SUBJECT: Algebra 1a GRADE: High School TIMELINE: 4 th Quarter
advertisement
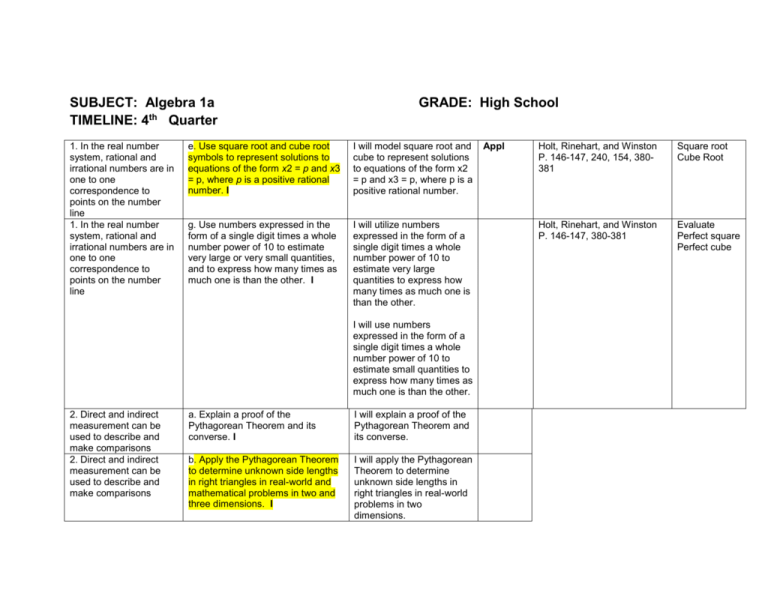
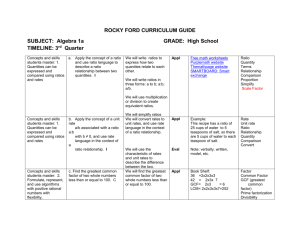
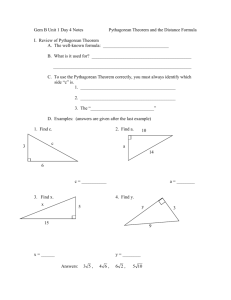
SUBJECT: Algebra 1a TIMELINE: 4th Quarter 1. In the real number system, rational and irrational numbers are in one to one correspondence to points on the number line 1. In the real number system, rational and irrational numbers are in one to one correspondence to points on the number line GRADE: High School e. Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. I I will model square root and cube to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. g. Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times a whole number power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. I I will utilize numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times a whole number power of 10 to estimate very large quantities to express how many times as much one is than the other. I will use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times a whole number power of 10 to estimate small quantities to express how many times as much one is than the other. 2. Direct and indirect measurement can be used to describe and make comparisons 2. Direct and indirect measurement can be used to describe and make comparisons a. Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. I I will explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. b. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. I I will apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world problems in two dimensions. Appl Holt, Rinehart, and Winston P. 146-147, 240, 154, 380381 Square root Cube Root Holt, Rinehart, and Winston P. 146-147, 380-381 Evaluate Perfect square Perfect cube I will apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world problems in three dimensions. I will apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in mathematical problems in two dimensions. I will apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in mathematical problems in three dimensions. Concepts and skills students master: 2. Variables are used to represent unknown quantities within equations and inequalities Concepts and skills students master: 2. Variables are used to represent unknown quantities within equations and inequalities Concepts and skills students master: 2. Variables are used to represent unknown Appl d. Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers. I e. Write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem. I We will solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations in algebraic form. We will write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem. Analysis f. Show that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have infinitely many solutions; represent solutions of such inequalities on number line We will show that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have infinitely many Analysis Examples: Finding the cost of concrete for a tetherball court. Determining the amount of gas needed to drive to Disney World. Example; Xavier’s allowance is more than Cindy’s. Algebraic form Constraint See above Infinite quantities within equations and inequalities diagrams. I Concepts and skills students master: 1. Objects in space and their parts and attributes can be measured and analyzed a. Develop and apply formulas and procedures for area of plane figures i. Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes. I ii. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. I Solutions by representing solutions of such inequalities on number line diagrams. We will develop and apply formulas to find the area of triangles, quadrilaterals, and polygons. Analysis & Synt We will use the formulas we’ve developed and other problem solving strategies to find the area in real-world situations. Appl Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes SMARTBOARD:Smart exchange Area Square units Plane figures Polygons Formulas Quadrilaterals Compose Decompose