Project Charter Guideline
advertisement
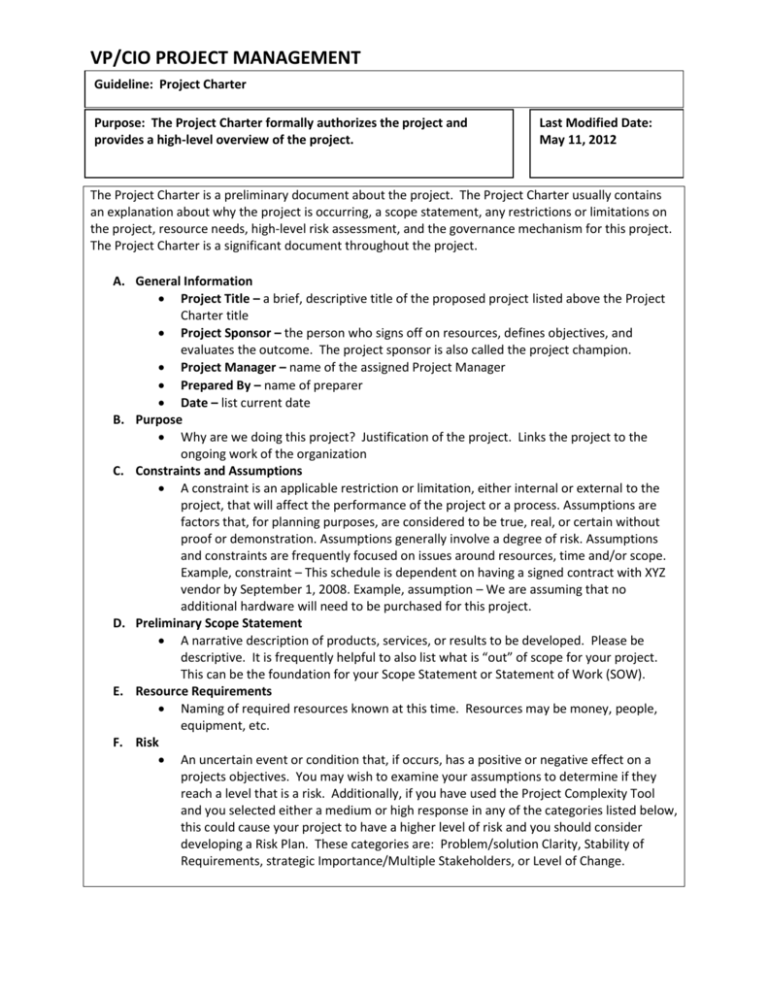
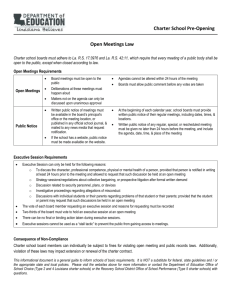
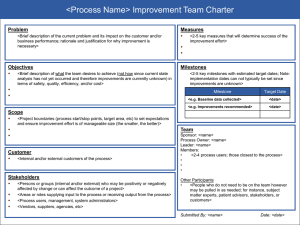
VP/CIO PROJECT MANAGEMENT Guideline: Project Charter Purpose: The Project Charter formally authorizes the project and provides a high-level overview of the project. Last Modified Date: May 11, 2012 The Project Charter is a preliminary document about the project. The Project Charter usually contains an explanation about why the project is occurring, a scope statement, any restrictions or limitations on the project, resource needs, high-level risk assessment, and the governance mechanism for this project. The Project Charter is a significant document throughout the project. A. General Information Project Title – a brief, descriptive title of the proposed project listed above the Project Charter title Project Sponsor – the person who signs off on resources, defines objectives, and evaluates the outcome. The project sponsor is also called the project champion. Project Manager – name of the assigned Project Manager Prepared By – name of preparer Date – list current date B. Purpose Why are we doing this project? Justification of the project. Links the project to the ongoing work of the organization C. Constraints and Assumptions A constraint is an applicable restriction or limitation, either internal or external to the project, that will affect the performance of the project or a process. Assumptions are factors that, for planning purposes, are considered to be true, real, or certain without proof or demonstration. Assumptions generally involve a degree of risk. Assumptions and constraints are frequently focused on issues around resources, time and/or scope. Example, constraint – This schedule is dependent on having a signed contract with XYZ vendor by September 1, 2008. Example, assumption – We are assuming that no additional hardware will need to be purchased for this project. D. Preliminary Scope Statement A narrative description of products, services, or results to be developed. Please be descriptive. It is frequently helpful to also list what is “out” of scope for your project. This can be the foundation for your Scope Statement or Statement of Work (SOW). E. Resource Requirements Naming of required resources known at this time. Resources may be money, people, equipment, etc. F. Risk An uncertain event or condition that, if occurs, has a positive or negative effect on a projects objectives. You may wish to examine your assumptions to determine if they reach a level that is a risk. Additionally, if you have used the Project Complexity Tool and you selected either a medium or high response in any of the categories listed below, this could cause your project to have a higher level of risk and you should consider developing a Risk Plan. These categories are: Problem/solution Clarity, Stability of Requirements, strategic Importance/Multiple Stakeholders, or Level of Change. VP/CIO PROJECT MANAGEMENT Guideline: Project Charter Purpose: The Project Charter formally authorizes the project and provides a high-level overview of the project. Last Modified Date: May 11, 2012 G. Governance Every project will have a governance mechanism. Very large projects may have multiple governance bodies. Governance is a body of people who have an interest in the outcome of the project and have the ability to affect the outcome of the project. H. Approval If the project crosses division boundaries, this is the signature of the project sponsor, Senior Director, or AVP. If the project is contained within a division but crosses managerial boundaries, this is the signature of the Senior Director. A hard copy signature is recommended with a date.