Random( )
advertisement
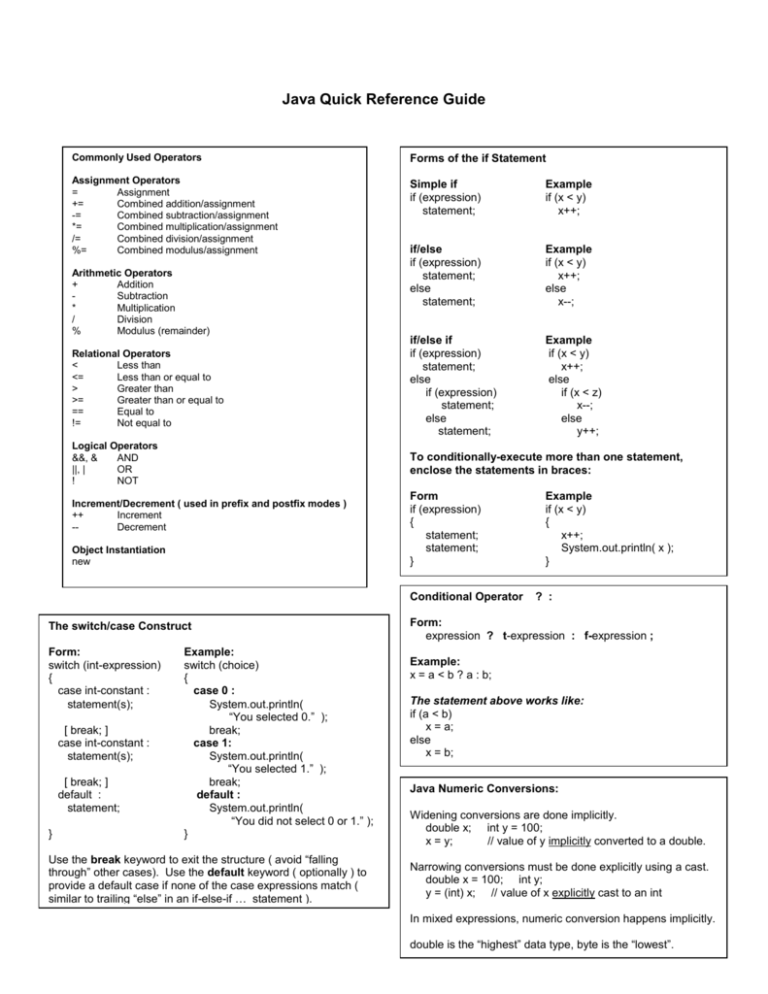
Java Quick Reference Guide
Commonly Used Operators
Forms of the if Statement
Assignment Operators
=
Assignment
+=
Combined addition/assignment
-=
Combined subtraction/assignment
*=
Combined multiplication/assignment
/=
Combined division/assignment
%=
Combined modulus/assignment
Simple if
if (expression)
statement;
Example
if (x < y)
x++;
if/else
if (expression)
statement;
else
statement;
Example
if (x < y)
x++;
else
x--;
Relational Operators
<
Less than
<=
Less than or equal to
>
Greater than
>=
Greater than or equal to
==
Equal to
!=
Not equal to
if/else if
if (expression)
statement;
else
if (expression)
statement;
else
statement;
Example
if (x < y)
x++;
else
if (x < z)
x--;
else
y++;
Logical Operators
&&, &
AND
||, |
OR
!
NOT
To conditionally-execute more than one statement,
enclose the statements in braces:
Arithmetic Operators
+
Addition
Subtraction
*
Multiplication
/
Division
%
Modulus (remainder)
Increment/Decrement ( used in prefix and postfix modes )
++
Increment
-Decrement
Object Instantiation
new
Form
if (expression)
{
statement;
statement;
}
Conditional Operator
The switch/case Construct
Form:
switch (int-expression)
{
case int-constant :
statement(s);
[ break; ]
case int-constant :
statement(s);
[ break; ]
default :
statement;
}
Example:
switch (choice)
{
case 0 :
System.out.println(
“You selected 0.” );
break;
case 1:
System.out.println(
“You selected 1.” );
break;
default :
System.out.println(
“You did not select 0 or 1.” );
}
Use the break keyword to exit the structure ( avoid “falling
through” other cases). Use the default keyword ( optionally ) to
provide a default case if none of the case expressions match (
similar to trailing “else” in an if-else-if … statement ).
