AP Physics B Formula Study Sheet
advertisement
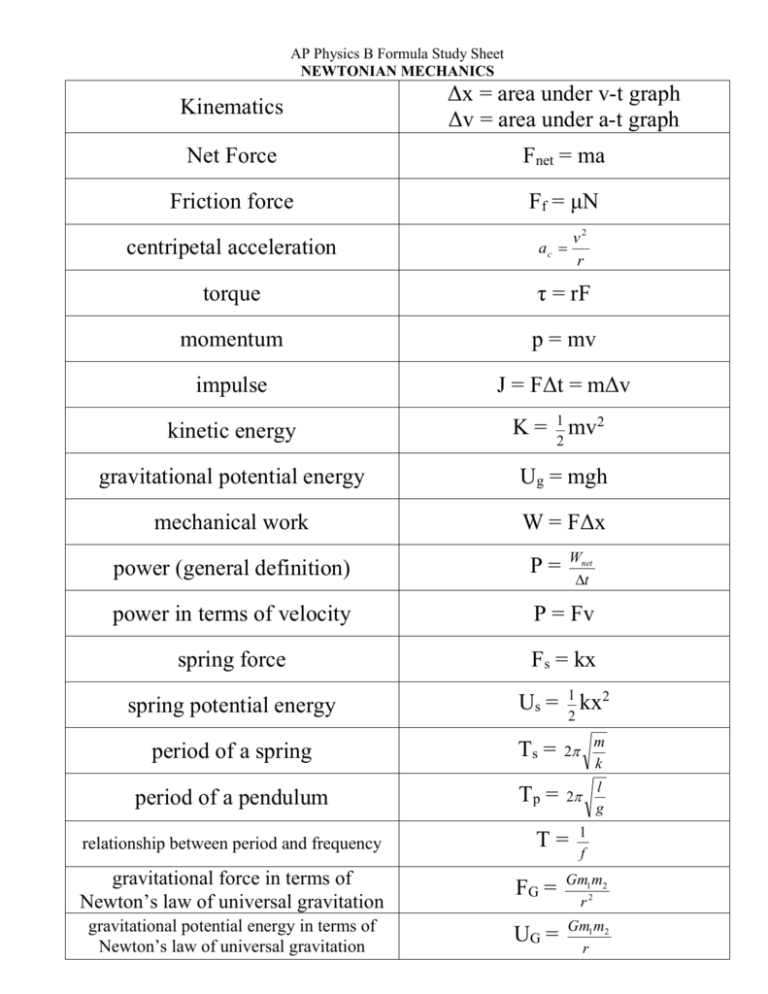
AP Physics B Formula Study Sheet NEWTONIAN MECHANICS Kinematics Δx = area under v-t graph Δv = area under a-t graph Net Force Fnet = ma Friction force Ff = μN centripetal acceleration v2 r ac torque τ = rF momentum p = mv impulse J = FΔt = mΔv kinetic energy K = 1 mv2 gravitational potential energy Ug = mgh mechanical work W = FΔx 2 Wnet t power (general definition) P= power in terms of velocity P = Fv spring force Fs = kx spring potential energy Us = 1 kx2 2 period of a spring Ts = 2 m k period of a pendulum Tp = 2 l g relationship between period and frequency T= 1 f gravitational force in terms of Newton’s law of universal gravitation FG = Gm1m2 r2 gravitational potential energy in terms of Newton’s law of universal gravitation UG = Gm1m2 r FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS absolute pressure in a fluid P = P0 + ρgh gage pressure P = ρgh buoyant force Fbouy = ρVg fluid flow continuity A1v1 = A2v2 volume flow rate A1v1 Bernoulli’s principle P + ρgy + 1 ρv2 = constant 2 F A P= pressure (general definition) ideal gas law PV = nRT = NkBT internal energy in a gas Kavg = 3 kBT velocity of a gas molecule 2 vrms = 3RT M = 3k B T thermal work W = PΔV or area under graph change in internal energy ΔU = Q + W efficiency (general) ideal (Carnot) efficiency e= ec = Wnet Qin TH TC TH ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Electrostatic force Fe = Electrostatic field E= Electrostatic potential energy Ue = kq1 q 2 r2 kq1 r2 kq1 q 2 r kq1 r Electrostatic potential V= Charge on a capacitor Q = VC Capacitance Energy stored in a capacitor C= 0 A d UC = ½ QV = ½ CV2 Current (definition) I= Q t Resistance of a wire R= l A Ohm’s Law Power in a circuit Equivalent resistor for series Equivalent resistor for parallel Equivalent capacitance for series Equivalent capacitance for parallel V = IR P = IV = V2 R = I2R Req = R1 + R2 + … 1 Req = 1 1 ... R1 R2 1 Ceq = 1 1 ... C1 C 2 Ceq = C1 + C2 +… Magnetic force on a moving charge in a magnetic field Magnetic force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field Magnetic field around a current carrying wire Magnetic flux Average EMF generated by a changing magnetic field EMF generated by a loop moving into or out of a magnetic field Force BIl’s qvB ε Blvd when the flux is changing. Take ast FB = qvBsinθ FB = BIlsinθ B= 0 I 2r Φm = BAcosθ εavg = t ε = Blv m WAVES AND OPTICS Velocity of a wave v = fλ Index of refraction c n= v Snell’s Law n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2 n1sinθ1 = n2sin90 or Critical angle n2 sinθc = n 1 1 1 1 si s o f Mirror & lens equation Magnification M= Focal length in terms of radius of curvature Diffraction pattern path difference hi s i ho so f= R 2 mλ = dsinθ xm = Diffraction pattern spacing m L d ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS Energy of a photon E = hf = pc Maximum kinetic energy of an emitted electron deBroglie wavelength of an emitted electron -φ + hf = Kmax Rest energy of a mass ΔE = (Δm)c2 λ= h p