Native American Art Lesson - Sara Boston`s e-folio
advertisement
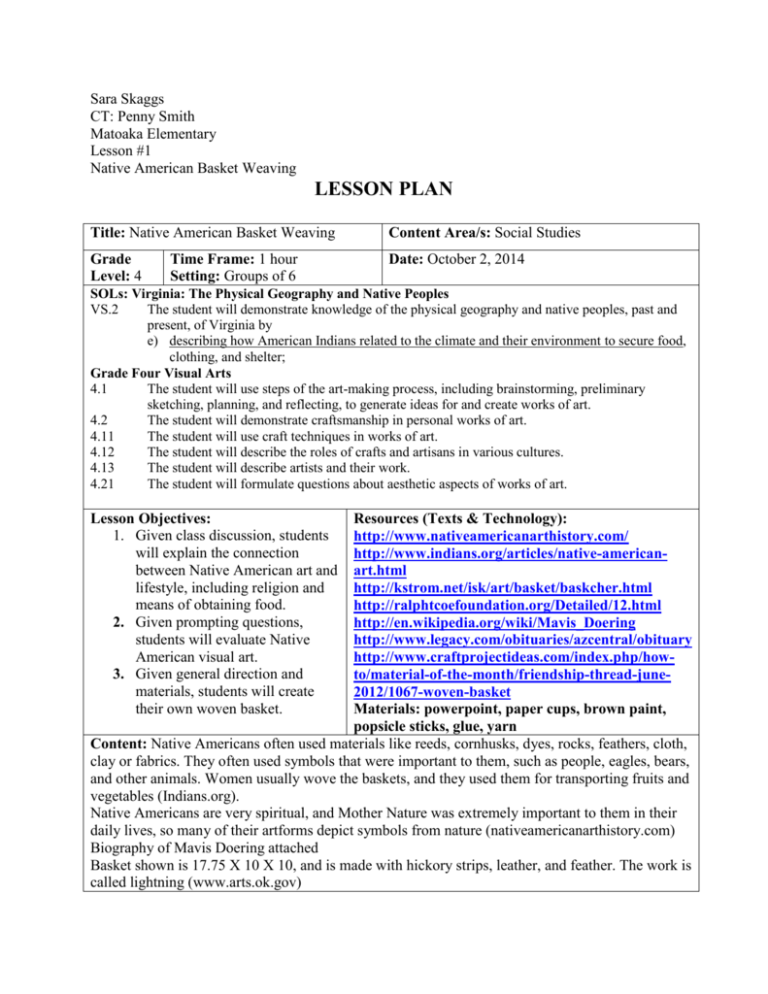
Sara Skaggs CT: Penny Smith Matoaka Elementary Lesson #1 Native American Basket Weaving LESSON PLAN Title: Native American Basket Weaving Grade Level: 4 Time Frame: 1 hour Setting: Groups of 6 Content Area/s: Social Studies Date: October 2, 2014 SOLs: Virginia: The Physical Geography and Native Peoples VS.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the physical geography and native peoples, past and present, of Virginia by e) describing how American Indians related to the climate and their environment to secure food, clothing, and shelter; Grade Four Visual Arts 4.1 The student will use steps of the art-making process, including brainstorming, preliminary sketching, planning, and reflecting, to generate ideas for and create works of art. 4.2 The student will demonstrate craftsmanship in personal works of art. 4.11 The student will use craft techniques in works of art. 4.12 The student will describe the roles of crafts and artisans in various cultures. 4.13 The student will describe artists and their work. 4.21 The student will formulate questions about aesthetic aspects of works of art. Lesson Objectives: 1. Given class discussion, students will explain the connection between Native American art and lifestyle, including religion and means of obtaining food. 2. Given prompting questions, students will evaluate Native American visual art. 3. Given general direction and materials, students will create their own woven basket. Resources (Texts & Technology): http://www.nativeamericanarthistory.com/ http://www.indians.org/articles/native-americanart.html http://kstrom.net/isk/art/basket/baskcher.html http://ralphtcoefoundation.org/Detailed/12.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mavis_Doering http://www.legacy.com/obituaries/azcentral/obituary http://www.craftprojectideas.com/index.php/howto/material-of-the-month/friendship-thread-june2012/1067-woven-basket Materials: powerpoint, paper cups, brown paint, popsicle sticks, glue, yarn Content: Native Americans often used materials like reeds, cornhusks, dyes, rocks, feathers, cloth, clay or fabrics. They often used symbols that were important to them, such as people, eagles, bears, and other animals. Women usually wove the baskets, and they used them for transporting fruits and vegetables (Indians.org). Native Americans are very spiritual, and Mother Nature was extremely important to them in their daily lives, so many of their artforms depict symbols from nature (nativeamericanarthistory.com) Biography of Mavis Doering attached Basket shown is 17.75 X 10 X 10, and is made with hickory strips, leather, and feather. The work is called lightning (www.arts.ok.gov) Instructional Procedures: Introduction: Tell students about the significance of the lesson and explain lesson objectives. Present students with pictures of baskets woven by Mavis Doering. Ask objective level questions. (7 mins) Focus: Explain that these are pictures of baskets woven by a modern Cherokee woman named Mavis Doering, and that she creates baskets to celebrate her Native American heritage. Ask Reflective level questions. (8 mins) Student Engagement: Tell students about biography about Mavis Doering. Ask interpretive level questions. Explain that the Native Americans we have been studying used baskets like these for foraging food, as well as for gathering crops. Show more pictures of baskets. Explain that these baskets had designs in them that celebrate nature, which was very important to the religion of Native Americans. Explain that Native Americans obtained food by hunting, gathering, and