Chapter 9_Shea
advertisement

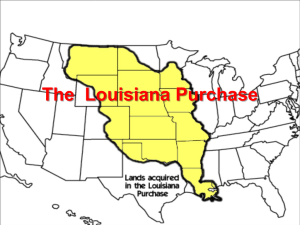
Mairin Shea Mr. Jackson APUSH Chapter 9 Terms and Dates Dates: 1803- Marbury vs. Madison case (the first case that the Supreme Court declared a federal law unconstitutional) 1804-1806- Journey of Lewis and Clark from St Louis to the Pacific and back. 1807-Emabrgo Act 1808- International slave trade is outlawed 1811- Battle of Tippecanoe 1814- Treaty of Ghent signed 1815-Battle of New Orleans Terms: Marbury v. Madison (1803)- The first U.S. Supreme Court decision to declare a federal law (the Judiciary Act of 1801) unconstitutional. Established that the Supreme Court was the one who decided whether or not laws were constitutional, not the state legislatures or the executive. Marbury had been sent a letter of appointment, or commission, as justice of the peace in DC by President Adams two days before he left office. It was still undelivered when Madison took office as secretary of state, and Jefferson directed him to withhold it. Marbury then sued for a court order directing Madison to deliver his commission. The Courts unanimous decision was that Marbury deserved his commission but denied that the court had jurisdiction in the case. (348-350) Chief Justice John Marshall- Chief Justice John Marshall (federalist) established a precedent of courts declaring a federal law invalid b/c it violates the Constitution. So even though Marbury never gained his judgeship, Marshall established the Supreme Court as the final judge of constitutional interpretation. Chief Justice from 1801-1835, over the course of five presidents. He established the foundations for American jurisprudence, the authority of the Supreme Court, and the constitutional supremacy of the national government over the states. (349-350) Barbary pirates-On the Barbary Coast of North Africa (Mediterranean Sea) the rulers of Morocco, Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli had for years practiced piracy and extortion. After the Revolution they captured American ships and enslaved the crews. The US govt had previously made blackmail payments but in 1801 the pasha of Tripoli upped demands and declared war on USA. War lasted 1801-1805. The US paid the ransom of $60,000 and the pasha released American crew. (351) Louisiana Purchase- (1803) Single greatest achievement of the Jefferson administration. It doubled the territory of the USA: comprised of the entire Mississippi River valley west of the river itself. Livingston went to Paris in 1801 as US minister to France. Negotiations went until 1803. Napoleon sold the Louisians Territory b/c needed money to finance war in Europe. Treaty of Cession 1803: US obtained Lousiana Territory for $15 million. It was a constitutional dilemma b/c nowhere in the Constitution did it mention purchase of territory. (352-353) “Corps of Discovery”-(1804-1806) Thomas Jefferson was eager to learn about west of the Mississippi. He assigned a group numbering almost 50 led by Lewis and Clark which set out from near St Louis to ascend the Missouri River. Met Native Americans, mapped, lived off the land, kept journals, etc. They were gone for nearly 2½ years. Important b/c their journals and discoveries led to the immense amounts of Americans traveling and settling West.(353-355) Aaron Burr- A New Yorker Federalist who was very extreme. Federalist Thomas Pickering hatched a scheme to link NY to New England through Burr. They needed him to be elected as governor of NY. Alexander Hamilton called him dangerous. In 1804 Hamilton and Burr had a duel. Hamilton was killed by a shot to the heart from Burr. This led to the end of Burr’s political career and Pickering’s scheme.(356) Impressment-The British navy used press gangs to kidnap men in British and colonial ports who were then forced to serve in the British navy. (361) Embargo Act-(1807)After the killing and kidnapping by the British of the Americans aboard the Chesapeake in 1807, Jefferson decided instead of rushing to war to promote “peaceable coercion.” 1807 he persuaded congress to pass the Embargo Act which stopped all exports of American goods and prohibited American ships from leaving for foreign ports. He intended for France and Britain to suffer. However, illegal trade flourished. Smugglers benefited while American ships sat idle. The British enjoyed a monopoly on legitimate trade. After 15 months of ineffectiveness, Jefferson accepted failure and repealed the embargo in 1809. (361) Tecumseh-A Shawnee leader who saw the clarity of the consequences of Native American disunity. He traveled from his base at Tippecanoe River to Canada to the Gulf of Mexico in an effort to form a confederation of tribes to defend Native American hunting grounds. While he was gone from his capital “Prophetstown” on the Tippeconoe River, his followers attacked Harrison and this demoralized the Native Americans who then fled to Canada. Tecumseh also fled to British protection in Canada. (364) William Henry Harrison-governor of the Indiana Territory. In 1811 he gathered troops to stop Tecumseh. He was attacked by Tecumseh’s followers. Only later did he realize he had inflicted a defeat on the Native Americans. (364) War hawks-in 1811 congressional members form the southern and western districts who clamoured for a war to seize Canada and Florida were dubbed “war hawks.” Among them were Henry Clay and Richard Mentor Johnson of Kentucky, and Felix Grundy of Tennessee. John Randolph of Roanoke christened these “new boys” the war hawks. (366) Battle of New Orleans-Major General Andrew Jackson had been busy shoring up the defenses of Mobile and New Orleans. He put an end to British efforts to organize Indian attacks on American settlements. He began to erect defensive abrrierson the approaches of New Orleans as the British fleet under General Sir Edwards Pakenahm took up positions just south of New Orleans. Pakenhams slow approach gave Jackson time to make good defenses. Pakenham was contemptuous of Jackson’s smaller multiethnic force. The assault was on January 8, 1815. The British lost. The Battle of New Orleans occurred after a peace treaty had been signed in Europe.(371) Treaty of Ghent-Americans wanted British to stop impressment and provide compensation for the seizure of American ships. British wanted territory in Maine and New York, removal of American warships from Great Lakes, etc. The US victory at Lake Champlain weakened British resolve. The Treaty of Ghent was signed Christmas Eve 1814.(372) Hartford Convention-While diplomats discussed peace in Europe, a different meeting was taking place in Hartford, CT. December 15, 1814, New Englander delegates held a convention to discuss limiting the Republican and southern influence. They wanted to abolish the counting of slaves in apportioning state representation in Congress, etc. (374). Their call for a later convention in Boston carried a threat of secession if the demands were ignored. The threat quickly evaporated as the news of Treaty of Ghent and New Orleans reached them and the Federalist party never recovered from the stigma of disloyalty stamped on it by the Hartford Convention. (374)