Tutorial4_cryptography
advertisement

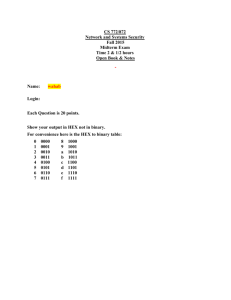
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF COMPUTING AND INFORMATICS Computer Science Department Private Bag 13388 | 13 Stock Street | Windhoek, NAMIBIA Tel: (+264 - 61) 207 – 2510 | Fax: (264 – 61) 207 – 9258/2051 http://sit.polytechnic.edu.na transforming into Namibia University of Science and Technology Network Security NWS620S – Tutorial 4 Network Attacks Encryption is the translation of data into a secret code so that only authorised entities can read it. Encrypting data is considered a very effective way of achieving data security. To access encrypted data, you must have access to a secret key that enables you to decrypt it. Unencrypted data is called plain text; encrypted data is referred to as cipher text. There are two types of encryption: Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption/public key encryption In symmetric key encryption both the sender and the receiver have the same key. One of te earliest forms of symmetric key encryption techniques is the Caesar cipher. Ceasar cipher is a substitution encryption technique in which each element in the plaintext is mapped into another element. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example Julius Ceasar from which the name is derived used a shift of 3 would get: plaint ext ciphe rtext A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Table 1 If we encrypt Julius Ceasar with this scheme we would get: Grifrp Zbxpxo A more complicated substitution cipher is the Vigenere Cipher which is a method of encrypting alphabetic text by using a series of different Caesar ciphers based on the letters of a keyword. For example if we use key “ec” Same table 1 for C and for E it would be: plaint ext ciphe rtext A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I Table 2 J K L M N O P Q R S T U To encrypt Julius Ceasar would yield: Ergfpp Xbvpvo plaintext J key E ciphertext E U C R L E G I C F U E P S C P C E X E C B A E V S C P A E V R C O Tasks 1. 2. 3. 4. Encrypt your name with Ceasar cipher with a shift of 3 Encrypt “I am a second year student” with Ceasar cipher with a shift of 6 Decrypt “l oryh qhwzrun vhfxulwb” Decrypt “Anzvovn Havirefvgl bs Fpvrapr” encrypted with Ceasar cipher with a shift of 13. 5. Encrypt your name using the key “ec” with the Vigenere Cipher 6. Decrypt “n fbay vy cgx aejug” encrypted with a Vigenere cipher key fun. Homework 1. Why is the cryptanalysis of Ceasar cipher easy? a. How can it be done? 2. Explain how Vigenere is an improvement of Ceasar Cipher a. is it easy to cryptanalyse Vigenere cipher? b. Describe how cryptanalysis of Vigenere cipher can be done