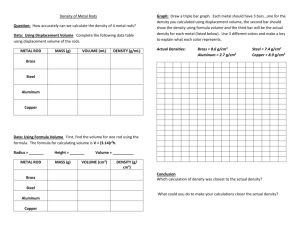
Name Up to 5 points extra credit on test, due W 9/17 at the
advertisement

Name _______________________________ Up to 5 points extra credit on test, due W 9/17 at the beginning of class Chemistry Section I/II Review 1) Know the definitions of the following terms. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. r. Law of conservation of mass – states that matter can’t be created or destroyed Hypothesis – a possible explanation for an observation Element – contains only one type of atom and can’t be broken down by ordinary means Amu – the unit most commonly used for atomic mass Compound – composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a specific ratio Mixture – composed of two or more substances physically combined without a specific ratio Dmitri Mendeleyev – first organized the periodic table Chemical change (including examples/evidence) – a change that results in the production of a new substance; indicators include: bubbles, color change, production of light and heat Metal – found on the left side of the periodic table staircase (most elements are metals) Nonmetal – found on the right side of the periodic table staircase Halogen – group VII A (7A or 17) on the periodic table; second to last column Noble gas - group VIII A (8A or 18) on the periodic table; the last column Alkali metal - group I A (1A or 1) on the periodic table; the first column Alkali earth metal - group II A (2A or 2) on the periodic table; second column from left Transition metal – the center section of the periodic table ranging from group 3-12 Inner transition metal – the 2 rows of elements at the bottom of the periodic table Metalloid – found on the periodic table staircase Main group/representative elements – the first 2 columns and the last 6 columns on the periodic table 2) Circle the intensive properties in the following list: mass, density, volume, color, boiling point Intensive properties are independent of the amount ex) density, color & boiling point Extensive properties depend on the amount ex) mass & volume 3) You have two blocks of iron. One has a mass of 7.8 g, the other has a mass of 150.0 g. a. Do they have the same volume? Explain. No, they do not have the same volume. They are both made of iron, so they both have the same density. In order to have the same volume, they would have to be the same mass. b. Do they have the same density? Explain. Yes, they are both made of iron. 4) You have two blocks of different metals. One is a 150.0 g block of aluminum with a density of 2.7 g/cm3; the other is a 150.0 g block of gold with a density of 19.3 g/cm3. If you submerge each in water, which block will displace a larger volume of water? Explain why. Aluminum is much less dense than gold, therefore 150.0 g of Aluminum would take up much more space than 150.0 g of gold. Because the Aluminum is bigger, it would displace more water. 5) Calculate the volume of the gold block from question 4). V=m D V = 150.0 g 19.3 g/cm3 V = 7.77 cm3 6) Consider two objects that each weigh 20.0 g. One is made of lead and has a density of 11.4 g/mL. The second object is made of aluminum and has a density of 2.7 g/mL. Which object takes up more space? What volume does each occupy? The aluminum would take up more space because it is less dense. Lead: V = m V = 20.0 g 11.4 g/cm3 D Aluminum: V = 1.75 cm3 V=m D V = 20.0 g V = 7.41cm3 2.7 g/cm3 7) Identify the piece of equipment that would be the most appropriate for measuring the volume of each of the following. Also circle “displacement” if the water displacement method would be used. a. Gatorade graduated cylinder ruler displacement b. Key graduated cylinder ruler displacement c. Sand graduated cylinder ruler displacement d. Tissue box graduated cylinder ruler displacement 8) Know the different parts of the periodic table, and be ready to label or identify these parts. Feel free to practice by coloring in and labeling the periodic table below. 9) Give each of the following pieces of information for aluminum. a. Atomic symbol Al b. Atomic number 13 c. (Average) atomic mass 26.982 amu 10) 3.4 mL of water are added to a graduated cylinder. Then, a small marble is added to the water, raising the volume to 5.6 mL. a. Draw the original and final meniscus on the graduated cylinder on the right. b. Calculate the volume of the marble. V = 5.6 – 3.4 V = 2.2 cm3