the alphabet. RF.K.2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes). 3 RF.K.1 Foundational Literacy Concepts Print Concepts Left to right Space between words Letters represent words Punctuation Capitalization Alphabetic principles:letter sound match a. Recognize and produce rhyming words. b. Count, pronounce, blend, and segment syllables in spoken words. c. Blend and segment onsets and rimes of single-syllable spoken words Recognizing upper case and lower case letters. Recognizing letter sounds Speaking and Listening SL.K.1 Discussion Norms – Accountable Talk SL.K.1 Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about Turn Taking kindergarten topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. Accountable Talk Stems a. Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., listening to others and Ask and answer questions taking turns speaking about the topics and texts under discussion). Share thinking b. Continue a conversation through multiple exchanges. SL.K.2 Confirm understanding of a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media by asking and answering questions about key details and requesting clarification if something is not understood. SL.K.3 Ask and answer questions in order to seek help, get information, or clarify something that is not understood. SL.K.4 Describe familiar people, places, things, and events and, with prompting and support, provide additional detail. SL.K.5 Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional detail. SL.K.6 Speak audibly and express thoughts, feelings, and ideas clearly. Writing W.K.1 Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose opinion pieces in which they tell a reader the topic or the name of the book they are writing about and state an opinion or preference about the topic or book (e.g., My favorite book is...). W.K.3 Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to narrate a single event or several loosely linked events, tell about the events in the order in which they 4 W.K.3 Narrative Writing Refine and share their knowledge through writing and speaking Observe and participate in all stages of the writing process Draft occurred, and provide a reaction to what happened. W.K.5 With guidance and support from adults, respond to questions and suggestions from peers and add details to strengthen writing as needed. W.K.6 With guidance and support from adults, explore a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in collaboration with peers. W.K.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., explore a number of books by a favorite author and express opinions about them). L.K.1 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Print many upper- and lowercase letters. b. Recognize and name end punctuation c. Form regular plural nouns orally by adding /s/ or /es/ L.K.2 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. a. Capitalize the first word in a sentence and the pronoun I b. Recognize and name end punctuation. c. Write a letter or letters for most consonant and short-vowel sounds (phonemes). d. Spell simple words phonetically, drawing on knowledge of sound-letter relationships. STRAND : History Content Standard I: Students are able to identify important people and events in order to analyze significant patterns, relationships, themes, ideas, beliefs, and turning points in New Mexico, United States, and world history in order to understand the complexity of the human experience. K-4 Benchmark I-B—United States: Understand connections among historical events, people, and symbols significant to United States history and cultures. K.1. Demonstrate an awareness of community leaders. 5 Revise Edit Publish Use the pictures in the story to figure out what is happening in the story LK.1, LK.2 Use of Conventions in speaking and writing. Correct letter formation of most upper and lower case letters. Correct use nouns, plural nouns, and verbs Capitalize first word in sentence and /I/ Locate ending punctuation Alphabetic Principle: letter sound match SS History I-B.1 Community Learn that people must work together Communicate effectively Identify a community and determine the roles and responsibilities of its members. Integrated Instructional Framework Theme: Building a Classroom Community Unit Connection to Social Studies Culminating Task Throughout the unit, students will learn Students are able to communicate their understanding of how text is organized by about the roles and responsibilities of using visual art and speaking to represent their thinking. community member inside and outside of the school setting. Students will learn how to be They will create a visual representation of their classroom community in a story that a successful friend and student at school by includes character(s), settings, roles, and responsibilities. They will present and recognizing appropriate behaviors and describe the characters, setting, and what the people in the community did. Students interactions will identify that they were illustrators by creating the visual and an author when Social Studies Theme they are describing their work. Week 1: Getting to know my class Week 2: Community Members Week 3: Classroom Community: How to be a Friend Week 4: Classroom Community: How do we solve problems? Interactive Read Aloud (RL.K.3, RL.K.5, RL.K.7, RI.K.6) Instructional Practice Teacher Read-Alouds demonstrate the power of stories. By showing students how to engage with text, we give them energy for learning how reading works. By showing them how to search for meaning, we introduce strategies of understanding we can reinforce in shared, guided, and independent reading. Week Text Instructional Focus 1 Chrysanthemum by, Kevin Henkes Story Elements: Character & Setting Structure: Beginning, middle, end 2 Who Works Here? Structure: teaching us, giving facts Pearson: 1st Grade, Unit 1 Wk 