4th Grade Art Curriculum
advertisement

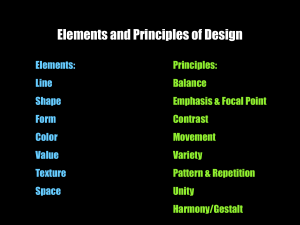
Content of Art Understanding and differentiating art, artists, and culture Using visual media to communicate or to express oneself Some topics include: Lives of artists, cultural differences in art, styles of art, careers in art Analyzing, interpreting, and critiquing art Some topics include: Local architecture, public sculpture, art exhibitions, historic work, student work Art Heritage Art Studio Art Criticism Aesthetics Some topics include: visual thinking, keeping sketchbooks, techniques of painting, 3-dimensional concepts, technology expression, graphic communication Valuing and understanding visual forms in natural and human environments Some topic include: The meaning of art, urban planning, historic preservation, environmental awareness Elements of Art Elements Line Shape Space Value Form Color Texture Examples Straight, wavy, spiral, vertical, horizontal, diagonal, curved, zig zag, implied lines, gesture drawing, actual lines, parallel lines, expressive lines, gesture lines, contour lines, crosscontour line, line qualities: thick, thin, broken, continuous, dotted, textures Organic shapes/free form; shapes; geometric shapes; diamond; oval; rectangle; triangle; circle; square; 2-dimensional Positive space; negative space; foreground; background; middle ground; overlapping; perspective; one point perspective; two point perspective; vanishing point; far away; depth; linear perspective; atmospheric perspective; close up Contrast; shading; highlight; tone; gradation; blending; stippling; hatching; crosshatching; hatching; shading Geometric forms; organic forms; simulated form; actual form; concave; convex; 3dimensional; cube; pyramid; sphere; cylinder; sculpture; sculptor; architecture; soft sculpture; found-object sculpture; assemblage; height; width; depth Hue; primary colors; secondary colors; intermediate colors; tertiary colors; mood; warm colors; cool colors; color scheme/families; tint; shade; intensity; monochromatic colors; analogous colors; complementary colors; neutral colors; pigment; translucent; opaque; color wheel Tactile texture; visual texture; actual texture; implied texture; rough; smooth Principles of Art Principles Emphasis Balance Pattern Rhythm Unity Variety Proportion Movement Art appreciation Examples Emphasis; focal point; dominance; contrast; main idea Radial balance; symmetrical balance; asymmetrical balance; formal balance; informal balance; informal balance; inverted symmetry Repetition Rhythm; regular rhythm; pattern; alternating rhythm; progressive rhythm; random rhythm Unity; harmony Variety; details Proportion; profile; three-quarter view; front view; distortion; exaggerated; scale; standard proportion; altered proportion Movement; motion; action; progressive movement; static movement; stopped action Art appreciation; critical method; description; analysis; interpretation; evaluation Careers in Art Industrial design; interior design; graphic design; illustration; computer-aided animation; landscape design; architecture; architect; illustrator; graphic designer Grade Level: 4th TEKS for Grade 4 (1) Perception. The student develops and organizes ideas from the environment. The student is expected to: (A) communicate ideas about self, family, school, and community, using sensory knowledge and life experiences; and (B) choose appropriate vocabulary to discuss the use of art elements such as color, texture, form, line, space, and value and art principles such as emphasis, pattern, rhythm, balance, proportion, and unity. (2) (A) (B) (C) Creative expression/performance. The student expresses ideas through original artworks, using a variety of media with appropriate skill. The student is expected to: integrate a variety of ideas about self, life events, family, and community in original artworks; design original artworks; and invent ways to produce artworks and to explore photographic imagery, using a variety of art media and materials. (3) (A) (B) (C) Historical/cultural heritage. The student demonstrates an understanding of art history and culture as records of human achievement. The student is expected to: identify simple main ideas expressed in art; compare and contrast selected artworks from a variety of cultural settings; and identify the roles of art in American society. (4) Response/evaluation. The student makes informed judgments about personal artworks and the artworks of others. The student is expected to: (A) describe intent and form conclusions about personal artworks; and (B) interpret ideas and moods in original artworks, portfolios, and exhibitions by peers and others. Project Resources: Optional Resources: Elements of Art Line-pages 256 Shape-page 256 Form-page 256 Space-page 256 Value-page 256 Color-page 256-257 Texture-page 257 Art-Grade 4. Illinois: Pearson, Scott Foresman, 2007 Books and Internet Sites-pages 284-287 Fine Art Images: Divided by Elements of Art and Principles of Design-pages 256-258 Fine Art Images: Divided by Techniques and Media-pages 258-260 List of Artists-pages 235-237 List of Artworks-pages 274-276 Pictorial Reference of Elements of Art-pages 220-226 Pictorial Reference of Principles of Design-pages 227-233 Picture Glossary-pages238-248 Student Safety-page 234 Teacher Glossary-pages 290-300 Teacher Safety-page 289 Technique Handbook-pages 264-273 Unit 1 Overview-pages 16a-16b Unit 2 Overview-pages 50a-50b Unit 3 Overview-pages 83a-83b Unit 4 Overview-pages 118a-118b Unit 5 Overview-pages 152a-152b Unit 6 Overview-pages 186a-186b Principles of Design Balance-page 257 Emphasis-page 257 Proportion-page 257 Pattern-page258 Rhythm-page 258 Unity-page 258 Variety-page 258 Educator Researched Information District, Regional, State, or National Professional Development Sources Assessment: Rubric- Teacher generated or from Unit by Unit Teacher Resource Booklet ( From adopted Textbook) Student evaluations written or oral Final Product