What are nucleic acids? What do they do? Responsible for storage

What are nucleic acids? What do they do?
Responsible for storage and processing of cell info
-strucutre of every protein is encoded by nucleotide sequence
2 types: DNA and RNA
What is specific to DNA? What is specific to RNA?
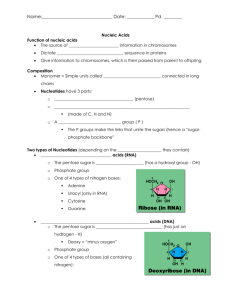
DNA: directs cell function, stores genetic info, found only in nucleus of eukaryotes
-uses sugar deoxyribose
RNA:used info stored in DNA to synthesize proteins and other RNAs. Found throughout cell.
-uses ribose as sugar
-3 different types
--mRNA: carries DNA info from the nucleus to ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs.
--tRNA: brings specific amino acids to the ribosomes
--rRNA: helps form structure of ribosomes.
Compare and contrast nucleic acids and proteins.
Proteins are single stranded polymers made of 20 amino acids. The primary structure of a protein is the amino acid sequence. Alpha-helices and Beta-sheets are protein secondary structure.
Nucleic acids are single-stranded polymers made of 4 nucleotides. The primary structure of the nucleic acid is the nucleotide sequence. The double helix is a nucleic acid secondary structure.
What does a nucleotide consist of? Draw it out and label.
O
O
–
P
O
–
H
2
C
O
H
2
C
CH
2
O
HC
H
2
C
CH
2
Base
CH
2
CH
CH
Base
Phosphate
Sugar
H
2
C CH
2 did not put OH's and H's on sugar ring
Remember, they are there.
What are the 5 bases? Which bases are the purines and which are the pyrimidines?
Cytosine, Uracil and thymine=pyrimidines (CUT the PY)
Adenine and Guanine=purines
What is a nucleoside? Draw one and label bonds.
H
2
C
H
2
C
CH
2
H
2
C
CH
3
O
HC
CH
CH
CH
2
Base
N-glycosidic bond
Sugar
H
2
C CH
2 did not put OH's and H's on sugar ring
Remember, they are there.
Draw a dinucleotide composed of cytosine and adenine (DNA).
NH
2
HC
O
O
–
P
O
–
O
HC
CH
2
O
HC
N
CH
N
O
HC CH
2
O
O
–
P O HC
N
O CH
2
O
HC
N
CH
HC CH
2
OH
Cytosine
NH
2
N
N
CH
Adenine