Geology Study Guide 1. What is Pangaea? A supercontinent made

Geology Study Guide
1. What is Pangaea?
A supercontinent made of the present-day continents
2. For a material to be considered a mineral, which characteristic must it have?
Be naturally occurring
3. What role does subduction play in Earth’s rock cycle?
It causes surface rocks to be pushed deep into the Earth.
4. The rock cycle shows how rocks continually:
Change over time
5. A divergent boundary at two oceanic plates can result in a _______________________________.
Valley
6. In which environment would sedimentary rocks most likely form?
In a body of water on Earth’s surface
7. Metamorphic rock is formed by:
Pre-existing rock going through heat and pressure
8. What evidence suggests that continents were once joined?
The puzzle-like fit of coastlines
9. A crack or a fracture in Earth’s crust along which movement occurs is:
A fault
10. What is the rock cycle?
The largest and slowest cycle, consists of geological, physical, and chemical processes, and forms and modifies rocks over millions of years.
11. What theory states Earth’s surface consists of plates that move relative to one another?
Continental Drift
12. What was the earliest form of life?
Single-celled organisms
13. Which factor is greater at Earth’s core than on its surface?
Pressure
14. What causes Erosion?
Wind, Water, Ice
15. What is the process in which broken down rocks are moved into one location in a river?
Deposition
16. Most earthquakes occur along plate boundaries because:
The rigid plates break when they are exposed to too much force.
17. How does water get from one part of the water cycle to another?
By changing state
18. Wegener’s proposal of a supercontinent was supported by
Rock, fossil, and climate data.
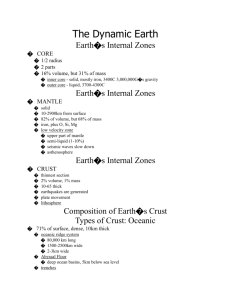
19. Lists Earth’s layers from the surface to the center?
Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
20. Weathering involves:
Mechanical and chemical breakup of rocks.
21. A core is:
Inner part of the Earth made of liquid metal and the center of the Earth made of solid metal.
22. What are the physical properties scientist use to identify rocks?
Luster, Color, Transparency, Acid, Hardness, Grain, and Streak.
23. Where do most volcanoes erupt?
Along divergent plate boundaries
24. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s surface:
Is broken into rigid plates.
25. What are the most destructive earthquake waves?
L
26. Volcanoes form when magma:
Flows through the crust.
27. Which part of an ancient reptile would you expect to see in a rock fossil?
Bone
28. The Earth’s mantle is:
Magma layer of rock.
29. What are the bones found within a fossil called?
Original Remains
30. An example of convection is:
A boiling pot of water
31. Which kind of rock forms when molten rock cools?
Igneous
32. The geologic time scale was developed using:
Changes in fossils.
33. The rock cycle and the movement of tectonic plates are:
Caused by processes within Earth.
34. The vibration caused by the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a fault line in Earth’s crust is
An earthquake.
35. The Earth’s crust is:
The thin and solid outermost layer of Earth.
36. Most earthquakes occur:
Along plate boundaries.
37. Patterns in the fossil record show that species on Earth:
Change over time
38. Volcanoes form along convergent boundaries as a result of:
Subduction and rising magma.
39. What have scientists learned more about by studying earthquakes?
The composition and structure of Earth’s interior
40. Pieces of rock can settle from water and get compacted and cemented into:
Sedimentary rock
41. What is the 'magnitude' of an earthquake?
The amount of energy that is released by a quake
42. What is a major cause of extinctions?
Environmental change
43. What is a crystal?
A solid in which the atoms form a repeating pattern
44. Which type of fossil helps determine the age of rock layers?
Index fossils
45. What are tectonic plates?
Slabs of rock move relative to one another and part of the crust that moves on top of magma.