2.4-2.5 Guided Notes
advertisement

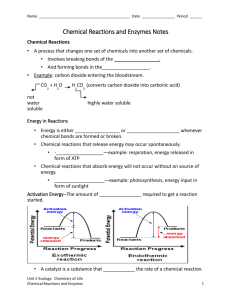
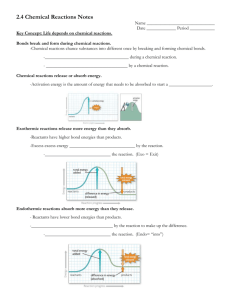
Biology Chapter 2.4-2.5 Guided Notes I. II. Life depends on chemical reactions a. Bonds break and form during chemical reactions. i. Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by breaking and forming chemical bonds. 1. Reactants are changed during a chemical reaction. 2. Products are made by a chemical reaction. b. Bond energy is the amount of energy that breaks a bond. i. Energy is added to break bonds. ii. Energy is released when bonds form. c. A reaction is at equilibrium when reactants and products form at the same rate. d. Chemical reactions release or absorb energy. i. Activation energy is the amount of energy that needs to be absorbed to start a chemical reaction. ii. Exothermic reactions release more energy than they absorb. 1. Reactants have higher bond energies than products. 2. Excess energy is released by the reaction. iii. Endothermic reactions absorb more energy than they release. 1. Reactants have lower bond energies than products. 2. Energy is absorbed by the reaction to make up the difference. Enzymes are catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. a. A catalyst lowers activation energy. i. Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. 1. decrease activation energy 2. increase reaction rate b. Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. i. Enzymes are catalysts in living things. 1. Enzymes are needed for almost all processes. 2. Most enzymes are proteins. c. Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. i. Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. ii. Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds. iii. An enzyme’s function depends on its structure. d. An enzyme’s structure allows only certain reactants to bind to the enzyme. i. substrates ii. active site e. The lock-and-key model helps illustrate how enzymes function. i. substrates brought together ii. bonds in substrates weakened Biology Chapter 2.4-2.5 Guided Notes I. Life depends on _________________________________________ a. Bonds _________________ and form during chemical reactions. i. Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by breaking and forming chemical bonds. 1. _____________________ are changed during a chemical reaction. 2. _____________________ are made by a chemical reaction. b. Bond energy is the amount of energy that breaks a bond. i. Energy is added to ___________________ bonds. ii. Energy is released when bonds ______________________. c. A reaction is at _______________________ when reactants and products form at the same rate. d. Chemical reactions release or absorb energy. i. _____________________________ is the amount of energy that needs to be absorbed to start a chemical reaction. ii. _____________________ reactions release more energy than they absorb. 1. Reactants have higher bond energies than products. 2. Excess energy is released by the reaction. iii. _____________________ reactions absorb more energy than they release. 1. Reactants have lower bond energies than products. 2. Energy is absorbed by the reaction to make up the difference. II. _______________________ are catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. a. A catalyst _______________________ activation energy. i. Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. 1. ______________________ activation energy 2. ______________________ reaction rate b. Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. i. Enzymes are catalysts in living things. 1. Enzymes are needed for almost all processes. 2. Most enzymes are ________________________. c. Disruptions in ______________________ can prevent enzymes from functioning. i. Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. ii. Changes in _____________________ and pH can break hydrogen bonds. iii. An enzyme’s function depends on its ______________________. d. An enzyme’s structure allows only certain reactants to bind to the enzyme. i. _______________________ ii. _______________________ e. The _________________________________________ helps illustrate how enzymes function. i. substrates brought together ii. bonds in substrates weakened