CP CHEMISTRY Name: Titration Demo Lab ___ period Background
advertisement

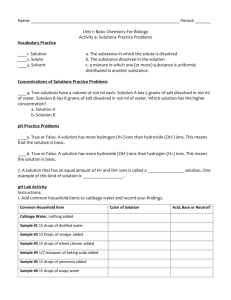
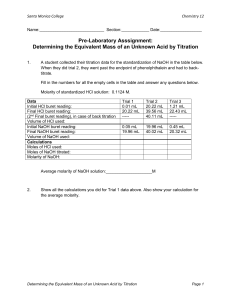
CP CHEMISTRY Titration Demo Lab Name: ________________________________ ___ period Background: Acid-base titrations involve the neutralization reaction between the hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. These ions combine to form neutral water molecules. When the number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions are equal in the titration flask, then the equivalence point has been reached. In order to see this point, indicators are used. They are one color in an acidic solution and another color in a basic solution. Some occur naturally as pigments in plant leaves. In this lab, red cabbage leaves will be used to make an indicator for the titrations of vinegar with sodium hydroxide and ammonia with hydrochloric acid. Purpose: Observe the properties of an indicator extracted from red cabbage leaves and use it to determine the concentrations of vinegar and ammonia solutions. Data: Table 1 – Cabbage Indicator Tube A B C D E Reagent Added Observation CP CHEMISTRY, Titration Demo Lab, page 2 Table 2 – Titration of Vinegar Volume of vinegar (mL) Molarity of NaOH (M) Volume of NaOH (mL) (initial buret reading) Volume of NaOH (mL) (final buret reading) Volume of NaOH used (mL) Table 3 – Titration of Ammonia Volume of ammonia (mL) Molarity of HCl (M) Volume of HCl (mL) (initial buret reading) Volume of HCl (mL) (final buret reading) Volume of HCl used (mL) CP CHEMISTRY, Titration Demo Lab, page 3 Analysis: 1. Calculate the molarity of the vinegar solution. 2. Calculate the molarity of the ammonia solution. Conclusions: 1. Would you use and acid or base as a standard when titrating against a solution of soda? Why? 2. Describe how you could use the red cabbage extract as a quantitative method for determining solution pH.