ELA-Pacing-Guide
GULFSTREAM MIDDLE SCHOOL
ELA Pacing Guide
2015-2016
Standards Instructional Pacing
Guide
August Pre-Test the week of
No Assessment
8/10/2015
Strategies
Argumentation
LAFS.6-8.W.1.1
** GrammarNotes in
Collections **
** Writing Interactive
Lessons **
** Collections **
***CFA administered the week of September
15 th ****
Cognitive Complexity Level 3
LAFS.6-8.W.1.1
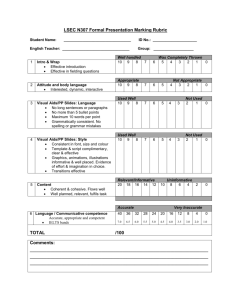
Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. a. Introduce claim(s) and organize the reasons and evidence clearly. b. Support claim(s) with clear
Basic components of an argument:
The claim (that typically answers the question: “What do I think?”)
The reasons (that typically answer the question: “Why do I think this?”)
The evidence (that typically answers the question: “How do I know this is the case?”).
Evidence-Based Argument Checklist:
Early in the piece, I offer a clear and interesting claim about the text.
The claim is arguable
—someone could use evidence to offer a different reasons and relevant evidence, using credible sources and demonstrating an understanding of the topic or text. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to clarify the relationships among claim(s) and reasons. interpretation or disagree with me.
I use lots of direct evidence from the text to support my claim.
The evidence I use shows that I know the text well and have thought about it more than just a superficial reading.
I organize my evidence into meaningful points and explain the evidence.
I make sure the reader understands why the evidence supports and advances my claim.
Designing an Evidence-based Argument:
What words, lines, ideas, and phrases seem important and interesting in this text? d. Establish and maintain a formal style. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from the argument presented.
(These ideas may come from responses to text-dependent questions or other close reading activities.)
What patterns do you see? What connections seem to exist among these important ideas and details?
What evidence-based claims would these patterns allow you to make about the text?
What conclusion that you can draw from the text that you could then support with evidence from the text?
Informative/Explanatory
LAFS.6-8.W.1.2
** GrammarNotes in
Collections **
** Writing Interactive
Lessons **
** Collections **
***CFA administered the week of October 26th h ****
Cognitive Complexity Level 4
LAFS.6-8.W.1.2
Write informative/explanatory texts to formatting (e.g., headings),
Basic components of an argument:
The claim (that typically answers the question: “What do I think?”) examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the
The reasons (that typically answer the quest ion: “Why do I think this?”) relevant content.
The evidence (that typically answers the question: “How do I know this is the case?”).
Evidence-Based Argument Checklist: a. Introduce a topic; organize
Early in the piece, I offer a clear and interesting claim about the text.
The claim is arguable
—someone could use evidence to offer a different ideas, concepts, and information, using strategies interpretation or disagree with me.
I use lots of direct evidence from the text to support my claim. such as definition,
The evidence I use shows that I know the text well and have thought about it classification, more than just a superficial reading. comparison/contrast, and cause/effect; include
I organize my evidence into meaningful points and explain the evidence.
I make sure the reader understands why the evidence supports and advances my claim. graphics (e.g., charts, tables), Designing an Evidence-based Argument: and multimedia when useful to What words, lines, ideas, and phrases seem important and interesting in this text? aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples. c. Use appropriate transitions to clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Use precise language and domain specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic. e. Establish and maintain a formal style. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from the information or explanation presented.
(These ideas may come from responses to text-dependent questions or other close reading activities.)
What patterns do you see? What connections seem to exist among these important ideas and details?
What evidence-based claims would these patterns allow you to make about the text?
What conclusion that you can draw from the text that you could then support with evidence from the text?
Informative/Explanatory
LAFS.6-8.W.1.2
** GrammarNotes in
Collections **
** Writing Interactive
Lessons **
** Collections **
***CFA administered the week of November 30th h ****
Cognitive Complexity Level 4
LAFS.6-8.W.1.2
Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. g. Introduce a topic; organize ideas, concepts, and information, using strategies such as definition, classification, comparison/contrast, and cause/effect; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. h. Develop the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples. i. Use appropriate transitions to clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. j. Use precise language and domain specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic. k. Establish and maintain a formal style. l. Provide a concluding a. statement or section that follows from the information or explanation presented.
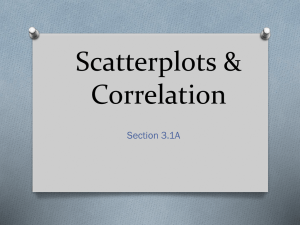
Basic components of an Informative/Explanatory essay:
Informative/Explanatory writing gives facts and information, explains how to do something, or tells readers about real people and events.
How informative/explanatory writing is organized depends on its purpose.
• Compare-and-Contrast describes the similarities and differences between things.
• Cause-and-Effect describes a cause and the result, or effect, of that cause.
•
Problem-and-Solution describes a problem and offers one or more solutions.
•
How-To tells readers how something happens or explains a step-by-step process.
•
Summary describes the main points of a piece of writing.
• Explanatory gives the meaning of a topic.
•
Research Report organizes information about a topic.
Topic
Definitions
Facts
Transitions
Precise Language
Concluding Statement
Some common types of informative/explanatory writing include the following:
•
Research Report
• Cause-Effect Report
• Problem-Solution Essay
•
How-To Essay
• Compare-and-Contrast Essay
Informative/Explanatory
LAFS.6-8.W.1.2
** GrammarNotes in
Collections **
** Writing Interactive
Lessons **
** Collections **
***CFA administered the week of January 24th h ****
Cognitive Complexity Level 4
LAFS.6-8.W.1.1
Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. a. Introduce claim(s) and organize the reasons and evidence clearly. b. Support claim(s) with clear reasons and relevant evidence, using credible sources and demonstrating an understanding of the topic or text. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to clarify the relationships among claim(s) and reasons. d. Establish and maintain a formal style. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from the argument presented.
Basic components of an Informative/Explanatory essay:
Informative/Explanatory writing gives facts and information, explains how to do something, or tells readers about real people and events.
How informative/explanatory writing is organized depends on its purpose.
•
Compare-and-Contrast describes the similarities and differences between things.
•
Cause-and-Effect describes a cause and the result, or effect, of that cause.
• Problem-and-Solution describes a problem and offers one or more solutions.
• How-To tells readers how something happens or explains a step-by-step process.
• Summary describes the main points of a piece of writing.
•
Explanatory gives the meaning of a topic.
• Research Report organizes information about a topic.
Topic
Definitions
Facts
Transitions
Precise Language
Concluding Statement
Some common types of informative/explanatory writing include the following:
•
Research Report
• Cause-Effect Report
•
Problem-Solution Essay
• How-To Essay
•
Compare-and-Contrast Essay