Climate
advertisement

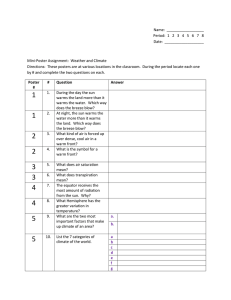
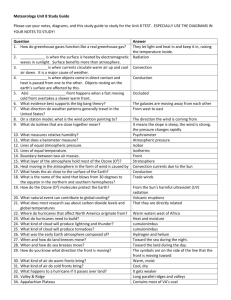
Weather vs. Climate Weather is the day to day conditions in our atmosphere. Sunny Precipitation Windy Tornados, hurricanes, etc. Weather also includes temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind, etc. We base our day to day activities on weather. Weather can change quickly but follows predictable patterns. Climate is the average conditions for an area over a period of time. This can be over a season or over a number of years. There are three main climate zones: 1. Tropical- This area is between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, along the equator. 2. Temperate- 4 seasons (This is where we live.) 3. Polar- at the poles (North and South Poles) Biomes are often identified by climate. Dry Humid Tropical, etc. Wind Wind is produced by the uneven heating and cooling of the Earth produces the wind. As the sun warms the Earth's surface, the atmosphere warms too. Some parts of the Earth receive direct rays from the sun all year and are always warm. Other places receive indirect rays, so the climate is colder. Warm air is less dense than cold air and rises higher in the atmosphere. Then cool air moves in and replaces the rising warm air. This movement of air is what makes the wind blow. For example..... There are two types of breezes along coastlines. 1. Sea Breeze- occurs during the day The sun warms up land more quickly than water, and warms the air about the ground. The warm air expands and rises and cool air comes in from the sea to replace the rising warm air. 2. Land Breeze- occurs at night The air also cools faster above the land than the sea, so at night the air above the water is hotter and rises. The cooler air above the land now goes out to sea to replace the rising air here. These predictable patterns make coast lines a great place to harness wind energy! The Study of Weather and Weather Maps The study of weather is called Meteorology. A meteorologist is a scientist that studies weather and the atmosphere. They use scientific principles to explain, understand, observe or forecast the earth's atmospheric phenomena. Thermometers are used to measure air temperature Anemometers are used to measure wind speed Changes in wind speed indicate weather changes. Barometers measure air pressure. High pressure indicates fair hot weather. Low pressure indicates cold or stormy weather. A Wind Vane is used to determine wind direction. Meteorologists use weather maps to share information about weather. Weather can be viewed and described using a weather map with weather symbols. Weather symbols are used to tell us about precipitation, warm fronts, cold fronts, high pressure, low pressure, etc. Weather maps show the day to day weather.