3 Big Book Difference between fiction and non fiction Using the photos to get information 6 3 Miss Bindergarten Takes a Field Trip Pearson: Kinder,, Unit1 Wk4 Big Book 4 Ormie the Pig (Video) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EUmvAOmV1o Story Elements: Character & Setting Using the illustrations to make inferences Problem & Solution Connection- when have you experienced a problem? What was your solution? Interactive Read Aloud Structure 1. Introduce the book 2. Preview & Predict 3. Read Aloud- Pausing for interaction: Teacher Think Aloud: Model student objective, Student think pair share, Vocabulary discussed 4. Wrap Up & Relate: Student connect teacher modeling and student share out to objective For Detailed Tasks, Assessments, and Resources check: Daily Check-In & Integrated Cluster Task Quarter Standards: RL.K.5, RL.K.7 Cluster Standards: SL.K.1-6, RL.K.1, RL.K. 4, RL.K.10, L.K.6 Resources https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/pre-k-reading-comprehension Video Example: Kindergarten classroom read aloud routine https://readingrecovery.org/images/pdfs/Conferences/NC11/Handouts/Miller_Cathy.pdf Handout explain read aloud structure. Includes questions, prompts, and planning resources. Shared Reading with a Close Reading Focus (RL.K.3, RL.K.5, RL.K.7, RI.K.6) Instructional Practice Some of the texts will be stories from interactive read aloud. The purpose during interactive read aloud was to model comprehension and reading strategies where now purpose shifts to revisiting the text for deeper understanding. Week Text Focus 7 1 Chrysanthemum by, Kevin Henkes - Story Elements 2 The Big Bad Badman: 7 Habits of Happy Kids pg.67 - How the characters work together Text to Text Connection: Chrysanthemum 3 Timothy Goes to School by, Rosemary Wells 4 Miss Bindergarten Takes a Field Trip (week 2 big book) - Problem and Solution Author’s message How the illustrations support the text K-2 Weekly Template Shared Reading with Close Reading Focus Introduce Text Foundational Skills Close Reading Vocabulary Read for Evidence Development Picture Walk Read the book, model Read the book, model introducing the text. fluency and point to fluency and point to Focus on genre, words. Invite students words. Invite students structure, and book to join in the reading. to join in the reading. elements. Model read with Model read with Vocab – work on expression. expression. context clues in the All read with All read with text. expression together expression together pointing to words. pointing to words. Vocabulary: Choose 1 below as an instructional focus to Reread the passage support foundational looking for skills: _____________________ 8 Close Reading Look For Patterns Read the book, model fluency and point to words. Invite students to join in the reading. Close Reading Developing a new understanding Read the book, model fluency and point to words. Invite students to join in the reading. Model read with expression. All read with expression together pointing to words. Model read with expression. All read with expression together pointing to words. In small groups reread the passage and the evidence from Ask students to reread the passage. Review anchor chart evidence Read the book, model fluency and point to words. Invite students to join in the reading. Model reading with expression. All read together with expression pointing to words. Sight words – work on recognition in context, spelling. Spelling Patterns (phonics) in the book. If I know a spelling pattern I can make lots of words. Concepts of Print: Capital Letters, Punctuation Phonological Awareness: Rhyming, Alliteration, Syllables, On-Set and Rhyme (lens). Have students highlight text evidence. Chart student responses in the first column of an anchor chart. yesterday. Have students work in small or whole group and find which pieces of evidence fit together. Chart the patterns you find in the second column of your anchor chart. and patterns. Turn and Talk about noticing’s. Student Response – First I was thinking ______ now I am thinking _____ because…. For Detailed Tasks, Assessments, and Resources check: Quarter Standards: RF.K.1a-c, L.K.1a-c, RL.K.3, W.K.3 Cluster Standards: SL.K.1-6, RL.K.1, RL.K.4, RL.K.10, RI.K.1, RI.K.4, RI.K.5, RI.K.10, W.K.7, L.K.2, L.K.6 Resources Falling in Love with Close Reading: Lessons for Analyzing Texts- Life by, Christopher Lehman *See your IS to get book https://www.learninga-z.com/commoncore/close-reading.html Website explains Close Reading and helpful instructional strategies. http://youngteacherlove.blogspot.com/2015/01/understanding-close-reading-last-of.html Blog gives student friendly examples, anchor charts, and suggested routine http://www.readingrockets.org/content/pdfs/SharedReading.pdf 9 Handout explains shared reading structure. Includes description, setting, resources, types of materials, and process. Guided Reading (RF.K.1, RF.K.2, L.K.1) Students participate in small group differentiated instruction. Text is determined based on student reading level and strategy needs. Instruction for kindergarteners starts at Pre-A level is solely based on foundational skills and emergent reading strategies. Jan Richardson: Pre-A & Emergent lesson should be used Resources http://www.janrichardsonguidedreading.com Jan Richardson website includes many resources including printable lesson plans, visuals, word work activities, videos, and student work samples. http://teacher.scholastic.com/reading/bestpractices/guidedrea ding.htm Scholastic website authored by Gay Su Pinnel, leading researcher in guided reading. Provide background information, leveled book recommendations, and classroom structure. For guided reading presentations and more resources go to lcps.blackboard.comlog in go to LCPS all elementary PD Click on left menu “Elementary PD” Click on “Guided Reading” and see all the available resources. 