Minerals Study Guide: Definitions, Properties, and Uses
advertisement

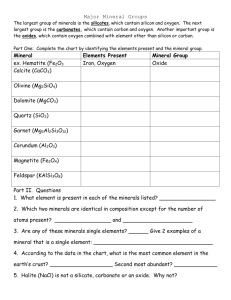
Study Guide Chapter 3 Minerals Quiz Friday 10/30 Name____________________________Parent Signature_______________________ STUDY FOR ATLEAST 30 MINUTIES & MEMORIZE THESE DEFINITIONS AND NOTES!! Mineral: a naturally formed, inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure Element: a substance that can NOT be seperated or broken down into simplier substances by chemical means Compound: a substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds Crystal: a solid whose atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in definite pattern Silicate Mineral: a mineral that contains a combination of silicon, oxygen, and one or more metals Non-Silicate Mineral: a mineral that does NOT contain compounds of silicon and oxygen Luster: the way in which a mineral reflects light Streak: the color of the power of a mineral Cleavage: the splitting of a mineral along smooth, flat surfaces Fracture: the manner in which a mineral breaks along either a curved or irregular surfaces Hardness: a measure of the ability of a mineral to resist scratching Density: the ratio of mass of a substance to the volume of the substance Ore: a natural material whose concentration of economically valuable minerals is high enough for the mineral to be mined profitably. Reclamation: the process of returning lands to its original condition after mining is completed. Minerals must be: o Non-living or inorganic o Solid o Have a crystalline structure o Be formed in nature Minerals can be either elements or compounds (2 or more elements). Mineral crystals are solid, geometric forms that are produced by repeating patter of atoms. Minerals are classified as Silicate minerals or Non-Silicate based on the elements of which they are composed (chemical composition) Silicates contain both Silicon & Oxygen and make up 90% of the Earth’s Crust. o Quartz o Mica o Feldspar Non-Silicates do not contain the combination of Silicon or Oxygen. They can contain one or the other but not both. o Native Elements-only made of 1 type of element o Carbonates o Halides o Oxides o Sulfates o Sulfides Properties that can be used to identify minerals are: o Color (not the best test) o Luster o Streak o Cleavage o Fracture o Hardness o Density o Special Properties-fluorescence, chemical reaction, magnetism, taste, radio activity (tested by Geiger Counter) Environments in which minerals form may be located at or near the Earth’s surface or deep below the surface. The two types of mining are surface mining and subsurface mining. o Surface Mines- Open Pit, Surface Coal Mines, Quarries o Sub-surface requires that a passage way be dug to reach the ore Two ways to reduce the effects of mining are the reclamation of mined land and recycling of mineral products Some Metallic and non-metallic minerals have important economic and industrial uses.