P86 Efficacy and safety profile of single dose intravenous Ferric
advertisement
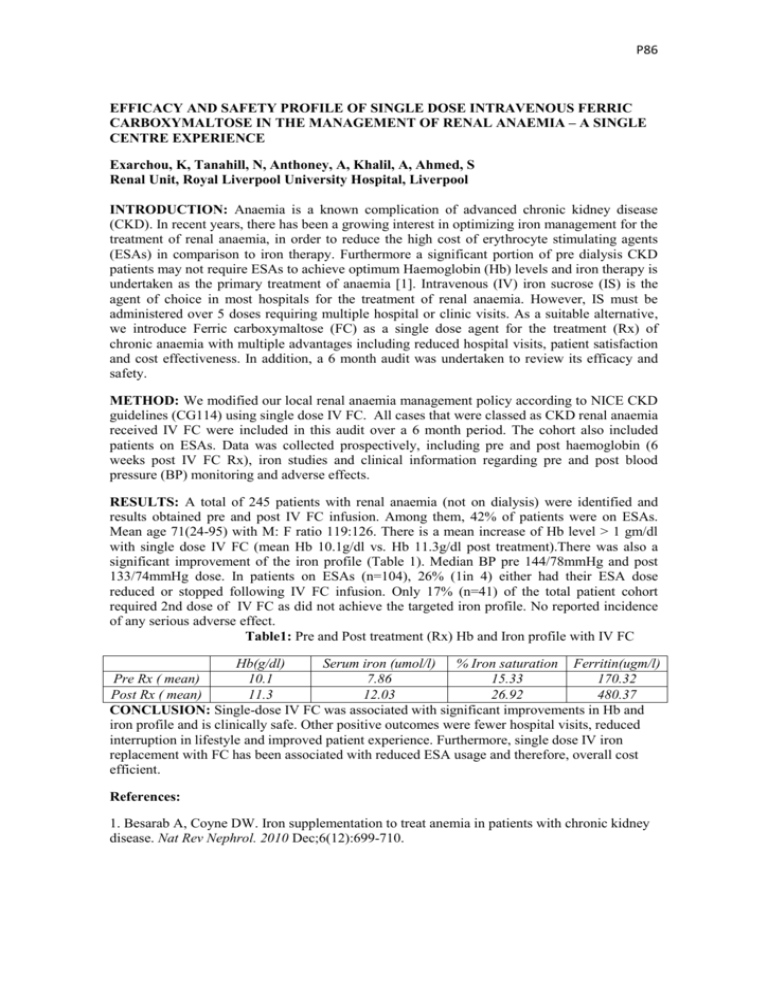
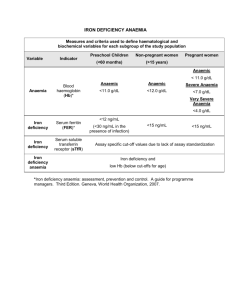
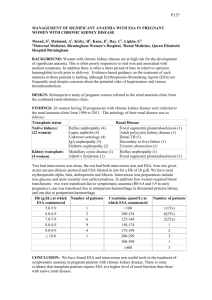
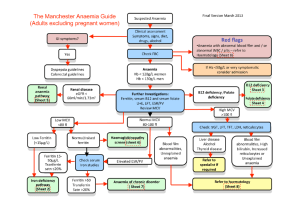
P86 EFFICACY AND SAFETY PROFILE OF SINGLE DOSE INTRAVENOUS FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RENAL ANAEMIA – A SINGLE CENTRE EXPERIENCE Exarchou, K, Tanahill, N, Anthoney, A, Khalil, A, Ahmed, S Renal Unit, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool INTRODUCTION: Anaemia is a known complication of advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD). In recent years, there has been a growing interest in optimizing iron management for the treatment of renal anaemia, in order to reduce the high cost of erythrocyte stimulating agents (ESAs) in comparison to iron therapy. Furthermore a significant portion of pre dialysis CKD patients may not require ESAs to achieve optimum Haemoglobin (Hb) levels and iron therapy is undertaken as the primary treatment of anaemia [1]. Intravenous (IV) iron sucrose (IS) is the agent of choice in most hospitals for the treatment of renal anaemia. However, IS must be administered over 5 doses requiring multiple hospital or clinic visits. As a suitable alternative, we introduce Ferric carboxymaltose (FC) as a single dose agent for the treatment (Rx) of chronic anaemia with multiple advantages including reduced hospital visits, patient satisfaction and cost effectiveness. In addition, a 6 month audit was undertaken to review its efficacy and safety. METHOD: We modified our local renal anaemia management policy according to NICE CKD guidelines (CG114) using single dose IV FC. All cases that were classed as CKD renal anaemia received IV FC were included in this audit over a 6 month period. The cohort also included patients on ESAs. Data was collected prospectively, including pre and post haemoglobin (6 weeks post IV FC Rx), iron studies and clinical information regarding pre and post blood pressure (BP) monitoring and adverse effects. RESULTS: A total of 245 patients with renal anaemia (not on dialysis) were identified and results obtained pre and post IV FC infusion. Among them, 42% of patients were on ESAs. Mean age 71(24-95) with M: F ratio 119:126. There is a mean increase of Hb level > 1 gm/dl with single dose IV FC (mean Hb 10.1g/dl vs. Hb 11.3g/dl post treatment).There was also a significant improvement of the iron profile (Table 1). Median BP pre 144/78mmHg and post 133/74mmHg dose. In patients on ESAs (n=104), 26% (1in 4) either had their ESA dose reduced or stopped following IV FC infusion. Only 17% (n=41) of the total patient cohort required 2nd dose of IV FC as did not achieve the targeted iron profile. No reported incidence of any serious adverse effect. Table1: Pre and Post treatment (Rx) Hb and Iron profile with IV FC Hb(g/dl) Serum iron (umol/l) % Iron saturation Ferritin(ugm/l) Pre Rx ( mean) 10.1 7.86 15.33 170.32 Post Rx ( mean) 11.3 12.03 26.92 480.37 CONCLUSION: Single-dose IV FC was associated with significant improvements in Hb and iron profile and is clinically safe. Other positive outcomes were fewer hospital visits, reduced interruption in lifestyle and improved patient experience. Furthermore, single dose IV iron replacement with FC has been associated with reduced ESA usage and therefore, overall cost efficient. References: 1. Besarab A, Coyne DW. Iron supplementation to treat anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010 Dec;6(12):699-710.