Desoto County Schools 2011-2012 Pacing Guide

Desoto County Schools 2015-2016 Pacing Guide
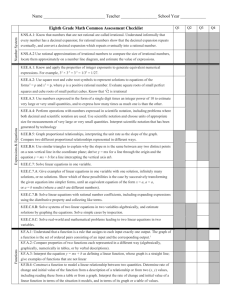
Eighth Grade Math
1
st
Nine Weeks
Unit 1: Introduction and Problem Solving (approx. 2 weeks)
Topic Description
Determine the slope from a graph
Unit 2: Simplifying with Variables (approx. 3 weeks)
Topic Description
Create equations with one variable including those with one solution
Create equations with infinitely many solutions
Create equations with no solutions
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients by combining like terms
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients including the use of the distributive property
Unit 3: Graphs and Equations (approx. 3 weeks)
Topic Description
Create equations with one variable including those with one solution
Create equations with infinitely many solutions
Create equations with no solutions
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients by combining like terms
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients including the use of the distributive property
Recognize a function from a table
Recognize a function from a graph
Compare functions represented by tables, graphs, verbal descriptions, or equations
Distinguish between linear and non-linear functions in slope-intercept form
Provide examples of non-linear functions
Represent a function in table or graph form
Calculate rate of change between two or more points
Generate a function rule from a graph or table of values
Approximately 8 weeks is allocated for instruction and assessment above.
This allows one week of flexibility and to account for nine weeks tests.
State Standard
8.EE.5
State Standard
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7b
8.EE.7b
State Standard
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7a
8.EE.7b
8.EE.7b
8.F.1
8.F.1
8.F.2
8.F.3
8.F.3
8.F.4
8.F.4
8.F.4
Desoto County Schools 2015-2016 Pacing Guide
Eighth Grade Math
2
nd
Nine Weeks
Topic Description
Unit 4: Multiple Representations (approx. 2.5 weeks)
Produce an equation in slope-intercept form
Compare functions represented by tables, graphs, verbal descriptions, or equations
Represent a function in table or graph form
Calculate rate of change between two or more points
Generate a function rule from a graph or table of values
Unit 5: Systems of Equations (approx. 3 weeks)
Topic Description
State Standard
8.EE.6
8.F.2
8.F.4
8.F.4
8.F.4
State Standard
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients by combining like terms
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients including the use of the distributive property
Recognize that the solution to a system of linear equations is their point of intersection
Solve systems of equations that have one solution
Graph system of equations
Estimate the solution to a system of equations from a graph
Determine if there is one solution, many solutions, or no solution to the system of equations
8.EE.7b
8.EE.7b
8.EE.8a
8.EE.8b
8.EE.8b
8.EE.8b
8.EE.8b
Solve mathematical problems leading to two linear equations in two variables 8.EE.8c
Solve real-world problems leading to two linear equations in two variables
Unit 6: Transformations– Section 6.1 Only (approx. 2.5 weeks)
8.EE.8c
Topic Description State Standard
Define rotations, reflections, and translations
Identify rotations, reflections, and translations
Identify corresponding sides and corresponding angles
Use prime notation to describe an image after a translation, reflection, or rotation
Apply the concept of congruency
Write congruent statements when comparing two-dimensional figures
Describe a sequence of rotations, reflections, and/or translations that prove congruency
Use a scale factor to determine the coordinates of a figure
Model with coordinates to describe the effects of translation, rotation, and reflections on two-dimensional figures
Apply the concept of similarity to write similarity statements
Reason that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained by a sequence of rotations, reflections. Translation, or dilation
Describe the sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, or dilations that exhibits the similarity between two-dimensional figures using words and/or symbols
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.2
8.G.2
8.G.2
8.G.3
8.G.3
8.G.4
8.G.4
8.G.4
Approximately 8 weeks is allocated for instruction and assessment above.
This allows one week of flexibility and to account for semester exams.
