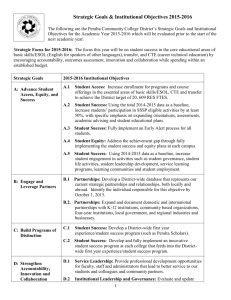
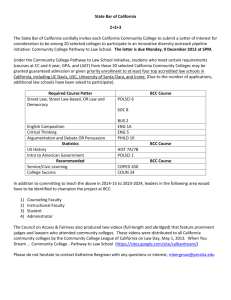
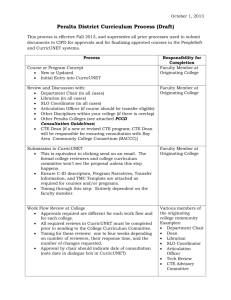
In the implementation process for SB 1440 and Education Code
advertisement

Peralta Community College District Peralta Community College District Program and Course Approval Process Manual For Faculty and Administrators Educational Services 3rd Edition, Draft 3.0 July 2013 1 Peralta Community College District Peralta Community College District Board of Trustees Cy Gulassa, President Abel Guillén, Vice President Meredith Brown Linda Handy Dr. William “Bill” Riley Bill Withrow Dr. Nicky González Yuen Student Trustees: Sharon Clegg Wai Li Dr. José M. Ortiz, Chancellor Presidents Dr. Deborah Budd, Berkeley City College Dr. Eric Gravenberg, College of Alameda Dr. Elñora Tena Webb, Laney College Dr. Norma Ambriz-Galaviz , Merritt College District Administration Educational Services Dr. Michael Orkin Vice Chancellor 2 Peralta Community College District Peralta Community College District Program and Course Approval Process Manual For Faculty and Administrators Prepared by: Jayne A. Matthews under the direction of Dr. Michael Orkin Vice Chancellor Educational Services 3rd Edition, Draft 3.0 July 2013 3 Peralta Community College District Preface This Program and Course Approval Process Manual represents an updating of the August 2002 Manual. It reflects the statutory and regulatory changes that have occurred in California over the past several years. It is expected to be a “living document” which means at any point-in-time there may be additions and corrections; therefore, it is our intention to periodically update this document. As we all work with this document, we will undoubtedly discover ways to make it more clear and comprehensible. Please notify Sheryl Queen, Curriculum and Systems Technology Analyst, who will collect this information for our next update. A copy of this manual will be available at the Peralta District Curriculum Website at http://web.peralta.edu/curriculum/. The Peralta Board of Trustees board policies and administrative procedures have been included where appropriate, both in text, references, and Peralta Web Page Links. Their complete text can be found at http://web.peralta.edu/trustees/board-policies. Policies and procedures have also been included from the California Community Colleges Chancellor’s office document, Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. This 3rd edition has undergone expert review and comment by representatives of the College Curriculum Committees and the Council on Instruction, Planning and Development (CIPD). It has been presented to the College Academic Senates, District Academic Senate, and the District Education Committee. Educational Services acknowledges the expertise and valuable contributions of all involved in the development of this manual. This Manual is available on the Peralta District website at www.peralta.edu located under the District Office, Educational Services. For comments or questions about this handbook or about program or course approval, please refer to your Curriculum Committee Chair. Dr. Michael Orkin Vice Chancellor Educational Services 4 Peralta Community College District Table of Contents Preface Table of Contents Introduction Part I Guidelines for Program and Course Development Program, Curriculum, and Course Development Work Flow Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues Description of a Good Faith Effort at Consultation Curriculum Issues which Require Consultation among Colleges Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation Background and Philosophy Program Appraisal/Discontinuance Evaluation Process Initiating a Discussion on Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation Possible Outcomes of Program Discontinuance/Program Consolidation Discussion Program Goal—Degree or Certificate Philosophy and Criteria for the Associate Degree and General Education Major or Area of Emphasis Certificates of Achievement Associate Degrees for Transfer (ADT) to the California State University System Transfer Model Curriculum (TMC) Course Identification Numbering System (C-ID) Guidelines for Associate Degree Applicable Courses Guidelines for Nondegree-Applicable Credit Courses Transferable Courses Relationship of Hours to Units To Be Arranged (TBA) Hours Compliance Advice Open Courses Prerequisites, Co-requisites, and Advisories Stand-Alone Credit Courses Selected Topics (Experimental Course) Policy Community Service (Fee-Based) Courses Contract Education Non-Credit Courses Distance Education Independent Study Course Repetition and Repeatability Policy Cooperative Work Experience Education American Cultures (AC) Requirement Credit by Examination Advanced Placement (AP) Equivalency Grading Policy: Pass/No Pass or Grade The Taxonomy of Programs Open-Entry/Open-Exit Instructional Material Fees Scheduling Courses in Shortened Time Frames Program and Course Review 5 Peralta Community College District Part II Processing New and Revised Courses and Programs Initiating New Course or Revision Substantive Change Substantive Changes to Courses under Uniform Course Numbering (UCN) Non-substantive Change When a Course Change Requires a New Course Number Course Outline of Record (COR) Completing the Course Outline of Record (COR) Creating a Fee Based Course Deactivating a Course or Program Reactivating a Course or Program Course Numbering System When a Course Change Requires a New Course Number Reusing Course Numbers Modularization Bloom’s Taxonomy Initiating New Programs or Revisions Program Outline Completing the Program Outline Part III Additional Related Information Curriculum Related Job Duties Faculty Originator Department Chair SLO Coordinator Articulation Officer Librarian Tech Review Committee Member Curriculum Committee Member