planting, and that baskets can be useful for any of these. Ask decisional questions. Instruct students to create their own work of art, and provide instruction about how to do so. (30 mins) Closing: Ask students to volunteer to share why they designed their baskets as they did, and allow them to ask any questions they have about the artform. Give post assessment. (15 mins) Assessment/s: Formative: Student responses to guiding questions throughout lesson Summative: Basket making and presentation of basket, written paragraph; pre/post assessment Extension Activitiy: Extension: Ask students to write a paragraph with the given prompt (Prompt: Write a paragraph explaining the three main ways Native Americans obtained food, and include examples of foods they commonly ate from each category). (15 minutes) Interdisciplinary Links: This lesson links to history because it records a historic culture and their ways of life, it links to art because it is centered around an artform, and it focuses on cultural studies of Native Americans. Including a written paragraph fulfills language arts objectives, and asking questions develops inquiry. Differentiation Strategies/Activities (State nature of differentiation): Gifted students will be asked to research other types of Native American art, and to discuss whether that form of art was also used in their daily lives, or whether it was used for other purposes, such as social commentary, or exclusively for aesthetic purposes. Reflection/Recommendations for Future use [this part is completed after the lesson]: Mavis Doering Biography Mavis Vercine Langley Doering was born on August 31, 1929 in Hominy, Oklahoma. She grew up in Oklahoma and California, and married James Doering in 1954. She is the third generation of basket weavers in her family. She studied early Native American basket weaving at libraries and museums in order to learn as much about her family traditions as possible. Doering is a member of the Cherokee tribe, and she creates baskets in the traditional Cherokee style, but tends to add her own, creative elements. Some examples of these include rocks, feathers, and baskets shaped like clay pots. Doering collects all of her own materials for basket weaving – from making her own dyes out of nut hulls and berries (although she did experiment with aniline dyes, which are chemically based dyes), to finding and using her own weaving materials. Materials she used included but were not limited to honeysuckle, rivercane, ash splits, buckbrush, reed, and white oak splits. Mavis put her work in many museums, such as Southern Plains Indian Museum, Coulter Bay Indian Art Museum, Wheelwright Museum of the American Indian, Fred Jones Jr. Museum of Art, Oklahoma Historical Society, the Kennedy Center in Washington DC, and the Smithsonian Institution Folklife Festival. On two separate occasions she received commissions from the state of Oklahoma to continue her basket making, and she apprenticed several other well-known basket weavers, including Peggy Brennan. She received the Oklahoma Governor’s Arts award in 1984 and was named Honored One at the Red Earth Festival in 1997. She was also a participant in Arizona’s First Celebration of Basketry Doering died in 2007, but her basket weaving has left a legacy and continues to tell her story (www.arts.ok.gov, www.legacy.com). Nelson Critical Thinking Questioning Objective Questions What do you think these are pictures of? How do you think they are constructed? What symbols do you see? What colors do you see used? Reflective Questions What do these baskets make you think of? Have you ever seen baskets similar to these? Where? What kinds of things have you