Reading strategies
advertisement

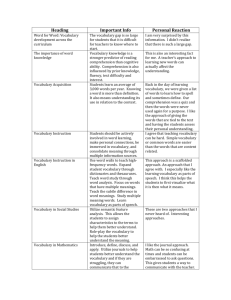
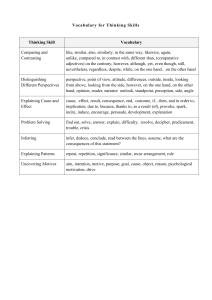
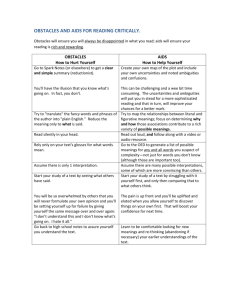
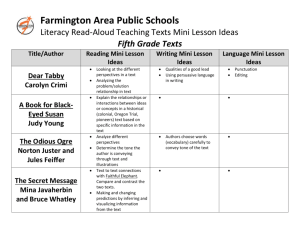
Plum Creek Literacy Festival 2013 Sectional: Dr. Vicki Anderson (9:00, 10:15) Where East and West Shall Meet: Teaching Reading Strategies to ELL/ESL Readers Reading is CONSTRUCTING MEANING FROM TEXT (of whole thoughts, not just individual words) Cue systems used in reading to construct the meaning of the whole text: • Graphophonic (visual information about orthography [spelling], knowledge of word sounds, knowledge of phonics) • Syntactic (how words go together; word functions [noun, verb, adjective, conjunction, etc.]) • Semantic (word meanings, phrase meanings, idiom meaning, etc..) Reading strategies ALL readers need to learn (and especially ELLs): • Sampling the text (so they know what is coming) • Predicting (using the cue systems, from letter to word to phrase to sentence to whole text level) • Inferring meaning (filling in knowledge by “educated guessing”) • Confirming and Disconfirming (checking if predictions were accurate, if text makes sense) • Integration (pulling info from all these strategies together to understand the meaning of the Context Cues to Infer Meaning from Context: • Reference (pronouns, demonstratives, definite articles, etc.) Example: The ________ creaked high on the rooftop. That was the scariest sound he had ever heard. • Contrast clues Example: Unlike a __________, a human being cannot stay for a long time underwater. • Punctuation Example: The __________, who is my next-door neighbor, likes to come over for coffee and cake. • Grouping Example: Shrimp, oysters, and _____ are all susceptible to a deadly bacteria known as “Red Tide.” • Restatement in the same or other clause Example: The judge _______ ; that is, she asked the defendant if he had any other evidence to submit. • Examples, illustrations, description To incorporate all these strategies, try this three-step approach to a text: Top-Down Approach: • Generating questions from title or picture • Activating vocabulary • Skimming for content, based on questions generated • Skimming for writer’s thesis Bottom-Up Approach: • Inferring meanings of words from context, looking up what is needed (vocabulary) • Understanding word parts (prefixes, suffixes, roots) • Understanding how language functions in context (idioms, grammar, etc.) Schema Interactive Approach: • Noting concepts of cohesion and coherence and connections between paragraphs • Inferring text purpose overall and purpose at the paragraph level and determining author bias, point of view, intended audience, etc.