Curriculum Specialist Curriculum Committee Chair Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) College Level Courses Critical Thinking Disabled Students Programs and Services Special Classes Students with Disabilities Peralta Community College Process Chart CB Code Listing Performance Objectives (Exit Skills) vs Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) Glossary of Acronyms Used in the Curriculum World Curriculum Review Planning Report 6 Peralta Community College District Introduction This Program and Course Approval Process Manual assists administrators, faculty, and staff in the development of programs and courses and the submission of these proposals for review. This Manual provides college faculty, administrators, and staff with the following: • Peralta Community College District’s program and course approval procedures. • A framework for consistent documentation of the content and objectives of programs and courses • Understanding of uniform practices in curriculum development as established in the field of curriculum design and instructional technology and as recommended by the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges By statute, the Board of Governors has statewide responsibility for approving all new instructional programs and courses offered by community colleges. This mandate is one of the earliest and most basic legislative charges to the Board and is detailed in California Education Code section 70901. The Board of Governors delegates its oversight responsibility for the community college curriculum and instruction to the State Chancellor’s Office. The California Education Code and the California Code of Regulations, Title 5, provide the mandate on the content of program and course proposals. The Chancellor’s Office reviews community college proposals within the context of Title 5 regulations. The California Education Code and the California Code of Regulations, Title 5, can be accessed at the Chancellor’s Office website at www.cccco.edu under the Legal Affairs Division. Community college program and course proposals require review and approval by the Chancellor’s Office prior to being offered at a community college. The Chancellor’s Office delegates specified parts of its authority to local districts on a conditional basis. For details refer to California Community Colleges, Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH) available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. Each course to be offered by a community college (exempting community service classes) shall be reported to the State Chancellor before the course is offered by the colleges. Colleges that receive Chancellor’s Office approval of a new credit or noncredit program or course are authorized to: • Publish the description of a new program or course in the catalog or publicize a new program or course in other ways (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 55005). • Offer programs and courses as they were described and approved in the proposal. • Collect state apportionment for student attendance in the required courses and restricted electives that are part of a credit program (Education Code, § 70901(b)(10); California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 55130 and § 58050). • Award a degree or certificate with the designated title and require specific courses for the completion of such degree or certificate (Education Code, §§ 70901(b)(10) and 70902(b)(2)). • List credit certificates and degrees on student transcripts (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, §§ 55060-55072). The governing board of each community college district shall establish policies for and approve courses of instruction and educational programs. Education Code Section 70902. 7 Peralta Community College District Individual colleges are mandated to uphold state standards for courses and programs based upon curriculum policies each district is mandated to establish. Education Code Section 70902. These responsibilities are carried out through a curriculum committee constituted as required by California Code of Regulations Title 5 . The complete and current text of all California statutes, including the California Education Code sections referred to herein, may be viewed at www.leginfo.ca.gov. The complete and current text of all regulations in the California Code of Regulations, Title 5, including those referred to in this Manual, may be viewed on at www.calregs.com. Additional complete and current information from the California Community College Chancellor’s Office regarding curriculum is available at http://www.cccco.edu/ in the Academic Affairs Division. 8 Peralta Community College District Part I Guidelines for Program and Course Development 9 Peralta Community College District Program, Curriculum, and Course Development The Peralta Community College District complies with and uses the most recent edition of the California Community Colleges, Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. Work Flow Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. See Part II, Processing New and Revised Courses and Programs for more details. The Peralta Community College District and the curriculum committees of the four colleges, under the purview of the Academic Senates of the four colleges (Alameda, Berkeley City, Laney, and Merritt) use the curriculum management system, CurricUNET, for program, curriculum, and course development, and as a database for all curriculum documents. Each of the colleges has in place an approval process for courses and programs in the CurricUNET system, which includes distance education (DE) and student learning outcomes (SLOs). Faculty have primary responsibility for curriculum management. Once curriculum actions have been finalized by the individual College Curriculum Committees, those