Objective Questions Chapter 3
advertisement

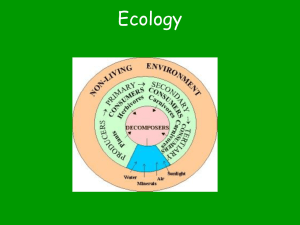
Chapter 3 Objective Questions Ecosystem Ecology OKAY GUYS!!! This is a kicker chapter and VERY IMPORTANT FOR YOU TO UNDERSTAND! Reversing the Deforestation of Haiti 1. Look at the picture of Haiti on the left and the Dominican Republic on the right. Which country do you think has taken better care of their forest resources? 2. How much money do you think you live on per day? How much do most Haitians live on? 3. What was used as a fuel source for cooking by the Haitians? 4. What happened to the forest? What percentage remains? 5. How does cutting down trees impact soils? 6. What happens when it rains because of this? 7. What did the US Agency for International Development do to try and correct the problem? Ecosystem ecology examines interactions between the living and the nonliving world. 1. What is an ecosystem? 2. What determines the components of a given ecosystem? Ecosystem Boundaries 1. What determines the boundaries of an ecosystem Ecosystem Processes 1. How do ecosystems interact with other ecosystems? Energy flows through ecosystems. 1. Distinguish between herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. 2. What happens to energy as it is moved from one system to another, such as in the food chain? Photosynthesis and Respiration 1. Differentiate between producers, autotrophs, and consumers, heterotrophs. 2. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? 3. Respiration? Trophic Levels, Food Chains, and Food Webs 1. The flow of energy through systems is a HUGE topic in this course and understanding it is important for you to make connections as we move through the material. 2. What is the difference between consumers and heterotrophs in the food chain? 3. Depending on where you start, the food chain will follow from producers to different consumer levels. How is the food chain on the right different from that on the left in Figure 3.5? 4. Be very familiar with the trophic levels. What does the word trophic come from and mean? 5. How does energy move through a food chain? 6. How does a food web differ from a food chain? 7. What are scavengers? Detritovores? Decomposers? What important role do they play in the food web? Ecosystem Productivity 1. What determines how much life one will find in an ecosystem? Why? 2. What is gross primary productivity (GPP)? 3. What is net primary productivity (NPP)? 4. How do we determine NPP? 5. What compounds need to be measured if we are measuring for photosynthesis? 6. What measurements would this be recorded as? 7. Important – How much of the actual solar energy that reaches producers is actually converted into chemical energy via photosynthesis? 8. What is the range of NPP in an ecosystem? Check out Figure 3.7 for better understanding. 9. Of the 1% captured by the producer, how much is used for the producers own respiration processes? 10. What is the remaining percentage used for? Familiarize yourself with the math here. 11. Productivity grows best in the presence of what factors? 12. If you look at the globe of the Earth, where do you find the most productivity? 13. In aquatic ecosystems, where is the productivity greatest? Energy Transfer Efficiency and Trophic Pyramids 1. What is biomass? 2. What determines the amount of biomass produced? 3. What is the standing crop? 4. What is the difference between standing crop and productivity? 5. What is ecological efficiency? 6. How much can be converted in to energy from one trophic level to the next? 7. What does the trophic pyramid show? 8. Where is most energy and biomass found? 9. How does this flow of energy help determine population sizes? 10. How does this relate to what determining what types of crops to grow for caloric values? Which would yield more calories – soybeans or beef? Why? Matter cycles through the biosphere. Again, HUGE topic in APES and a little cumbersome to learn, but you can do it! 1. What comprises the biosphere? How deep is it? 2. What happens to the energy that comes in? 3. What are biogeochemical cycles? 4. What are pools? Flows? 5. What are the main elements living organisms are composed of? The Hydrologic Cycle 1. What is transpiration? 2. What is evapotranspiration? 3. What is runoff? 4. In what ways do humans alter the hydrologic cycle? Make sure you understand Figure 3.10. The Carbon Cycle 1. How do producers obtain the elements of C, N, P, S, K, Mg, and Ca? Consumers? Decomposers? 2. Why is carbon the most important element in living organisms? Think back to the chapter on chemistry. 3. What six processes drive the carbon cycle? Which are categorized as fast? Slow? 4. What happens to carbon producers take in as CO2? 5. What are two things that happen to CO2 that is absorbed by the ocean? 6. What happens to dead organisms in the ocean? 7. What is this amount of carbon from the slow process of sedimentation equal to? 8. How do humans alter the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere? 9. Why is combustion a problem when compared to the natural processes in nature, such as decomposition and respiration? 10. How did the Industrial Revolution change atmospheric carbon concentrations? 11. What does excess CO2 do to temperature in the atmosphere? 12. What does tree harvesting, or deforestation, do? Make sure you understand Figure 3.11 The Nitrogen Cycle 1. What are macronutrients? 2. What is a limiting nutrient? 3. What are the building blocks of proteins and in what molecules in living systems are they found? 4. What percentage of the atmosphere is nitrogen and in what form does it exist? Is it usable by producers in this form? 5. What is nitrogen fixation? What organisms can accomplish this? 6. What is formed in this process? 7. How does lightning or combustion fix nitrogen? Usable by plants? 8. What did man learn how to do which in turn has accelerated the nitrogen cycle? 9. What does assimilate mean? 10. What happens during ammonification and what organisms do this? What is excreted? 11. What is nitrification? 12. What type of charge do nitrate ions possess? What happens in leaching? 13. What is denitrification? 14. Nitrogen is a limiting factor in what type of ecosystems? 15. Man has added extra nitrogen to the soils and how has this impacted the cycle and other ecosystems? Make sure you understand Figure 3.12 The Phosphorous Cycle 1. For what purposes do organisms use phosphorous? 2. What phase is not found in this cycle? 3. Why would it be considered a limiting factor in aquatic environments? 4. What is the source for phosphorus on land? 5. Why is it not readily easily leached out of soils like nitrogen is? 6. What happens when there is leached phosphorus in aquatic environments? 7. What eventually happens to this increase in biomass? Why does this create a hypoxic condition? What in turn results to living organisms in the water? 8. What are two major sources of P? 9. What is a dead zone? Check out page 384 and familiarize yourself with the term eutrophication. Make sure you understand Figure 3.13. Ecosystems respond to disturbance. 1. What is a disturbance? Do they have to be natural? 2. What is a watershed? 3. Describe the Hubbard Brook watershed study – what is the bedrock like? 4. How does water enter and leave? 5. What happens when you cut down trees (clear cut) and other vegetation in areas that feed watersheds? 6. What did the scientists discover in their study when they did this? 7. Where does all the water in a watershed eventually end up? Resistance versus Resilience 1. What is resistance in an ecosystem? High vs. low examples? 2. What is resilience? High vs. low examples? 3. What is restoration ecology? The Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis 1. What does the intermediate hypothesis state? 2. How are populations impacted? Understand the chart in Figure 3.19 Ecosystems provide valuable services. 1. What does it mean to say a species has an instrumental value? 2. What is intrinsic value? 3. What are ecosystem services? 4. What are the 5 categories of ecosystem services? Provisions 1. What are provisions? Examples? 2. DO THE MATH on Raising Mangoes Regulating Services 1. Give an example. Support Systems 1. Why is pollination of such importance to us? 2. How do healthy ecosystems help our water supply? Resilience 1. Why is biodiversity important here? Cultural Services 1. Examples? Intrinsic Values of Ecosystems 1. Examples? Working Toward Sustainability What are some environmental concerns that arise from the development of golf courses? Work the FRQ and the Measuring Your Impact to practice your math essay writing skills. The multiple-choice questions are great examples of what you will see on the APES exam.