Comparing Covalent and Ionic Compounds
advertisement

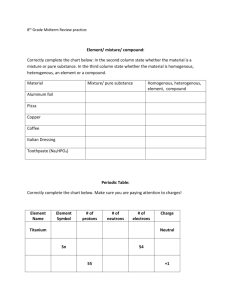
Name: ________________________________ Date:_________________ Block: ______ IPS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT – COMPARING COVALENT AND IONIC COMPOUNDS – Background Information Compounds are either covalent or ionic, depending on the nature of the forces that hold them together. In ionic compounds, the force of attraction is between oppositely charged ions. This attraction is called an ionic bond. In covalent compounds, atoms are held together by an interaction between adjacent nuclei and shared electrons. These different forces account for many of the properties of ionic and covalent compounds, such as degree of volatility (ability to turn into a gas) and solubility (ability to dissolve). In this investigation you will examine the properties of a representative ionic compound, sodium chloride, and a representative covalent compound, paraffin. The properties studied will be volatility, ease of melting, and solubility in water. Purpose Compare and contrast the properties of ionic and covalent compounds. Materials sodium chloride paraffin two crucibles aluminum foil clay triangle Bunsen burner flint two test tubes ring stand with ring safety goggles apron Procedure 1. Put on safety goggles and apron. 2. Carefully smell each compound. If you can detect an odor, assume that the compound has a high volatility. If there is no smell, assume the compound has a low volatility. Record your observations in the data table. 3. Wrap the crucibles with aluminum foil. Place a small amount of each substance in separate crucibles (See Figure 1) and heat with the Bunsen burner. Time how long it takes to melt each substance. As soon as each substance begins to melt turn off the flame. Record your observations in the data table. 1 Name: ________________________________ Date:_________________ Block: ______ 4. Half fill two test tubes with room temperature water. Put a small amount of each substance in separate test tubes. Place your thumb over the top of each test tube and shake. If the substance dissolves record that the substance is soluble. If the substance does not dissolve record that the substance is insoluble. 5. Clean up. Do not put paraffin in the sink, but you may put it in the trash. Sodium chloride may be placed in the trash or sink. When your station is clean, raise your hand to be dismissed. Remember, do not remove your apron or safety goggles until you are dismissed from your lab station. Observations DATA TABLE Substance Volatility Melting Time Solubility Sodium chloride Paraffin 1. Which compound was more volatile? ___________________________________ 2. Which compound melted more quickly? _________________________________ 3. Which compound dissolved more easily in water? _________________________ Analysis and Conclusion 1. Explain why the type of bond could determine the volatility of a substance. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Does the strength of a bond have anything to do with the time it takes to melt a substance? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2 Name: ________________________________ Date:_________________ Block: ______ 3. Water is a polar molecule. This means that it has a negatively charged side and a positively charged side. Predict which substance will dissolve more easily, an ionic compound or a non-polar covalent compound. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Critical Thinking and Application 1. What does your data tell you about the melting points of ionic and covalent compounds? How can you tell? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which do you think would be more dangerous near an open flame? Why? ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 3. Which type of compound would you expect to have a higher boiling point? Why? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4. Suppose you had a mixture of an ionic compound and a covalent compound. How would you separate the two compounds? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 3 Name: ________________________________ Date:_________________ Block: ______ 5. What was the purpose of this lab? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. What procedure was used to fulfill the purpose of this lab? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. What were the results from the lab? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4