Palmetto High School 2014-2015 CP Chemistry Pacing Guide Unit
advertisement
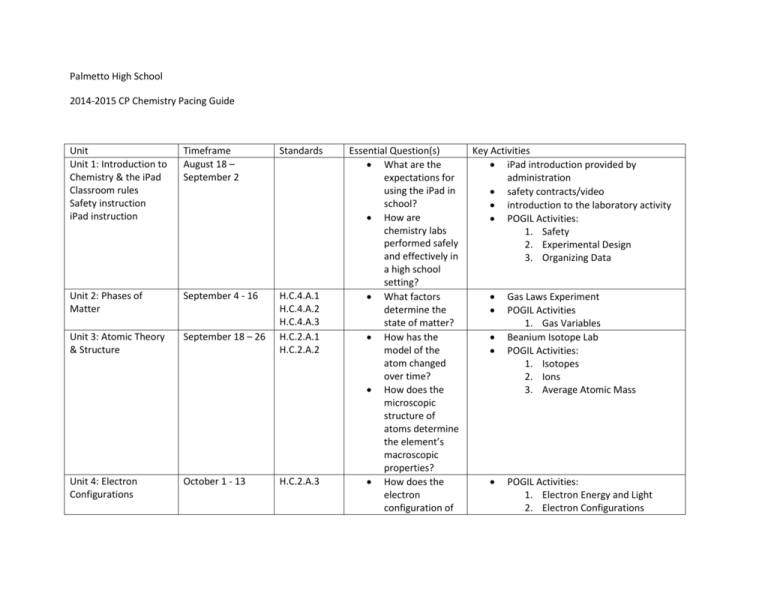
Palmetto High School 2014-2015 CP Chemistry Pacing Guide Unit Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry & the iPad Classroom rules Safety instruction iPad instruction Timeframe August 18 – September 2 Standards Unit 2: Phases of Matter September 4 - 16 Unit 3: Atomic Theory & Structure September 18 – 26 H.C.4.A.1 H.C.4.A.2 H.C.4.A.3 H.C.2.A.1 H.C.2.A.2 Unit 4: Electron Configurations October 1 - 13 H.C.2.A.3 Essential Question(s) What are the expectations for using the iPad in school? How are chemistry labs performed safely and effectively in a high school setting? What factors determine the state of matter? How has the model of the atom changed over time? How does the microscopic structure of atoms determine the element’s macroscopic properties? How does the electron configuration of Key Activities iPad introduction provided by administration safety contracts/video introduction to the laboratory activity POGIL Activities: 1. Safety 2. Experimental Design 3. Organizing Data Gas Laws Experiment POGIL Activities 1. Gas Variables Beanium Isotope Lab POGIL Activities: 1. Isotopes 2. Ions 3. Average Atomic Mass POGIL Activities: 1. Electron Energy and Light 2. Electron Configurations Unit 5: Bonding October 15 – 29 H.C.3.A.3 H.C.3.A.4 Unit 6: Nomenclature November 5 – 19 H.C.3.A.2 Unit 7: Empirical Formulas November 21 – December 8 H.C.3.A.7 Unit 8: Chemical Reactions Part 1: December 10 – 12 Part 2: January 5 13 H.C.6.A.1 H.C.6.A.3 January 15 – 29 H.C.6.A.2 Unit 9: Equilibrium an atom affect the properties of the atom? Why do atoms form bonds? What determines the type of bond that will form between different elements? What are the rules for naming compounds? How can the formula of an unknown compound be experimentally determined? What happens on a microscopic scale when chemical reactions occur? How is chemical equilibrium established? What happens when chemical equilibrium is Spectroscope Activity POGIL Activities: 1. Cracking the Periodic Table Code Types of Bonds Experiment POGIL Activities: 1. Naming Ionic Compounds 2. Naming Molecular Compounds 3. Naming Acids Compound Naming Race Determine Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide Lab POGIL Activities 1. Types of Reactions Types of Reactions Lab Experiment POGIL Activities: 1. Equilibrium Equilibrium & LeChatelier’s Principle Lab Unit 10: Stoichiometry February 2 – 23 H.C.6.A.4 Unit 11: Thermochemistry February 25 – March 9 H.C.7.A.1 H.C.7.A.2 Unit 12: Kinetics March 11 – 19 H.C.7.A.3 H.C.7.A.4 Unit 13: Solutions Part 1: March 24 26 Part 2: April 6 – 10 H.C.5.A.1 H.C.5.A.2 H.C.5.A.3 Unit 14: Acids & Bases April 14 – 28 H.C.5.A.4 upset? How can the amount of product produced be calculated from given amounts of reactants? How is energy involved in chemical reactions? What factors affect the speed of chemical reactions? How can the speed of chemical reactions be controlled? How do the components of a solution affect the solution’s chemical and physical properties? What are practical applications of acid/base reactions? What makes an POGIL Activities: 1. Mole Ratios 2. Limiting Reagents Stoichiometry Lab Experiment POGIL Activities: 1. Calorimetry 2. Bond Energy Thermochemistry Lab Experiment Rate of Reactions Lab POGIL Activities: 1. Saturated & Unsaturated Solutions 2. Solubility 3. Molarity POGIL Activities: 1. Acids & Bases 2. Calculating pH 3. Strong vs. Weak Acids Acid/Base Lab Experiment Unit 15: Nuclear Chemistry April 30 – May 18 H.C.2.B.1 H.C.2.B.2 H.C.2.B.3 Unit 16: Organic Chemistry May 20 – 22 H.C.3.A.5 H.C.3.A.6 acid a “strong acid”? How are fusion and fission reactions similar/different? How can nuclear reactions benefit/harm humans/the environment? Why does carbon form so many different compounds? Why are carboncontaining compounds so important? LDC Module Building molecular models activity.