Lab activity acids and bases docx
advertisement

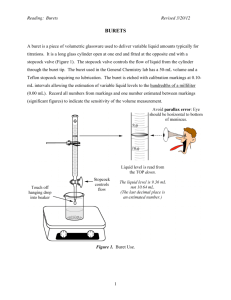
Lab Acid-Base Titration Procedure Setting up the Known Base Solution 0.05 M NaOH 1. Attach glass titration buret to buret clamp and ring stand. Place funnel that fits into the top of titration buret. Make sure the buret is securely clamped onto ring stand and buret knob is securely on so it will not fall out 2. Fill buret with NaOH solution and record starting volume to 2 decimal places. Tap buret gently so there are no air bubbles in the buret. Setting up the Unknown Acid Solution HCl that will be TITRATED 1. Attach a second glass titration buret to buret clamp and ring stand. Place funnel that fits into the top of titration buret. Make sure the buret is securely clamped onto ring stand and buret knob is securely on so it will not fall out 2. Fill buret with UNKNOWN HCl solution and record starting volume to 2 decimal places. Tap buret gently so there are no air bubbles in the buret. 3. Add 10 mL HCl solution from buret into a 50 ml or 100 ml beaker. Record end volume to two decimal places. 4. Add 10 drops of indicator solution phenolthalein to the beaker. 5. Place white paper under beaker to observe color changes easily. 6. Measure the pH of the acid with a probe and universal pH paper. Titrating the Acid HCl 7. Titrate the beaker solution slowly. Do this by turning the buret knob so a steady addition of drops of NaOH base are added . 8. Stop the addition of base when you see the pink color staying for about 5 seconds in the HCl 9. Measure the pH again. 10. Continue titrating slower this time . You will notice the HCl phase in and out of pink color. When you think you are getting close to the solution making a complete change in pink, start adding a few drops at a time until the solution stays pink for 10 seconds or more. 11. Record the final pH of the solution. 12. Record the final volume of the NaOH added. This is called the end point volume. Trials 2 and 3 repeat steps 1-12 above Data – a) Individual data showing 3 trials: total volume of NaOH added, molarity of unknown acid, final pH of solution using paper and probe. Also average volume NaOH used, average molarity of unknown acid, avg. pH of the 3 trials. b) Class data showing averages only of any 3 groups ( including yours) : average volume of NaOH added, molarity of unknown acid, final pH of solution using probe. Calculations for each trial – show work – and avg. Using the end point volume of base solution at the point of color change, calculate the exact concentration of the acid solution using the known concentration of the base, total volume of base used( which is the end point volume) , and volume of acid titrated based on this formula: Molarity1 x Volume1 M1V1 = Molarity2 x Volume2 = M2V2 acid = Units : M = mol/L V = L . base