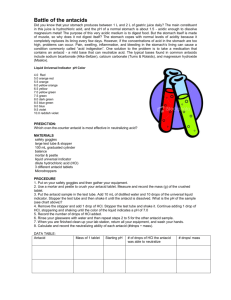
Lesson 11: Antacid Lab: STUDENT (Westfall) Did you know that
advertisement

Lesson 11: Antacid Lab: STUDENT (Westfall) Did you know that your stomach makes 1 -2 litres of gastric juice daily. This juice is made up of hydrogen and chlorine. It is called hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is used to kill germs you eat with your food. It also helps digest proteins. The pH of a normal stomach is about 1.5. This is acidic enough to dissolve magnesium metal! Your stomach is made of 3 layers of muscle tissue. You would think the acid would eat away at the muscle of your stomach. But are you in pain right now? No. Why not? The stomach constantly makes a lot of mucus to protect the inside of the stomach from the acid. This mucus is eaten away by the acid daily. So we are constantly making mucus all the time. However, if you make too LITTLE MUCUS, the acid will eat at the muscle and you will feel pain. If you make TOO MUCH ACID, you might be in pain also. One solution to the problem is to take a medication that contains an antacid. An antacid is a mild base that can neutralize the stomach’s acid. The typical bases found in common antacids are listed below: alka-seltzer Tums Rolaids Maalox Milk of magnesia Baking soda A typical pharmacy may offer 30 different antacids to choose from. It is estimated that Americans spend billions of dollars on antacid pills alone. Wow, don’t we have digestion issues in North America? Which antacid would you choose? Do you want the cheapest or the most effective to help the burning sensation in your stomach? In this lab, you will compare different brands of antacid tablets’ neutralizing ability. Hopefully, you will discover which antacid is the most effective at neutralizing stomach acid. Purpose: to see which antacid neutralizes the most stomach acid. Observations: alka-seltzer = Tums = Rolaids = Maalox = Milk of magnesia = Baking soda = Interpretations: 1. Why was it necessary to stir the mixture as the acid is added? Give one reason. 2. Why did the colour of the indicator change when the acid was added? 3. Which antacid neutralized the best? Explain why you think that. Conclusions: 1. Why did you stop the neutralization at pH 2 rather than at pH 7? 2. Would you want an antacid tablet to dissolve instantly or over a period of time? Explain. 3. What is one possible advantage of liquid antacids over a solid tablet? 4. What is one possible advantage of solid antacid tablets over a liquid antacid solution? 5. What other things would you consider when buying an antacid? Name two.