used baskets for? What do you think is most important about the baskets’ design? Interpretive Questions Why do you think Native Americans made decorative baskets? What do you think they used the baskets for? What do you think the symbols mean? How were baskets important to the lifestyle of Native Americans? Do you think the baskets were there for decoration, or for work? Decisional Questions How can you relate to this form of art? How have the Native American traditions of gathering affected your life? How does this artist show appreciation for her surroundings? How can you use baskets in your world? What symbols are important to you that you would put on a basket? Pre-Post Assessment Native American Lifestyle and Art 1. In what three ways did Native Americans get food? ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Name one modern artist who creates Native American art ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. What kinds of symbols did Native Americans use in their artwork? ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Draw a picture of artwork that Native Americans used in their daily lives Pre-Post Assessment Expected Outcomes Native American Lifestyle and Art 1. In what three ways did Native Americans food? Native Americans got the food that they ate through hunting animals and gathering food such as herbs, berries, nuts, and wild fruits and vegetables. Some planted crops as well. 2. Name one modern artist who creates Native American art Mavis Doering 3. What kinds of symbols did Native Americans use in their artwork? Native Americans often used religious symbols, or symbols of nature 4. Draw a picture of artwork that Native Americans used in their daily lives Students might draw a basket, or a rendition of a Native American using a basket Social Studies Critical Thinking Visual Arts Art Production and Interaction Total: 40 pts Exceeds Expectations Meets Expectations Below Expectations Demonstrated knowledge of the Native American practices of farming, hunting, and gathering by explaining in written paragraph what Native Americans often ate and how they obtained that food. (9-10pts) Provided thoughtful reflections in response to Nelson’s 4 Critical Thinking categories (9-10pts) Demonstrated knowledge of Native American practices (2) of farming, hunting, or gathering by explaining in written paragraph what Native Americans often ate and how they obtained that food (7-8pts) Provided thoughtful reflections in response to 3 of Nelson’s Critical Thinking categories (7-8pts) Analyzed how Doering creations influenced visual characteristics that represent Native American means of obtaining food (7-8pts) Demonstrated limited knowledge of Native American practices of farming, hunting, and gathering (5-6pts). Successfully created a basket, paid some attention to details; cooperates (7-8pts) Did not create a basket, or had below age level difficulty; did not interact with others, or did not pay attention to detail (5-6pts) Analyzed how Doering creations influenced visual characteristics that represent Native American culture and lifestyle, including religious beliefs, cultural customs, and means of obtaining food (9-10pts) Successfully created a basket, paid attention to details; helpful to others (9-10pts) Contributed 2 or fewer responses to critical thinking questions (5-6pts) Made few connections between Doering’s art and Native American culture (5-6pts) Points Mavis Doering Baskets. The first basket will be the primary model displayed to the students. Additional Native American Baskets: Artist unknown Cherokee basket Cherokee woman with gathering basket on her back Iroquois ribbonwork basket Student model: