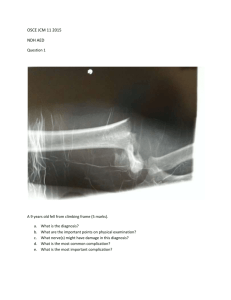
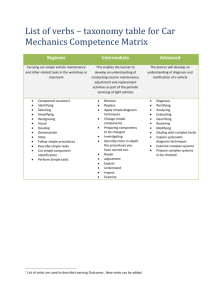
Dent3QuesMod2
advertisement

"Approved" on faculty meeting propaedeutics internal Medicine protocol № from 2014. Head department, prof._______________Homazyuk TA LIST OF QUESTIONS TO FINAL MODULE CONTROL IV COURSE DENTAL FACULTY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Structure scheme history. Sequence examination of the patient and the presentation of history in Supervision. Set a previous, clinical final diagnosis Syndromic diagnosis and features of the differential diagnosis. Top syndromes in renal disease: edema syndrome, nephrotic syndrome, renal hypertension, renal eclampsia, renal colic, acute renal failure, chronic renal failure. Acute glomerulonephritis. Definitions. The clinical symptoms. Complications. Diagnosis. Treatment. forecast The role of rehabilitation foci of infection in the prevention of acute glomerulonephritis. Chronic glomerulonephritis. Definitions. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinic. Morphological variations of course. Diagnosis. Complications. Principles of treatment. Chronic kidney disease. Nephrotic syndrome. Uremia. Emergency. Acute pielonefryt (GP). Definitions. Forms of motion. Risk factors GA. Clinic. Diagnosis. Complications. Treatment. Weather. Chronic pyelonephritis (CP). Definitions. Etiology. Clinic. Course. Complications. Treatment. Prevention. The role of the dentist in the prevention of PD. Acute renal failure (ARF). Definitions. Classification. Pathogenesis. Clinic. Stages of ARF. Diagnosis . Course and prognosis. Treatment. Prevention. Chronic renal failure (CRF). Definitions. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Classification. Clinic. The main clinical syndromes of chronic renal failure. Course. Diagnosis. Treatment. Prevention. The role of the dentist in prevention. Diabetes mellitus (DM). Classification. Etiology. Pathogenesis. National program "Diabetes Mellitus." Diabetes mellitus. Clinic. Diagnosis. Complications. Treatment. Features of Dental Clinical management of patients with diabetes . Diabetes mellitus type II. Distribution. Etiology. Insulin resistance. Diagnosis. Complications (macro and microangiopathy, chronic renal failure, diabetic foot). Treatment. Prevention. Commas in diabetes. Hiperlikemichna, hypoglycemic, hyperosmolar. Differential diagnosis. First Aid. Changes in the oral cavity in patients with diabetes and tactics dentist in the treatment of diabetic patients. Thyrotoxicosis (diffuse toxic goiter). Determining distribution. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinical manifestations: general, nerve, ophthalmic, changes in the cardiovascular system, metabolic processes. Course. Methods of diagnosis of hyperthyroidism. Complications. Changes in the oral cavity. Treatment. Hypothyroidism. Definitions. Distribution. Etiology. Pathogenesis. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. Clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism. Diagnosis. Complication. Principles of treatment of hypothyroidism. Changes in the oral cavity and tactics dentist. Hypoparathyroidism. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinic. Diagnosis. Course. Treatment. Seizures in hypoparathyreosis. Providing emergency care. Changes in the oral cavity and tactics dentist at hypoparathyreosis. Hyperparathyroidism. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinic. Diagnosis. Course. Treatment. Weather. Changes in the oral cavity. Tactics dentist. Diseases of the adrenal glands. Adrenal insufficiency. Addison's disease. Etiology. Risk Factors. Diagnosis. Treatment. Complications: Addison crisis, adrenal coma. Emergency. Changes in oral mucosa with Addison's disease . Secreting adrenal adenoma. Cushing's syndrome. Clinical signs (including from the mucosa of the mouth and zuboschelepovoyi system). Primary hyperaldosteronism (aldosteroma syndrome Kona). Etiology. Pathogenesis. Diagnosis. Determination of aldosterone in the blood and urine. The clinical symptoms. Hypertension. First aid in hypertensive crisis. Pheochromocytoma. Etiology. Clinic. Diagnostic criteria. Definition vanilil - almond acid in urine. Computed tomography, radioisotope studies of the adrenal glands. Diseases of the pituitary gland. Clinical forms. Acromegaly. Clinical features. Diagnosis. Treatment. Gigantism, dwarfism. Cushing 's disease. Hipopituitaryzm. Diabetes insipidus. Characteristics. Diagnosis. Course. Complications. Treatment. Differential diagnostic signs of change of the tongue and oral mucosa in diseases of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders. Iron deficiency anemia. Definitions. Common signs of anemia, including in the mouth. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Diagnosis. Pathognomonic symptoms of iron deficiency anemia in the mouth. Treatment. Weather. Prevention. The role of the dentist in prevention. First aid for acute massive blood loss. Megaloblastic anemia. Definitions. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinical manifestations mehaloblostnyh anemia, including in the mouth. Diagnosis. Pathognomonic symptoms in the mouth with megaloblastic anemia. Treatment. Weather. Prevention. The role of the dentist in prevention Hypo-, aplastic and hemolytic anemia. Definitions. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinical manifestations of anemia, including in the mouth. Diagnosis. Pathognomonic symptoms in the mouth with hypo- aplastic and hemolytic anemia. Treatment. Weather. Prevention. The role of the dentist in prevention. Hematoonkologyi disease. Current views on the etiology and pathogenesis (onco- and protooncogene). The concept of tumor transformation, progression and dissemination . WHO classification . General principles of treatment (and accompanying software cytostatic therapy, complications) hematoonkology disease. Assessment of effectiveness. The role of the dentist in the diagnosis, treatment, symptoms and complications of therapy hematoonkology disease. Acute lymphoblastic (B and T cell) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma. Clinical implications of basic syndromes. Diagnosis. Course. Treatment. Features manifestations in the oral cavity and their treatment. Acute myeloid (Mo - M7) and chronic myelocytic leukemia (chronic miyeloleykemiya, erythremia). Myelodysplastic syndromes. Tumours of histiocytes and dendrytychnyh cells. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. Clinical implications. Major syndromes. Diagnosis. Course. Differential diagnosis. Treatment. Features manifestations in the oral cavity and the dentist's role in their treatment. Agranulocytosis, etiology and pathogenesis, clinical manifestations of immune Agranulocytosis. The main signs. Complications. The concept of the cytostatic disease. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis tsytopenichnoho syndrome and agranulocytosis. Disorders of hemostasis (hemorrhagic disease). Modern classification, clinical manifestations, general principles of laboratory diagnosis of primary, secondary hemostasis and fibrinolysis. Prevention. Thrombocytopenia and Thrombocytopathy (hereditary and acquired ). Diagnosis. Treatment. Trombocytopenic purpura disease (thrombocytopenic purpura). Diagnostic criteria. Course. Complications. Treatment. First aid for bleeding. Changes in the oral cavity. Features of providing dental care to patients with disorders of primary hemostasis. Hemophilia (A, B, C) and other hereditary and acquired coagulopathy. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinical implications. Features tactics doctor - dentist. Treatment. Von Willebrand disease. Clinical manifestations, course. Diagnosis. Weather. Principles of treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding. Tactics dentist in interventions in the oral cavity in patients with hemophilia. Hemorrhagic vasculitis (Schonlein-Henoch disease). Etiology. Pathogenesis. The clinical picture. The main forms (skin, joint, abdominal, renal). Manifestations in the oral cavity. Treatment. Vazopatiyi. Causes. Clinical manifestations in the oral cavity. Diagnosis. Prevention. Features stop bleeding in vasculitis and vazopatiyah in dental practice. The concept of allergies. Pathogenesis and types of allergic reactions. Allergic reactions of immediate type . Anaphylaxis . Acute toxic- allergic reactions (HTAR), urticaria, angioedema. Serum sickness. Etiology. The mechanism of development. Types and forms of anaphylaxis . Clinic. Course. Treatment. First aid in severe anaphylactic and forms. Secondary immunodeficiencies. Definitions. Etiology. Pathogenesis. Clinical features. Diagnosis. Basic approaches to the treatment of secondary immunodeficiencies. Dental aspects of immune system diseases.