Desoto County Schools 2015-2016 Pacing Guide
Eighth Grade Math
3
rd
Nine Weeks
Unit 6: Similarity – Section 6.2 Only (approx. 1 week)
Topic Description
Define rotations, reflections, and translations
Identify rotations, reflections, and translations
Identify corresponding sides and corresponding angles
Use prime notation to describe an image after a translation, reflection, or rotation
Apply the concept of congruency
Write congruent statements when comparing two-dimensional figures
Describe a sequence of rotations, reflections, and/or translations that prove congruency
Use a scale factor to determine the coordinates of a figure
Model with coordinates to describe the effects of translation, rotation, and reflections on two-dimensional figures
Apply the concept of similarity to write similarity statements
Reason that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained by a sequence of rotations, reflections. Translation, or dilation
Describe the sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, or dilations that exhibits the similarity between two-dimensional figures using words and/or symbols
Unit 7: Slope and Association (approx. 3.5 weeks)
Topic Description
Graph 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥
Determine the slope from a graph
Compare similar information represented in graphs and equations using the rate of change
Produce an equation in slope-intercept form
Use similar triangles to explain slope
Compare functions represented by tables, graphs, verbal descriptions, or equations
Distinguish between linear and non-linear functions in slope-intercept form
Provide examples of non-linear functions
Construct a scatter plot for data comparing two variables
Interpret the data form a scatter plot
Identify patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and none linear association
Construct a line of best fit to represent the data in a scatter plot
Interpret the meaning of the slope and intercept of a linear equation in terms of the situation
Solve problems using the equation of a linear model
Interpret the data in a two-way table to recognize patterns
Construct a two-way table from data to determine a relationship between the variables
Use relative frequencies of the data to describe relationships (positive, negative, or no correlation)
Unit 8: Exponents and Functions (approx. 3 weeks)
Topic Description
Recall the properties of exponents
Apply the properties of integer exponents to produce equivalent numerical expressions.
Convert between standard form and scientific notation
Compare numbers written in scientific notation
Solve expressions where numbers are written in both decimal and scientific notation
Apply scientific notation to real-world problems to compare quantities and make sense about their relationships
Recognize a function from a table and a graph
Distinguish between linear and non-linear functions in slope-intercept form
Provide examples of non-linear functions
Explain verbally the interpretation of a graph
Construct a graph from a verbal representation
3
rd
Nine Weeks Continued
State Standard
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.1
8.G.2
8.G.2
8.G.2
8.G.3
8.G.3
8.G.4
8.G.4
8.G.4
8.SP.1
8.SP.2
8.SP.3
8.SP.3
8.SP.4
8.SP.4
8.SP.4
State Standard
8.EE.5
8.EE.5
8.EE.5
8.EE.6
8.EE.6
8.F.2
8.F.3
8.F.3
8.SP.1
8.SP.1
State Standard
8.EE.1
8.EE.1
8.EE.3
8.EE.3
8.EE.4
8.EE.4
8.F.1
8.F.3
8.F.3
8.F.5
8.F.5
Desoto County Schools 2015-2016 Pacing Guide
Eighth Grade Math
Unit 9: Angles – Section 9.1 Only (approx. 1 week)
Topic Description
Create a formula for the sum of the interior angles of a polygon
Create a formula for the measurement of one interior angle of a regular polygon
Create a method of determining the measurement of an exterior angle of a polygon
Recognize the relationship of the angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal
Determine the measurement of the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal
Apply the angle-angle theorem to prove similar triangles
Approximately 8.5 weeks is allocated for instruction and assessment above.
This allows half a week of flexibility and to account for nine weeks tests.
State Standard
8.G.5
8.G.5
8.G.5
8.G.5
8.G.5
8.G.5
Desoto County Schools 2015-2016 Pacing Guide
Eighth Grade Math
4
th
Nine Weeks
Unit 9: The Pythagorean Theorem – Section 9.2 Only (approx. 2.5 weeks)
Topic Description State Standard
Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers
Write rational numbers as a decimal expansion
Convert a repeating decimal expansion into a rational number
Show informally that every number has a decimal expansion
Compare values of irrational numbers
Label the approximate location of irrational numbers on a number line.
Recall small perfect squares
Identify small perfect squares and square roots
Solve equations using small perfect square roots
Model a representation to prove the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse
Implement the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side lengths in right triangles
Apply knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem to real-world situations involving two-dimensional figures
Apply knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem to real-world situations involving three-dimensional figures
Calculate the distance between two points in a coordinate system using the Pythagorean Theorem
Unit 9: Surface Area and Volume (approx. 2 weeks)
Topic Description
Recall small perfect cubes
Identify small perfect cubes and cube roots
Solve equations using small perfect cube roots
Recall the formulas for volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres
Determine and apply the appropriate formulas in order to solve real-world problems for a given shape
Determine the radii or height when given the volume of a cone, cylinder, or sphere
8.NS.1
8.NS.1
8.NS.1
8.NS.1
8.NS.2
8.NS.2
8.EE.2
8.EE.2
8.EE.2
8.G.6
8.G.7
8.G.7
8.G.7
8.G.8
State Standard
8.EE.2
8.EE.2
8.EE.2
8.G.9
8.G.9
8.G.9
Approximately 4.5 weeks is allocated for instruction and assessment above.
This allows 4.5 weeks of flexibility and to account for state tests and semester exams.