Unit 8 Vocab and Questions Due: States of Matter and IMFs
advertisement

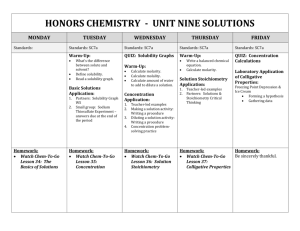
Unit 8 Vocab and Questions States of Matter and IMFs (Chapters 10 and 11) Due: Learning Goals: Be able to… 4.1 Aqueous Solutions/ Electrolytes: 1. Predict whether a substance is a nonelectrolyte, strong electrolyte, or weak electrolyte from its chemical behavior. 2. Predict the ions formed by electrolytes when they dissociate or ionize. 4.5 Concentrations of Solutions: 3. Calculate molarity, solution volume, or number of moles of solute given any two of these quantities. 4. Calculate the volume of a more concentrated solution that must be diluted to obtain a given quantity of a more dilute solution. 13.1,2,3 Solutions: 5. Describe the energy changes that occur in the solution process in terms of the solutesolute, solvent-solvent, and solute-solvent attractive forces; describe the role of disorder in the solution process. 6. Rationalize the solubilities of substances in various solvents in terms of their molecular structures and intermolecular forces. 7. Describe the effects of pressure and temperature on solubilities. 13.4 Concentration Expressions: 8. Define mass percentage, parts per million, mole fraction, molarity, molality, and calculate concentrations in any of these concentration units. 9. Convert concentration in one concentration unit into any other (given density of the solution where necessary) 13.5 Colligative properties: 10. Determine the concentration and molar mass of a nonvolatile non-electrolyte from its effect on the colligative properties of a solution. 11. Explain the difference between the magnitude of changes in colligative properties caused by electrolytes compared to those caused by nonelectrolytes. 12. Describe effects of solute concentration on the vapor pressure, boiling point, freezing point, and osmotic pressure of a solution, and calculate any of these properties given appropriate concentration data. 13.6 Colloids: 13. Be able to describe how a colloid differs from a true solution Main Goals restated/made more concise: 1. Perform calculations with different solution concentrations such as molarity, mass percent, molality, and mole fraction. 2. Discuss the effects of temperature, pressure, and structure on solubility. 3. Perform calculations with Raoult’s law 4. Understand colligative properties such as boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. 5. Use colligative properties to determine the molar mass of a solute. AP Tip: Questions from this section could appear in both the MC and FRQ section. Questions on the solubility or miscibility of substances in one another may appear in the essay section. Questions involving the determination of molar mass by freezing point depression could also appear in the lab essay. Unit 8 Vocab and Questions States of Matter and IMFs (Chapters 10 and 11) Textbook Questions: 31 total textbook questions Chapter 4 Electrolytes: 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 Solution Composition; Molaritiy: 50, 52, 54, 62 Chapter 13 The Solution Process: 1, 3 Saturated Solutions; Factors Affecting Solubility: 9, 10, 11, 12, 19, 20, 22 Concentrations of Solutions: 23, 25, 27, 29, 31 Colligative Properties: 43, 44, 45, 46, 52, 53, 54 Vocabulary: Chose 16 words total (Picture, Definition, Sentence) Chapter 4 Chapter 13 1. Aqueous solution 1. solvation 2. Solvent 2. hydration 3. Solute 3. entropy 4. Electrolyte 4. crystallization 5. Nonelectrolyte 5. saturated 6. Concentration 6. unsaturated 7. Molarity 7. supersaturated 8. Dilution 8. solubility 9. solubility 9. miscible 10. immiscible 11. Henry’s Law 12. Mass percentage 13. Parts per million (ppm) 14. Molality 15. Mole fraction 16. Colligative property 17. Raoult’s Law 18. Molal boiling and freezing point constants 19. Colloids 20. Tyndall effect 21. Hydrophobic 22. hydrophillic Due: