CTS Heat and Temp
advertisement

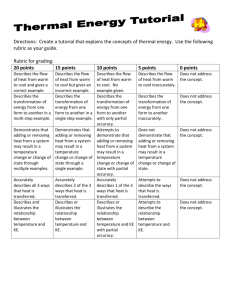
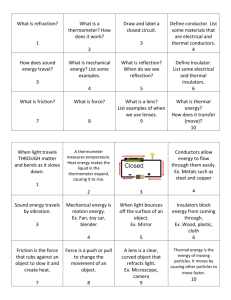
CTS Heat and Temperature LeaPs 2010 Adult Content Knowledge: Heat moves in three ways: conduction, convection and radiation Heat, energy flows spontaneously from hot to cold Most everything that goes on in universe is a transformation of energy for example an exploding star Many types of energy Heat is the total amount of energy in a materials (Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy) Temperature is scale that measures the amount of heat – added or removed Different temperature scales – F, C and K (absolute zero) Energy can shift one form to another, but total amount is constant Energy tends to “leak out” as heat Dispersal of Energy –accumulated waste energy from system ends up as heat released to environment Systems go from order to disorder unless energy is added Instructional Implications: When designing instruction it’s as important to consider HOW to teach as WHAT to teach. Things give off heat K-2 it is all about the sun Don’t confuse heat with cold Warm objects warms a cooker object Touching, at distance (heat transfer) 1 place that provides definition of word up front -> Energy Don’t have to distinguish heat from T by 5th grade Boiling Point, Melting Point, solubility Types of Energy Heat transfer Problematic because can’t see There is almost always heat loss in any transfer Amount heat Must be able to measure The Kelvin scale, but not calculating it Concepts K2 Sun warms land and water Heat moves warmer to cooker Sun’s Energy Conductors and insulators Heat produced in many ways Optics Warm stuff heats cook stuff Energy not created or destroyed Heat transferred by movement of atoms through materials or across space by radiation Sun’s energy produces change on earth Heat energy always a product of energy transformation generally not useful Different forms of energy (A. C. Helms: acronym for recalling the different forms of energy) Lt interacts with matter Energy interacts with matter Heat moves in predictable ways 3-5 MS Misconceptions Even after yrs of instruction, students do not distinguish well between heat and temperature when they are explaining thermal phenomena. The belief that temp is the measure of heat is very resistant to change. Middle school students do not always explain the process of heating and cooling in terms of heat being transferred. Think cold is transferred from cold objects to warm objects or both heat and cold are transferred at the same time. Do not always explain heat-exchange phenomena as interactions. Believe some substances can’t heat up: flour, sugar, air, etc) Metals get hot quickly because they “attract heat”, “suck heat in” or “hold heat well” Middle School: different materials have different temps if they feel different---therefore they do not recognize the universal tendency to temperature equalization. Few understand molecular basis of heat transfer even after instruction. Tend to think of heat as a substance largely in part to language and cultural influences. Tend to think heat has fluid characteristics. Hot and cold are not part of the same continuum. Cold is the opposite of heat. Know heat rises, hot things expand, heat travels through metals..but CAN NOT explain why. Think that temperature is a property of a material. Heat is hot, but temperature can be cold or hot (common with 10-12 year olds) No difference between heat and temperature: “Temperature is heat” (10-16 yr olds) Less than 25% of 13-14 yr olds correctly predicted an average temperature when differing temps of materials (water) are mixed when given beginning temps of all the liquid. Amount of material effects the temperature. Conductors and insulators are opposites with insulators having no degree of conducting ability.