Acids and Bases Quiz Answers
advertisement

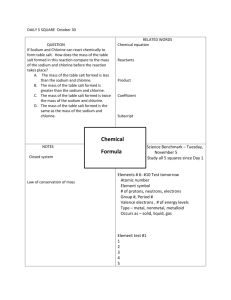
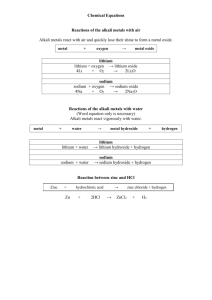
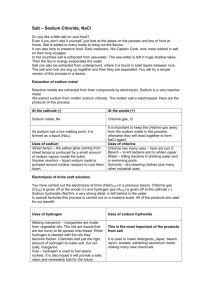
Name _____________________________ PHYSICAL SCIENCE TWO 2012 Answers ACIDS & BASES QUIZ Section A: Multiple Choice Questions 1. A B C D When a metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, the products are: A salt and oxygen gas. A salt and hydrogen gas. A salt and water. Water and carbon dioxide. 2. A B C D Which one of the following statements about bases is true? Bases: Unlike dangerous acids, are generally quite safe. Are just stronger types of acids. Are found in citrus fruits. Are used in many cleaning products. 3. A B C D Adding liquid X to water decreases its pH. This shows that the liquid X is: An acid. A base. Neutral. Water. 4. Which list shows the four substances in order from the strongest acid to the strongest base? Sulphuric acid, acetic acid, pure water, cloudy ammonia, sodium hydroxide Acetic acid, sulphuric acid, pure water, sodium hydroxide, cloudy ammonia Pure water, sulphuric acid, cloudy ammonia, acetic acid, sodium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide, cloudy ammonia, pure water, acetic acid, sulphuric acid A B C D 5. A B C D When an acid and base react together, which substances would you always expect to be produced? A salt and oxygen gas A salt and hydrogen gas A salt and water Water, a salt and carbon dioxide 6. A B C D A reaction in which an acid reacts completely with a base to produce water is called: An acidic reaction A decomposition reaction A neutralisation reaction A precipitation reaction. 7. A B C D Antacid tablets contain: A special medicinal acid extracted from ants Alternative acids for dissolving food that are milder than stomach acid Substances designed to speed up the reaction of stomach acid in food A chemical that dissolves in the stomach to release a base. Part B: Short Answer 1. Balance each of the following equations AND state the type of equation: precipitation, ionic, neutralisation or combustion (3 x 2 = 6). a. C3H8 (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + H2O (g) C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (g) Combustion Reaction b. Ba2+ (aq) + PO43– (aq) → Ba3(PO4)2 (s) 3Ba2+ (aq) + 2PO43– (aq) → Ba3(PO4)2 (s) Precipitation/Ionic Reaction c. Ba(OH)2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (aq) + H2O (l) Ba(OH)2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l) 2. Neutralisation Reaction Write a fully, balanced chemical equation to describe a chemical reaction in which solid sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid to form carbon dioxide gas and a solution of sodium chloride and water (2). NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) 3. Calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HNO3 solution (1). pH = -log10 [H+] = -log10 0.01 = 2 4. Calculate the hydrogen ion (H+) concentrations of orange juice with a pH of 3.5 (1) [H+] = 10-pH = 10-3.5 = 3.16 x 10-4 M or 0.000316 M 5. Blood has a pH of 7.4. A urine sample has a pH of 5.4. How many times more acidic is the urine than blood (1)? Change in pH in 2 indicates that urine is 102 = 100 times more acid than blood. 6. You are provided with 20 mL of a solution of pH 4. Explain how you could use this solution to prepare a solution of pH 5 (2 marks) A change in pH from 4 to 5 indicates a 10 fold decrease in concentration. Therefore you would need to dilute your solution from 20 mL to 200 mL by adding 180 mL of water. 2 DATA SECTION pH = -log10 [H3O+] POSITIVE VALENCY [H3O+] = 10-pH NEGATIVE VALENCY aluminium Al3+ bromide Br- ammonium NH4+ carbonate CO32- barium Ba2+ chloride Cl- calcium Ca2+ chromate CrO42- chromium Cr3+ dichromate Cr2O72- copper (I) Cu+ fluoride F- copper (II) Cu2+ hydroxide OH- hydrogen H+ hydride H- iron (II) Fe2+ iodide I- iron (III) Fe3+ nitrate NO3- lead (II) Pb2+ nitrite NO2- lead (IV) Pb4+ nitride N3- magnesium Mg2+ oxide O2- mercury Hg2+ permanganate MnO4- potassium K+ phosphate PO43- tin (II) Sn2+ phosphide P3- tin (IV) Sn4+ silicide Si4- silver Ag+ sulphate SO42- sodium Na+ sulphide S2- zinc Zn2+ sulphite SO32- 3