Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
advertisement

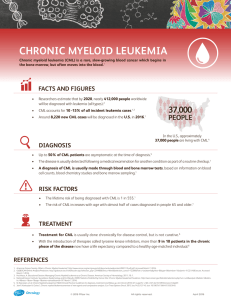
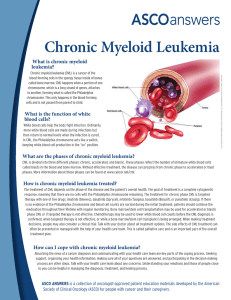
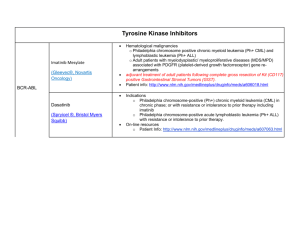
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia CML is one of four main types of leukemia. Hematologists and oncologists are specialists who treat people who have CML or other types of blood cancer. Most CML patients are treated with daily oral drug therapy. What Is CML? Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a cancer of the bone marrow and blood. CML is usually diagnosed in its chronic phase when treatment is very effective for most patients. CML is also called: chronic myelogenous leukemia chronic granulocytic leukemia chronic myelocytic leukemia. CML Phases chronic myeloid leukemia phase plays a large part in determining the type of treatment. CML has three phases: the chronic phase the accelerated phase the blast crisis phase Each phase describes CML's progression, determined by the number of blast cells - white cells that don't fully form as they should, blocking production of functioning blood cells - in the blood and bone marrow. Chronic Phase CML Most patients are diagnosed during CML's chronic phase when symptoms are mild or not noticeable. During this phase, the white cells can still fight infection. In most cases, long-term drug therapy can control chronic phase CML, and the patient can usually return to normal activities after treatment begins. A small number of people diagnosed and treated during the chronic phase progress to the accelerated phase. These patients appear to stop responding to treatment as the disease advances. Accelerated Phase CML If the patient is diagnosed during accelerated phase CML, the blood may have: a lower-than-normal number of red cells, which can cause anemia and fatigue a low number of platelets an increase or decrease in white cells a high number of blast cells The patient may also have a swollen spleen, which can cause stomach discomfort, and a general feeling of ill health. Blast Crisis Phase CML If the patient is diagnosed in CML's blast crisis phase, it is an indication of increased number of blast cells in bone marrow and blood. In this phase the patient may experience: infection bleeding a lack of energy or feelings of tiredness shortness of breath stomach pain (from an enlarged spleen) bone pain Once CML reaches this more severe, advanced phase, its effects on patients are similar to those caused by an acute leukemia and can be life threatening. For about 25 percent of people who reach this phase, CML takes on the appearance of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. http://www.lls.org/diseaseinformation/leukemia/chronicmyeloidleukemia/ http://trialx.com/curebyte/2011/07/05/clinical-trials-and-images-ofchronic-myelogenous-leukemia-cml/