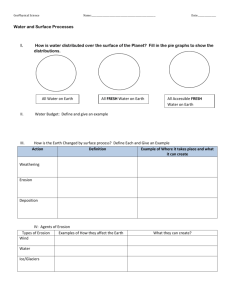
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Study Guide Use the textbook, your
advertisement

Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Study Guide Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Study Guide Answers Use the textbook, your notes, and lab knowledge to answer the following questions. Fill in the blanks provided 1. 2. 1. What do you call a particular frost action which is an example of mechanical weathering? 3. 2. The movement of wind, water, and soil from one place to another is called . 4. 3. ______helps prevent water erosion of soil. 4. A common offshore deposit of sand is called a . 5. When rocks are broken down into pieces they become . 5. 6. 6. Define Mechanical Weathering. 7. List the agents of mechanical weathering. 7. 8. List the agents of chemical weathering: 8. 9. Explain how water causes mechanical weathering? 10. How can water be an agent of chemical weathering? 9. 11. Define Weathering: 12. What is the agent of weathering that produces rust? What is the process called? 13. What is the major agent responsible for a mudflow? 14. Know the following land forms. You may refer to the textbook or to the graphic organizer. Sand Dune: Till: Landslide: Loess: Beach: Creep: Delta: Stratified Drift: 15. How are weathering, erosion and deposition similar? 16. How are weathering, erosion and deposition different? 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. LEAVE BLANK 15. 16. Weathering, Deposition, Erosion Study Guide Key Use the textbook, your notes, and lab knowledge to answer the following questions. Fill in the blanks provided 1. What do you call a particular frost action which is an example of mechanical weathering? Ice wedging 2. The movement of wind, water, and soil from one place to another is called Erosion. 3. Plants help prevent water erosion of soil. 4. A common offshore deposit of sand would be called a Sandbar. 5. When rocks are broken down into pieces they become Sand 6. Define Mechanical Weathering. The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by physical means. 7. List the agents of mechanical weathering. Ice, wind, water, gravity, plants, and animals 8. List the agents of chemical weathering: Water, air (oxygen), living organisms, carbon dioxide, acid precipitation 9. Explain can water cause mechanical weathering? It can cause abrasion and it can also freeze. Producing freeze/thaw (ice wedging). 10. How can water be an agent of chemical weathering? The properties of water can react with the properties of rocks and cause it to slowly break down. 11. Define Weathering: It the process by which rock materials are broken down by the action of physical or chemical processes. 12. What is the agent of weathering that produces rust? What is the process called? Oxygen, causing oxidation 13. What is the major agent responsible for a mudflow? Gravity 14. Define the following land forms. You may refer to the textbook or to the graphic organizer. Sand Dune: Till: Landslide: Loess: Beach: Creep: Delta: Stratified Drift: 15. How are weathering, erosion and deposition similar? They have similar agents, they all change the earth’s surface, they create sediments. 16. How are weathering, erosion and deposition different? Weathering BREAKS rock into sediment. Erosion MOVES sediment and deposition DROPS sediment.