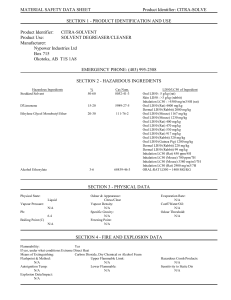
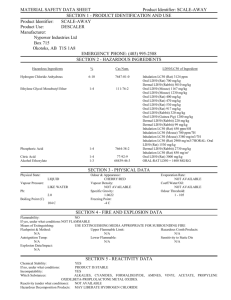
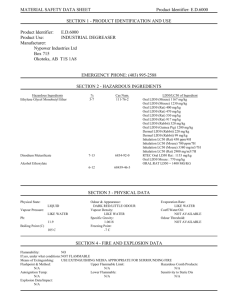
MSDS Template
advertisement
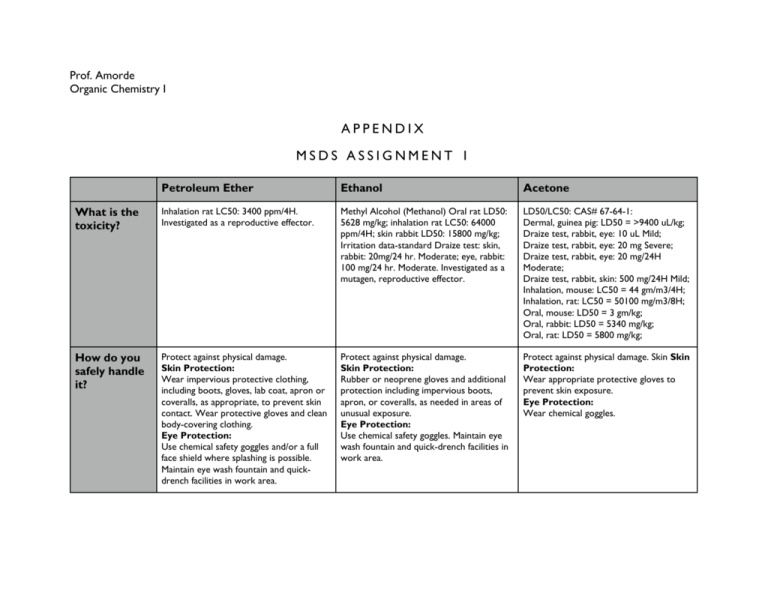
Prof. Amorde Organic Chemistry I APPENDIX MSDS ASSIGNMENT 1 Petroleum Ether Ethanol Acetone What is the toxicity? Inhalation rat LC50: 3400 ppm/4H. Investigated as a reproductive effector. Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) Oral rat LD50: 5628 mg/kg; inhalation rat LC50: 64000 ppm/4H; skin rabbit LD50: 15800 mg/kg; Irritation data-standard Draize test: skin, rabbit: 20mg/24 hr. Moderate; eye, rabbit: 100 mg/24 hr. Moderate. Investigated as a mutagen, reproductive effector. LD50/LC50: CAS# 67-64-1: Dermal, guinea pig: LD50 = >9400 uL/kg; Draize test, rabbit, eye: 10 uL Mild; Draize test, rabbit, eye: 20 mg Severe; Draize test, rabbit, eye: 20 mg/24H Moderate; Draize test, rabbit, skin: 500 mg/24H Mild; Inhalation, mouse: LC50 = 44 gm/m3/4H; Inhalation, rat: LC50 = 50100 mg/m3/8H; Oral, mouse: LD50 = 3 gm/kg; Oral, rabbit: LD50 = 5340 mg/kg; Oral, rat: LD50 = 5800 mg/kg; How do you safely handle it? Protect against physical damage. Skin Protection: Wear impervious protective clothing, including boots, gloves, lab coat, apron or coveralls, as appropriate, to prevent skin contact. Wear protective gloves and clean body-covering clothing. Eye Protection: Use chemical safety goggles and/or a full face shield where splashing is possible. Maintain eye wash fountain and quickdrench facilities in work area. Protect against physical damage. Skin Protection: Rubber or neoprene gloves and additional protection including impervious boots, apron, or coveralls, as needed in areas of unusual exposure. Eye Protection: Use chemical safety goggles. Maintain eye wash fountain and quick-drench facilities in work area. Protect against physical damage. Skin Skin Protection: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Eye Protection: Wear chemical goggles. Petroleum Ether What is the density? 0.66 g/mL Are there any No information found reproductive hazards? Ethanol Acetone 1.1 g/mL Investigated as a mutagen, reproductive effector. 0.8 g/mL TDLo(Oral, rat) = 273 gm/kg;Reproductive - Paternal Effects spermatogenesis (incl. genetic material, sperm morphology, motility, and count). What is the difference between acute exposure and chronic exposure? Acute toxicity looks at lethal effects following oral, dermal or inhalation exposure. It is broken into five categories of severity where Category 1 requires the least amount of exposure to be lethal and Category 5 requires the most exposure to the be lethal. What does flashpoint mean? The flash point of a flammable liquid is the lowest temperature at which it can form an ignitable mixture in air. At this temperature the vapor may cease to burn when the source of ignition is removed. What routes of exposure should we be most concerned about? Inhalation may cause symptoms of intoxication and peripheral nerve disorders and central nervous system depression. Symptoms of overexposure include loss of appetite, muscle weakness, impairment of motor action, dizziness and drowsiness. May also cause throat irritation. What is the structure? Chronic toxicity involves an analysis of long term exposure including life cycle stages. This method of analysis has less standardized testing as well as data. -17.6C, 0.F 12C (54F) Ingestion. Toxic. Symptoms parallel inhalation. Can intoxicate and cause blindness. Usual fatal dose: 100-125 milliliters. -20C (-4F) Inhalation of vapors irritates the respiratory tract. May cause coughing, dizziness, dullness, and headache. Higher concentrations can produce central nervous system depression, narcosis, and unconsciousness. Petroleum Ether What is the set-up of the separation funnel? What is the 3D image of the structure? Ethanol Acetone