Raccoon Development Chart - Wildlife Conservation, MN
advertisement
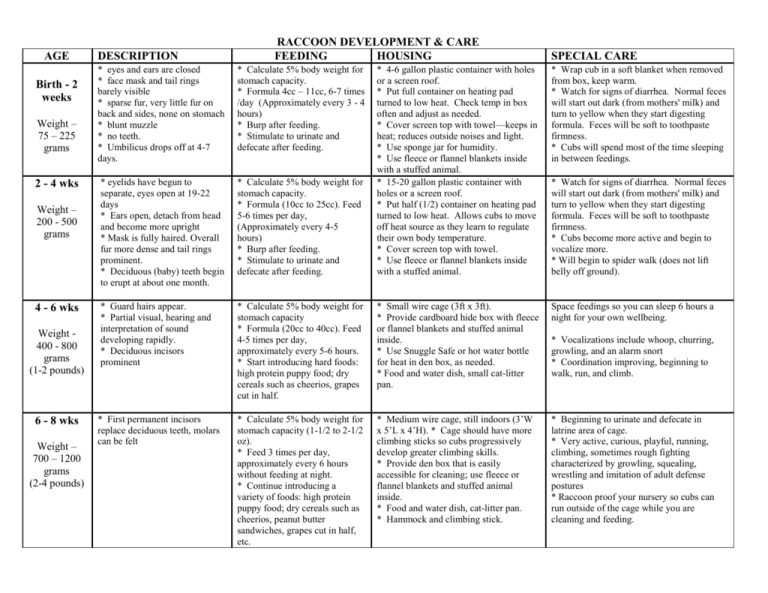
AGE Birth - 2 weeks Weight – 75 – 225 grams 2 - 4 wks Weight – 200 - 500 grams 4 - 6 wks Weight 400 - 800 grams (1-2 pounds) 6 - 8 wks Weight – 700 – 1200 grams (2-4 pounds) DESCRIPTION RACCOON DEVELOPMENT & CARE FEEDING HOUSING * eyes and ears are closed * face mask and tail rings barely visible * sparse fur, very little fur on back and sides, none on stomach * blunt muzzle * no teeth. * Umbilicus drops off at 4-7 days. * Calculate 5% body weight for stomach capacity. * Formula 4cc – 11cc, 6-7 times /day (Approximately every 3 - 4 hours) * Burp after feeding. * Stimulate to urinate and defecate after feeding. * eyelids have begun to separate, eyes open at 19-22 days * Ears open, detach from head and become more upright * Mask is fully haired. Overall fur more dense and tail rings prominent. * Deciduous (baby) teeth begin to erupt at about one month. * Calculate 5% body weight for stomach capacity. * Formula (10cc to 25cc). Feed 5-6 times per day, (Approximately every 4-5 hours) * Burp after feeding. * Stimulate to urinate and defecate after feeding. * Guard hairs appear. * Partial visual, hearing and interpretation of sound developing rapidly. * Deciduous incisors prominent * First permanent incisors replace deciduous teeth, molars can be felt SPECIAL CARE * 4-6 gallon plastic container with holes or a screen roof. * Put full container on heating pad turned to low heat. Check temp in box often and adjust as needed. * Cover screen top with towel—keeps in heat; reduces outside noises and light. * Use sponge jar for humidity. * Use fleece or flannel blankets inside with a stuffed animal. * 15-20 gallon plastic container with holes or a screen roof. * Put half (1/2) container on heating pad turned to low heat. Allows cubs to move off heat source as they learn to regulate their own body temperature. * Cover screen top with towel. * Use fleece or flannel blankets inside with a stuffed animal. * Wrap cub in a soft blanket when removed from box, keep warm. * Watch for signs of diarrhea. Normal feces will start out dark (from mothers' milk) and turn to yellow when they start digesting formula. Feces will be soft to toothpaste firmness. * Cubs will spend most of the time sleeping in between feedings. * Calculate 5% body weight for stomach capacity * Formula (20cc to 40cc). Feed 4-5 times per day, approximately every 5-6 hours. * Start introducing hard foods: high protein puppy food; dry cereals such as cheerios, grapes cut in half. * Small wire cage (3ft x 3ft). * Provide cardboard hide box with fleece or flannel blankets and stuffed animal inside. * Use Snuggle Safe or hot water bottle for heat in den box, as needed. * Food and water dish, small cat-litter pan. Space feedings so you can sleep 6 hours a night for your own wellbeing. * Calculate 5% body weight for stomach capacity (1-1/2 to 2-1/2 oz). * Feed 3 times per day, approximately every 6 hours without feeding at night. * Continue introducing a variety of foods: high protein puppy food; dry cereals such as cheerios, peanut butter sandwiches, grapes cut in half, etc. * Medium wire cage, still indoors (3’W x 5’L x 4’H). * Cage should have more climbing sticks so cubs progressively develop greater climbing skills. * Provide den box that is easily accessible for cleaning; use fleece or flannel blankets and stuffed animal inside. * Food and water dish, cat-litter pan. * Hammock and climbing stick. * Beginning to urinate and defecate in latrine area of cage. * Very active, curious, playful, running, climbing, sometimes rough fighting characterized by growling, squealing, wrestling and imitation of adult defense postures * Raccoon proof your nursery so cubs can run outside of the cage while you are cleaning and feeding. * Watch for signs of diarrhea. Normal feces will start out dark (from mothers' milk) and turn to yellow when they start digesting formula. Feces will be soft to toothpaste firmness. * Cubs become more active and begin to vocalize more. * Will begin to spider walk (does not lift belly off ground). * Vocalizations include whoop, churring, growling, and an alarm snort * Coordination improving, beginning to walk, run, and climb. 