T1 Class Test for 3O2 - 3O23A2GEOG
advertisement

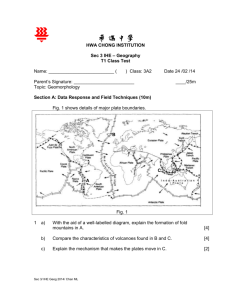
HWA CHONG INSTITUTION Sec 3 IHE – Geography T1 Class Test Name: __________________________ ( ) Class: 3O2 Date 26 /02 /14 Parent’s Signature: ________________________ Topic: Geomorphology ____/25m Section A: Data Response and Field Techniques (10m) Fig. 1 shows details of major plate boundaries. A C B Fig. 1 1 a) With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, explain the formation of fold mountains in A. [4] b) Compare the characteristics of volcanoes found in B and C. [4] c) Explain the formation of the Marianas Trench. [2] Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML Section B: Structured and Open Ended Questions (15m) 1) Explain the formation of the Hawaiian islands. [3] 2) Account for the presence of and risks of hydrothermal activity in the Yellowstone National Park area. [4] “People living in volcanic areas tend to focus on the benefits and overlook the hazards.” How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. [8] 3) Source Acknowledgement: 1a) Fig. A UCLA Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML Answers 1 a) With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, explain the formation of fold mountains in A. Eurasian Plate IndoAustralian plate b) Marks (1/2m) each: Plate movement: convergent Names of plates: IndoAustralian & Eurasian Compression/Sediments folded Fold Mtns: Himalayas Indo-Australian (Continental) plate converges w/ the Eurasian Indo-Australian subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate for a short distance Both plates are of same density, Compressing, contorting the edges / boundaries Sediments contorted and lifted to great heights forming the Himalayan Mtns Compare the characteristics of volcanoes found in B and C. B [4] Process Convection currents sink, causing the plates to collide Nazca Plate collides with the S. American Plate The thinner and denser oceanic descends beneath the continental plate: subduction occurs As the oceanic plate is subducted into the mantle, the edges are destroyed C Convection currents rise, causing the plates to move away from each other Magma rises through the cracks forming volcanoes Landforms The melting of subducting Volcanoes: Nyiragongo plate produces silica-rich magma It moves along cracks or fractures and escapes through vents to the land surface, forming a chain of Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML [4] volcanoes subduction volcanoes Volcanoes are steep and tall, Viscous lava Violent eruption c) Explain the formation of the Marianas Trench. Convection currents: movement within the mantle Material sinks into the mantle, leading the plates to collide As the Pacific Plate (oceanic) subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate (continental) A deep, long and narrow trench is formed Section B: Structured and Open Ended Questions (15m) 1) 2) Explain the formation of the Hawaiian islands. [3] In areas HOTSPOT Magma spreads out and melts lithosphere Rises though fractures, cools, solidifies and forms volcano after building up over time Plates moves and carries volcano with it Old volcanoes become extinct, grow denser with age and eventually sinks to form a seamount New volcano forms over new spot to eventually form a chain of volcanic islands (in this case, the Hawaiian islands) Account for the presence of and risks of hydrothermal activity in the [4] Yellowstone National Park area. Presence Hotspot area Magma comes from the mantle, Vast amount of viscous magma moving to the surface through fractures OR: Magma in the magma chamber heats up the water causing them to escape on the surface under immense pressure (gysers) Risks: Major eruption may occur, VEI 8 Regional and global proportions: would have an impact on the climate (block the sunlight, lower the temperature) Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML [2] 3) Animals, crops and people of immediate surrounding area would die Mass starvation, mass evacuation, Great impact on the world economy “People living in volcanic areas tend to focus on the benefits and overlook the hazards.” How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. [8] Answer Scheme for Open Ended Question: P1 Yes, people choose to live in volcanic areas due to the economic benefits (Agriculture) E Elaborate your answer… E L Give examples (and explain) on countries where violent eruption caused destruction (you may have 1 or 2 examples) Mt Etna: ash weathers into fertile soil = ideal for farming in the surroundings of Mt. Etna Nyiragongo: farmers benefit from the fertile soil – subsistence farming Java and Bali, Indonesia: supports the cultivation of crops: tea, coffee and rice – due to the most fertile soil area Mt. Pinatubo: ideal for rice growing: the volcano has not erupted since 1380 – so it has been a long term benefit In the 1991 eruption destroyed all crops on adjacent farmland, water supplies were cut off and became contaminated, buildings, roads, factories were completely destroyed. Not only did the eruption ruined the harvest in 1991, it made it impossible for 1992 1 million farm animals died due to starvation (lack of grass) Displacement of thousands of farmers and family Link back to the Qn: therefore, though the returns of good harvest attracted farmers to settle in the area, all was destroyed after the eruption. P2 E E Other economic activities, such as tourism are examples of long term benefits Because… Elaborate your answer… Geysers and volcanoes in Yellowstone Nat Park generates tremendous amount of revenue through tourists who visit the park every year (both local and foreign) Hot springs – are good for health, very popular in Korea and Japan (tourism) Precious stones: Kimberley in S. Africa (diamond trade) Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML L The ruins of Pompeii, Italy (popular tourist attraction): more than 3 million people visit the site every year Geothermal energy: Iceland – alternative energy: 70% of homes are heated by volcanic steam Warnings of volcanic eruptions will keep tourists away Ashes and lahars will destroy the infrastructure and roads, making it inaccessible and unsafe for tourists The after-effect may be long term as it takes time to rebuild the area or attractions Ash cloud from the Icelandic and Chilean volcanoes prevented / disrupted flights within the region – not only locals were affected, flights to neighbouring countries were also hindered Link back to the Qn: therefore, though the returns to the economy attracted many people to settle in the area, together with their buildings and industries, to be destroyed by the eruption. Environmental impact is important because the eruption can emit a tremendous amount of gases and particles which will be suspended in the atmosphere for a P3 long time, affecting not only the local area, but the region. E E L Elaborate your answer… The long term effect of ash in the atmosphere can also be observed in the weather Temperature measure after Mt. Pinatubo’s eruption showed that the average global temperature declined, causing a cooling effect. Though Pinatubo delayed global warming for several years, it is interesting to note that is may have a negative impact on the ozone layer The particles containing sulphur remains suspended in the atmosphere for several years They are important / contributes to the destruction of the ozone; enhancing ozone loss Link back to the Qn: Many people overlook the impact of eruptions on the environment. Conclusion: The long term benefits of living near volcanic areas far outweigh the risks and destruction caused by an eruption, which may not happen. Ironically the feature which benefits the population and area may also bring destruction. Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML Sec 3/ IHE Geog 2014/ Chan ML