10 Differentiated Centers Independent Reading Writing About Reading Word Sorts (Words Their Way) Sight Word Fluency Games Lexia Resources Jan Richardson, The Next Steps in Guided Reading, chapter. 1 pp. 6-37 Chapter explains how before small group instruction you must set up independent practices through center rotations. http://www.theschoolbell.com/Links/Dolch/Contents.html Sight Word Fluency Games and Activities https://www.thedailycafe.com/daily-5 The website introduce the Daily 5 structure for center rotation: Read to Self, Read to Someone, Work on Writing, Word Work, and Listening/Technology Assessment: Bi-Weekly Running Records Anecdotal Notes DRA at the end of the 9 week period Word Study (RF.K.1, RF.K.2, L.K.1) Word study should be included in guided reading, shared reading, read aloud, and/or mini lesson section as part of writer’s workshop. Word work skills can then become part of independent center work the following week. Whole Group Instruction: Word Wall/Name of the Day (5 minute quick practice) During the first nine weeks, teachers should use student names for word wall activities. Once student have can read, write, and identify letters in their name teachers can then use the same routine with high frequency words. 1) Write student name on paper 2) Read and name letters 3)Cut apart name and put in order 4) Add to word wall Whole Group Instruction: With Text Week Text 1 Friends- Poem Focus Recognize alliteration and rhyme 2 How To Help- Poem Count words and syllables 3 Family- Poem 4 With a Friend- Poem Recognize alliteration and rhyme Count words and syllables Blend and segment onset and rime Small Group: Word Study Word Sorts: Word Study Groups are based on Qualitative Spelling Inventory, Writing Samples, or Letter/Sound Assessments. Students are grouped according to their needs, not all students will be on the same sort. Use Word Sorts (Words Their Way books or teacher created sorts) to help students generalize learned spelling patterns. Once students have learned the sort and letter patterns, connect the skill to text by having students do a word hunt and collect words that follow the same pattern. They can find words in text or around the room and write them in their journals. (Teachers can create their own word sorts focusing on other spelling patterns.) Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 11 Day 4 Day 5 Introduce the word sort in small groups Students sort their words, check with self, partner or teacher Students do a Blind Sort or… Students do a Speed Sort Students do a Word Hunt in their guided reading book looking for words that contain the spelling feature. Assessment: Teacher gives students a writing sort with a few words from the sort and a few words that follow the pattern, but are not in the sort. Students can glue the sort into a journal For Detailed Tasks, Assessments, and Resources check: Quarter Standards: RF.K.1a-d, RF.K.2 a-c, L.K.1b,c Cluster Standards: SL.K.1-6 Resources Name of the Day Activities (Jan Richardson, Next Steps in Guided Reading pp.64) Name puzzles: names are written on an envelop and individual letters are put inside Build with magnetic letters: students builds name with letters Rainbow writing: student writes name with multiple colors http://www.readingrockets.org/article/word-study-instruction-k-2-classroom Teachers use a variety of hands on activities to help student explore the early phonological awareness and phonics skills including the letter sound relationships. http://www.readingrockets.org/strategies/blending_games These are games and activities to help teach blending and segmenting syllables and onset & rime. http://www.readingrockets.org/strategies/syllable_games Games/activities specific to syllables. http://www.readingrockets.org/strategies/onset_rime Games/activities specific to onset & rime. Whole Group Interactive Writing: (RF.K.1, RF.K.2,L.K.1, W.K.3) Student should be exposed to various writing instruction included modeled, shared, and interactive where the teacher facilitates but must also have opportunities for partner and independent writing throughout the literacy block. At this age, student may not always 12 move through all steps of the writing process (prewrite-draft-revise-edit-publish) yet through conversation and teacher modeling the students should begin to learn and experience that writing is a process. Week Predictable Chart: Topic Text Connection Focus 1 _________________ is my friend. Friends (poem) Personal narrative 2 I want to be a ______________ because ________________. How To Help! (poem) Opinion with explanation 3 I can _________________ at school. Timothy Goes to School (book) Personal narrative 4 My friend _____________ is ________________________. With a Friend (poem) Opinion with explanation Interactive Writing Structure Day 1 Day 2 1. Introduce Topic: _______ is my friend. (student who shared) 2. Model: Call on student: Mary is my friend. (Sarah) 3. Teacher records on page Day 3 Reread sentences physically tracking the print Cut apart and rebuild sentences Day 4 Day 5 Independent Writing Students are creating pages for class book based on predictable chart. For example: Students draw, label , or write about a time they played with a friend. For Detailed Tasks, Assessments, and Resources check: Quarter Standards: W.K.3, L.K.1 a, b, RF.K.1 a-d, RF.2.a-c Cluster Standards: RL.K.1, SL.K.1-6, W.K.1, W.K.5, W.K.6, W.K.7 Resources http://www.med.unc.edu/ahs/clds/files/how-to-handouts/PredChartWriting.pdf Shared writing activity resource to support emergent and conventional writers and readers. Provides structure while allowing students to generate their own ideas. 13 http://www4.esc13.net/uploads/low_incidence/docs/BTH2013/Friday/Jacobson_SharedPredictChartWriting.pdf Additional predictable resources including weeklong structure and topic ideas. 14