Example
if (x < y)
{
x++;
System.out.println( x );
}
? :
Form:
expression ? t-expression : f-expression ;
Example:
x = a < b ? a : b;
The statement above works like:
if (a < b)
x = a;
else
x = b;
Java Numeric Conversions:
Widening conversions are done implicitly.
double x; int y = 100;
x = y;
// value of y implicitly converted to a double.
Narrowing conversions must be done explicitly using a cast.
double x = 100; int y;
y = (int) x; // value of x explicitly cast to an int
In mixed expressions, numeric conversion happens implicitly.
double is the “highest” data type, byte is the “lowest”.
The for Loop
Form:
Example:
for (initialization; test; update)
statement;
for (count = 0; count < 10; count++)
System.out.println ( count );
for (initialization; test; update)
{
statement;
statement;
}
for (count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
System.out.print( "The value of count is " );
System.out.println ( count );
}
The do-while Loop
The while Loop
Form:
Example:
Form:
Example:
do
do
statement
while (exp);
sum += x;
while (x < 100)
while (expression)
statement;
while (x < 100)
y = y + x++;
do
{
do
{
statement;
statement;
} while (expression);
y = x + 5;
x++;
} while (x < 100);
while (expression)
{
statement;
statement;
}
while (x < 100)
{
y = y + x;
x++;
}
Create an array:
<type> obj-ref-var [ ] = new <type>[size];
<type> obj-ref-var [ ] = { <initializer list> };
int myArray[ ] = new int[20];
//create[ an array of 20 elements.
int myArray[ ] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//create an array of 5 elements set to the values in the initializer list.
Create a 2 dimensional array:
<type> obj-ref-var[ ][ ] = new <type>[rows][columns];
<type> obj-ref-var [ ] = { { <initializer list> }, { <initializer list> }, { <initializer list> }, ... };
float myArray[ ][ ] = new float [ 10 ] [ 50 ];
//create a 2D array with 10 rows and 50 columns.
Create an array of Objects:
<class> obj-ref-var [ ] = new <class>[size];
Rectangle rectangle[ ] = new Rectangle[10];
//create an array of 10 references to Rectangles.
Store an object reference in an array:
rectangle[0] = new Rectangle( 5, 10 );
Access a method of an object reference in an array:
double area = rectangle[0].getArea( );
All arrays have a public field named length which holds the number of elements in the array. If x is a reference to a twodimension array, x.length is the number of elements in the first dimension of the array. x[n].length is the length of an array in
the second dimension.
myArray[a][b][c].length would be the length of an array in the 4th dimension of myArray.
Random class ( must import
java.util.Random )
Random( )
Constructor - creates a new pseudorandom number generator. Default seed value is the system time in milliseconds.
Random generator = new Random( );
float nextFloat( )
Returns a random number between 0.0 and 1.0 (exclusive).
y = generator.nextFloat( );
int nextInt( )
Returns a random number that ranges over all possible int values ( positive and negative ).
x = generator.nextInt( ) [ or x = generator.nextInt( 10 ) returns a value in the range 0..9 ]
Math class
( in the package java.lang )
abs ( int num )
Returns the absolute value of num.
y = Math.abs( y );
pow ( double num, double power )
Returns the value num raised to the specified power.
Double area = Math.PI * Math.pow( radius, 2 );
Math.PI 3.141592635…
random ( )
Returns a positive random number as a double value between 0.0 (inclusive) and 1.0 (exclusive)
Int value = ( int ) ( Math.random( ) * 6 ) + 1;
sqrt ( double num )
Returns the square root of num as a double value. The value of num must be positive.
System.out.println( "The square root of 1234 is: " + Math.sqrt( 1234 ) );
Java enhanced For Loop - used with Arrays
for ( <type> param : array of <type>)
{
statement using param
}
Each iteration of the loop, param takes on a value in the array
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------int [ ] array = new int[ 10 ];
int sum = 0;
Standard For loop:
for ( int i = 0; i < array.length; i++ )
{
sum += array[ i ];
}
Enhanced For loop:
for ( int i : array )
{
sum += i;
}








