Statistical Techniques
advertisement

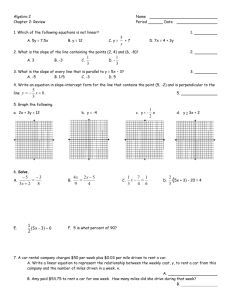
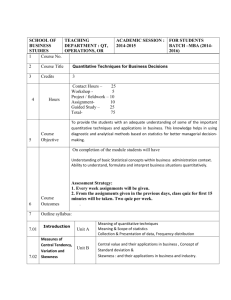
SEMESTER III (Marks 100 – 75 Lectures) OBJECTIVES: To enable the students to gain understanding of statistical techniques as are applicable to business. To give comprehensive knowledge of the subject to the students opting for professional and academic course where statistics is a part of the curriculum. 1. INTRODUCTION: (4 Marks -5 Letures) Meaning and definition of statistics. Function, Scope and Limitation of statistics. Basic statistical Concepts- Population, Sample, Variable, Attribute, Parameter and statistic. 2.COLLECTION OF DATA: Types of Data- primary & secondary data. (8 Marks-5Letures) Sources ,Methods of collecting primary data. Clasiffication-Univariate frequency distribution, Bi-variate frequency distribution. 3.GRAPHS AND DIAGRAMS: (12 Marks-10Letures) Histogram Frequency polygon Frequency curve and Ogives Simple Bar, Multiple and sub divided bar, pie diagrams. IV. SUMMARISATION MEASURES: (40 Marks-30Letures) Measures of Central Tendency- Meaning, Objectives Requisites of a good average Arithmetic Mean, Median Mode (Without grouping) – Geometric Mean, Harmonic Mean Partition values-Quartiles, Deciles, And Percentiles. Measure of Dispersion – Meaning, Objectives Requisites of a good Measure of DispersionAbsolute and relative measures Range, Quartile deviation, Mean Deviation, Standard deviation, Coefficient of range, Coefficient of Quartile deviation, Coefficient of Mean deviation and Coefficient of Variation. Skewness –Meaning Karl Person’s and Bowley’s measures of skewness and coefficient of skewness. Notion of Kurtosis. V. INDEX NUMBERS: Meaning (18 Marks-15Letures) Types, uses and limitation Methods of constructing price and quantity index numbers by unweighted and weighted methods Weighted Agrregative – Laspeyre’s, Paasche’s and Fishers’s formulae Weighted average of relatives - Arthmetic Mean and Geometric Mean Value index number – Fixed base, chain base indices, Base shifting, Deflating and splicing, Cost of living index numbers. VI. ANALYSIS OF TIME SERIES: (18 Marks-10Letures) Meaning and utility Components of time series Models of Time series – Additive and Multiplicative models. Measurement of Trend – semi averages, moving averages and methods of least squares (Straight line and second degree parabola). Books for Study and Reference: Gupta S.P Statistical Methods, Sultan Chand and Sons Sancheti D.C. and Kapoor V.K Statistics (Theory, methods and Application) Sultan Chand and Sons Levin Richard I and Rubin David S. Statistics for Management, Prentice Hall of India Gupta C.B Fundamental of Statistics, Himalaya Publishing House R.J.Shah Statistical Techniques. Neeta Mazumdar Statistical Techniques Rajhauns Vitaran, SEMESTER IV (Marks 100) CORRELATION AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS : Meaning and types of correlation methods of studying correlation. Scatter diagrams, Karl Person’s coefficient of correlation Spearman’s rank coefficient of correlation, Properties of Karl Person’s coefficient of correlation. Linear regression – meaning Regression lines and regression confidents. (30 MARKS-18 LECTURES) II . ELEMENTS OF PROBABILITY : Random experiments and events definition of probability Conditional probability. Addition and multiplication theorems (with proof). Mathematical expectation. (18 MARKS-16 LECTURES) III. (18 MARKS-12 LECTURES) THEORITICAL DISTRIBUTION : Random Variable. Binomial ,Poisson and Normal distribution (with properties) IV .METHODS OF SAMPLING : (4 MARKS- 4 LECTURES) Census enumeration and sample enumeration. Methods of samplingSimple random sampling, Systematic sampling, Stratified sampling, Cluster sampling, Purposive sampling, Quota sampling and Multi – stage sampling. V .TESTS OF HYPOTHESIS AND ESTIMATION : (12 MARKS-15 LECTURES) Sampling distribution. Standard error, Procedure of testing a hypothesis. Null and Alternative hypothesis. Type I & Type II errors. Critical region and level of significance. Test of significance for large samples. Sample mean and sample proportionconfidence limits population mean and population proportion VI. STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL: Meaning and Utility, Control charts for X,R,P&C (18 MARKS-10 LECTURES-) Books for Study and Reference: Gupta S.P Statistical Methods, Sultan Chand and Sons Sancheti D.C. and Kapoor V.K Statistics (Theory, methods and Application) Sultan Chand and Sons Levin Richard I and Rubin David S. Statistics for Management, Prentice Hall of India Gupta C.B Fundamental of Statistics, Himalaya Publishing House R.J.Shah Statistical Techniques. Neeta Mazumdar Statistical Techniques Rajhauns Vitaran,