4-6 Weeks Start vaccination schedule. First vaccines can be given as early as 4 weeks old. Two separate vaccines are needed: Merial Recombitek C3 or C4/CV - MLV that protects against Canine Parvovirus and Canine Distemper and Merial Pure Vax Feline 4 - MVL that protects against Feline Panleukopenia (Reference: http://www.kywildlife.org/uploads/IWRC_Raccoon_Parvo_2011.pdf). Repeat the set of vaccines in 3 weeks; You want 2 or 3 sets of vaccinations before they go to your outdoor cage. Final vaccines before release (at >16 wks of age) 6 - 8 Weeks Start worming schedule. Mix Panacur in flavored yogurt. If using liquid, draw up required dosage of Panacur in 3cc syringe, draw up flavored yogurt. This will hide the flavor of the Panacur and the syringe makes it easy to give. Worming with Panacur is done as a series of one dose each three (3) days in a row. Begin series 1 at 6 weeks; series 2 at 8 weeks; series 3 at 11 weeks; series 4 at 14 weeks; thereafter a series every 4 weeks is recommended while the raccoon is in rehabilitative care for the REHABILITATOR’S protection. AGE DESCRIPTION FEEDING HOUSING SPECIAL CARE * Permanent second incisors * Drinking 3-4 ounces of * Still indoors in a cage with a hide box * Cubs are playing games of pounce and 9 - 12 wks Weight 4 to 8 pounds 12+ weeks Weight 8 – 14 + pounds and first molars erupt at approx 2-1/2 months. Permanent third incisors erupt at 3 months. Permanent canines at 3-1/2 months. * Body is filling out and gaining muscle tone. * Face is full. They will gain approximately half (½) pound per week. They should be 16 to 20 pounds when you release them in the fall so that they are prepared for the winter. formula and still hungry for food in dish. * Reduce bottle feedings to twice a day. When weaning the cubs down from 3-4 bottle feedings to 2, substitute a dinner of puppy chow with added foods such as scrambled eggs, hotdogs, chicken, dry cereals such as cheerios, peanut butter sandwiches, fruits and vegetables. * Provide fresh food and water twice daily. The amounts will need to be increased often, until there is some left over. * Introduce as many natural food items as possible. Examples: strawberries, raspberries, wild grapes, blueberries, garden vegetables, crickets, earthworms, grubs, minnows, acorns, hazelnuts, etc. with fleece or flannel blankets inside. * Food and water dish, cat-litter pan. * Hammock and climbing stick. Add assortment of toys/alternate toys. Water dish for playing in. At approximately 12 weeks old or 6-8 pounds and weaned, move the cubs to an outdoor cage. * They should be in an outdoor care. Minimum standards suggest 6’Wx8’Lx6’H. * They will learn climbing skills, adapt to outdoor noises, and acclimate to weather conditions while in the outdoor cage. * The cage must have a suitable nesting box that is elevated off the ground and lots of logs and large branches for climbing up and down; swings to learn balance; large water dish for climbing in and floating berries and nuts in; straw, decomposing wood, or dirt to dig in. hide-and-seek with you and each other. * Explores room outside of cage: running, scrambling, hiding, exploring buckets, etc. “Raccoon proof” your area. * Displays defensive posture: raised hair on back, growling, hiding, and aggressiveness towards people other than you. * They begin weaning themselves from the bottle and it is obvious they are content with the food in their dish as they don’t rush the bottle or eat from it regularly. * Less frequent human visits, but cubs will still be very friendly. It is all right for them to continue to play with you and get hugs. Raccoons may stay with their mother/family for one year or more in the wild. Family bonds are important for their social development. The trust is also better for you as you will need to continue their vaccinations and worming schedule. * Should have minimum 2 each of Parvo and Distemper vaccines before release. * Release at approximately 20-24 weeks. NOTE: cubs are individuals and you need to assess their readiness for release. Approximate Conversions - For formula/liquids: 30 cc = 30 ml = 1 oz; For weight: 1 kg = 1000 grams = 2.2 pounds; 454 g = 1 pound Calculate stomach capacity - Stomach capacity for a raccoon is 5% body weight. Example: Convert body weight to grams. A 400g raccoon cub has a stomach capacity of 20 cc Take the 400 gram number; drop the last digit so 400 becomes 40; Divide 40 by 2 equals 20; Therefore a 400 gram raccoon cub has a 20cc stomach capacity. By Laura Lund, Revised 3-23-2013