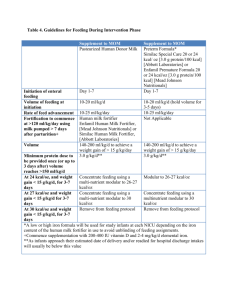
Ecology Study Guide (food webs) Answers
advertisement
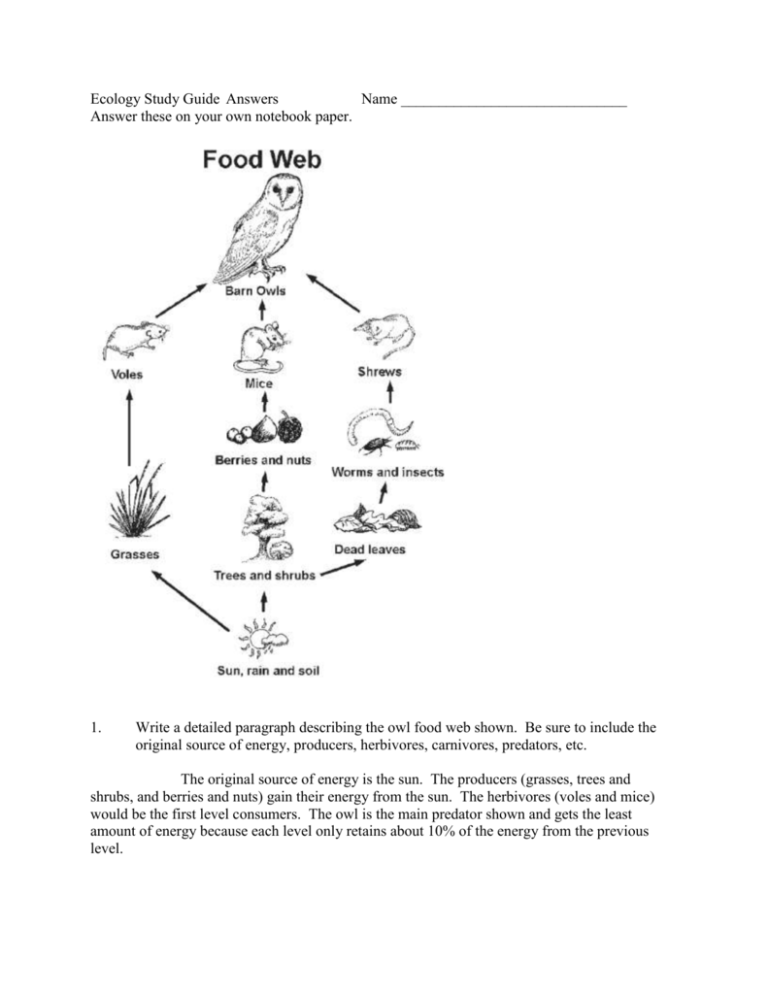
Ecology Study Guide Answers Name ______________________________ Answer these on your own notebook paper. 1. Write a detailed paragraph describing the owl food web shown. Be sure to include the original source of energy, producers, herbivores, carnivores, predators, etc. The original source of energy is the sun. The producers (grasses, trees and shrubs, and berries and nuts) gain their energy from the sun. The herbivores (voles and mice) would be the first level consumers. The owl is the main predator shown and gets the least amount of energy because each level only retains about 10% of the energy from the previous level. 2. Where do you see competition occurring? Competition occurs when you see a “V” shape in the food web. For example, the trees and shrubs compete with the grass for the sun’s energy. 3. Describe the possible first level consumers (herbivores), second level consumers (omnivores), and third level consumers (carnivores) from your owl pellet dissection experience. The first level consumers would be some insects such as beetles. Some second level consumers would be rats or shrews. The 3rd level consumer would be the owl itself. 4. Each level of a food pyramid only retains about ____10______ % of the energy from the previous level. As a fraction, this would be 1/10 . As a decimal, this is .1. A way to get 10% of a number is to divide by ____10_______. 5. If producers created 5,000 kcal of energy, how much of that would a first level consumer retain? 500 kcal How much would the second level consumer retain? 50 kcal How much would a third level consumer retain? 5 kcal producers 5,000 kcal 6. If producers created 3,200 kcal of energy, how much of that would a first level consumer retain? 320 kcal How much would the second level consumer retain? How much would a third level consumer retain? 3.2 32 kcal How could you summarize #5 and #6 all in a sentence? Each time you move up a level of consumer on the energy pyramid, you should move the decimal to the left one place, or just divide by 10. producers 3,200 kcal 7. Write a paragraph or two describing in detail the food web above. Everything begins with the sun giving energy to the producer, which is seagrass. The first level consumers (herbivores) eating the seagrass are labeled as “primary” (dugong, green turtle, bottlenose dolphin, and mackerel). The only omnivore shown is the bottlenose dolphin since he is shown to absorb energy from both seagrass and mackerel. The 3 secondary level consumers are all carnivores. The third (tertiary) level consumer is the killer whale, also a carnivore. One example of competition shown in this food web is that the killer whale and the great white shark both get energy from the bottlenose dolphin. Another example is that the bottlenose dolphin and the humpback whale compete for energy from the mackerel. 8. If some parasites such as tapeworms and roundworms caused disease in this Bottlenose Dolphin population shown above, explain exactly how that would affect every other part of the food web community shown. If the population of bottlenose dolphins decreased dramatically, the great white population would eventually not have enough food. There would be one less primary consumer competing for the seagrass. The humpback whale population may increase because it would have less competition for the mackerel. 9. How would these parts of a food chain be sequenced correctly? (circle one answer) Sun grain chicken Grain child eating eggs Grain chicken Sun cow sun chicken child eating eggs child eating eggs Child eating eggs 10. child eating eggs sun grain chicken grain sun Identify the correct energy flow patterns. (circle all correct possibilities) T V S U R X W Q TUV UVW QXU QWV VUT RXW QRS XQW STU XUT XUV SUV 11. Explain everywhere in the food web where you can determine that there is competition. (HINT: Look for the “V” shapes) R, X and W are all competing for Q V and T are competing for U 12. Explain in detail what would happen if X becomes scarce for any reason. R and W will be the only ones competing for Q then, so those populations might increase. However, since U only is shown eating X, that population would eventually die out after decreasing. If the U population dies out, then T and V would have less sources of food, which would decrease the S and W populations. 13. What happens to organisms in the food web as they die? What effect does that have? The organisms begin to decompose and the energy is returned to the soil, which is absorbed by the plants. This starts the whole process all over again and helps the next producers.