Geometry Room
advertisement

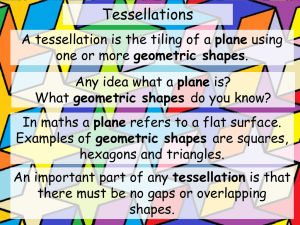
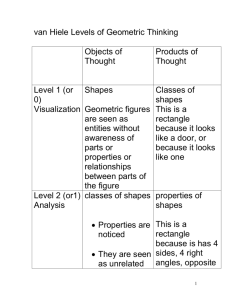
GOLD SEAL LESSON Subject(s) Mathematics Geometry Room Rigor/Relevance Framework Grade Level 4–6 K n o w l e d g e 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 Instructional Focus Student Learning Performance Task C D A B 2 3 4 Application 5 Writing: Students write for a variety of purposes and audiences with sophistication and complexity appropriate to the grade level. Language Arts Integration: Students synthesize individual language arts skills. Geometry: Students apply geometric concepts, properties, and relationships in a problem-solving situation. Students communicate the reasoning used in solving these problems. Tools and Technology: Students use appropriate tools and technologies to model, measure, and apply the results in a problem-solving situation. Students communicate the reasoning used in solving these problems. Problem Solving and Mathematical Reasoning: Students apply a variety of problem-solving strategies to investigate and solve problems from across the curriculum as well as from practical applications. Students will have an understanding of basic geometric elements (such as lines, rays, angles), as well as two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes. Students will draw or sketch a diagram of a room. Students will use a protractor. Students will work as members of a team. Students will be punctual when turning in assignments. Students will follow safety rules when using manipulatives. Overview Each student will design his or her image of an ideal classroom, detailing various geometric shapes found there. Students will identify and draw two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional shapes in the form of everyday objects. Students will write a description of their designs, showing in-depth understanding of geometric concepts and using appropriate content vocabulary. Description 1. When students arrive, ask them to name some objects in the class of various shapes and ask them to identify the shapes as a review of the basic geometry concepts that the students have learned in previous lessons (2-dimensional and 3-dimensional). 2. The teacher will provide examples of and lead discussion about geometric shapes found in the real world (soda cans as cylinders, tissue boxes as rectangular pyramids, photographs as rectangles, tennis balls as spheres, etc.). 3. Then explain that the children will be working in groups of three to create a drawing of a model classroom that must include various shapes. Then model © International Center for Leadership in Education 1 Performance Task (con’t) Assisting English Language Learners Essential Skills how to draw a diagram of a room with geometric shapes. The students are then instructed to draw a diagram of their present classroom using the geometric shapes. Circulate throughout the room to facilitate this task. When most students are done, ask several students to present their work to the class. Seeing how others draw the same room will help them gather ideas for when they create their own unique designs. 4. The students are then instructed to diagram a room in their home to gain more practice finding and drawing real-world examples of geometric shapes. These drawings will be hung up around the room and students will proceed to view them as a carousel walk-through. 5. Then distribute the assignment handout and grading rubric and review these with the class, clarifying any questions they may have. 6. Students will complete the assignment and present their findings and poster to the class at a later date. Ask English language learners to make flash cards for each of the items they find in their class (Step 1 of Performance Task) and the items they find in the real world (Step 2 of Performance Task). Expand 2 by including images students find in magazines, catalogs, and on the Internet. On the front side of the card, students will write the name of the shape in both English and in their native language. Dual vocabulary practice will help students to make comparisons more easily and encode English words in deeper context. On the back, students will draw the shape. As an alternative, students can write words and draw images in a math vocabulary journal. M4 Understand the properties of and apply parallel, perpendicular, and intersecting lines in problem-solving situations. M15 Classify angles by measure (acute, right, obtuse, and straight) and understand angle relationships (supplementary, complementary, and vertical). M41 Understand the properties and applications of the undefined terms of geometry (point, line, and plane) and their relationship with intuitive concepts (i.e., collinear points, coplanar points, opposite rays, and parallel lines). M34 Understand the properties and classification of polygons (triangles, the family of quadrilaterals, pentagon, hexagon, etc.) and apply knowledge of angle and side relationships of geometric shapes in problem-solving situations. M26 Know the classification and properties of three-dimensional figures (prisms, rectangular solids, pyramids, right circular cylinders, cones, and spheres) and be able to compute the volume and surface area of common solids. E25 Write in various formats such as learning logs, laboratory reports, notetaking, response journals, organizers, and portfolios. E20 Understand the nature and purpose of a variety of technical formats (essays, business letters, memos, investigative reports, brochures, critiques, instructions, policy statements, technical proposals, lab reports, etc.) and write in these formats. E10 Participate in (sometimes leading) one-on-one or group discussions by asking questions, asking for clarification, taking turns speaking, agreeing and/or disagreeing courteously, making informed judgments, and working toward a common goal. E31 Apply an understanding of graphics, layout, white space, italics, graphs, charts, and other visual aids to enhance informational reading, writing, or presenting. © International Center for Leadership in Education 2 My Geometry Classroom (activity sheet) Attachments/ Resources Submitted by: Rhonda Wilson, Henderson County School Scoring Guide Category 4 3 2 1 Mathematical Concepts Explanation shows Explanation shows Explanation shows Explanation shows very limited complete substantial some understanding understanding of the understanding of the understanding of the of the mathematical underlying concepts mathematical mathematical concepts needed to needed to solve the concepts used to concepts used to solve the problem(s). problem(s) OR is not solve the problem(s). solve the problem(s). written. Diagrams and Sketches Diagrams and/or sketches are clear and greatly add to the reader's understanding of the procedure(s). Accuracy Student accurately draws 90-100% of the shapes. Mathematical Terminology and Notation Diagrams and/or sketches are clear and easy to understand. Diagrams and/or Diagrams and/or sketches are sketches are difficult somewhat difficult to to understand or are understand. not used. Student accurately Student accurately More than 75% of draws almost all (85- draws most (75-84%) the shapes are drawn 89%) of the shapes. of the shapes. incorrectly. Correct terminology Correct terminology Correct terminology and notation are and notation are There is little use, or and notation are usually used, making used, but it is a lot of inappropriate always used, making it fairly easy to sometimes not easy use, of terminology it easy to understand understand what was to understand what and notation. what was done. done. was done. © International Center for Leadership in Education 3 My Geometry Classroom Your Job You must design and create a diagram for your idea of an ideal math classroom. You must include a minimum of five two-dimensional shapes and five three-dimensional shapes in the form of everyday objects. You must use a protractor to correctly identify and accurately illustrate the geometric shapes you draw. You must label the geometric shapes in your designs/diagrams. Final Product You must write a description of your designs, showing complete understanding of geometric concepts through your explanations of your choice of shapes. You must use appropriate content vocabulary in your description and explanation. You must organize your diagram and description on a poster to be presented to the class. © International Center for Leadership in Education 4