actions are forwarded to the district Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) for review and approval. Because the district/ four colleges use uniform course numbering (UCN), there are instances when consultation between colleges or among the colleges must occur (see below). That consultation must happen prior to actions being sent to CIPD. When a college submits a program (degree or certificate) to CIPD for approval, and that program will require approval by the State Chancellor’s Office, all required state paperwork must be completed prior to bringing the program to CIPD. Career Technical Education programs must be approved by the Bay Area Community College Consortium (BACCC) after approval by CIPD and before being sent to the California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office (CCCCO). All curriculum and program actions once approved by CIPD are forwarded to the Board of Trustees for approval. All courses and programs approved are reported to the CCCCO. All programs, curriculum, and courses are reviewed on a three-year cycle through Program Review. All programs complete an Annual Program Plan update. Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues Consultation among colleges regarding curriculum issues is necessary to ensure: Program integrity Appropriate use of district resources Program delivery to students in convenient locations Adequate enrollment in all programs at all colleges Description of a Good Faith Effort at Consultation Prior to proposing a substantive course change to the College Curriculum Committee, college representatives must contact by email (or by phone with a follow up email) the appropriate administrator and department chair at all affected colleges. The curriculum committee chair should be copied on this 10 Peralta Community College District email as well. If a regular district wide discipline meeting is part of the ongoing curriculum process in this discipline, the membership of that group will also be consulted. If there are unresolved disputes related to the valid curricular reasons outlined in the “Goals for Consultation among Colleges” or there has been no response from the consulted parties, curriculum chairs may move forward with their curriculum items and/or specific issues will be discussed and resolved at CIPD. Curriculum Issues which Require Consultation among Colleges Offering a new course, making a substantive change to an existing course, or course reinstatement when it is similar to any course offered at another college. Substantive change to existing UCN course New single course which overlaps courses offered as part of an approved program at another college New programs (certificates or degrees) or substantive changes to programs which are similar to any other program or contains similar courses offered at other colleges (whether or not these programs are in the same discipline) Borrowing a course References: PCCD Administrative Procedure 4020--Program, Curriculum, and Course Development Education Code Sections 70901(b), 70902(b), and 78016; California Code of Administrative Regulations Sections 51000, 51022, 55100, 55130 and 55150 Accreditation Standard II.A U.S. Department of Education regulations on the Integrity of Federal Student Financial Aid Programs under Title IV of the Higher Education Act of 1965, as amended 11 Peralta Community College District Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation Background and Philosophy In accordance with Title 5, Section 51022, College districts are required by current regulation and statute to develop a process for the modification, continuance or discontinuance of courses or programs and minimum criteria for the discontinuance of occupational programs. The process for program appraisal/discontinuance takes into account the following issues. Impact on student learning, goals, and needs Effect on the balance of the college curriculum Impact on educational and budget planning Regional economic and training issues Changes in regional economic and training conditions Collective bargaining issues Consideration of the college mission statement Fit with the college educational master plan and the department’s goals and objectives During times of budget reductions or comparable reasons which necessitate the reduction in class sections and reduction in faculty, it is possible that a college may not have sufficient course offerings to maintain a program or a major at the college. In such instances, as much as possible, consideration should be given to consolidation of class sections from two or more colleges at one college in order to preserve the program or major in order to meet student needs. The Program Review process, annual unit plans, and other strategic planning activities should be referenced and considered among sources of data and direction in this process, but it is important to emphasize that their primary purpose and use is not to target programs for discontinuance. It is also important to note that program discontinuance or consolidation should occur only after serious deliberation and after recommended intervention strategies have been implemented but still result in a program that falls outside the college’s mission or master plan or the division’s or department’s goals and objectives. The purpose of a program appraisal/consolidation/discontinuance process is to have criteria in place to guide a discussion in the event that the process is needed. The presence of a process should not be construed as an inducement to look for programs to discontinue or as a reason to avoid honest participation in an academic process such as Program Review. This process document shall be filed, if required, with the Office of the Chancellor of California Community Colleges (CCCCO). (Title 5, §51022.) Program Appraisal/Discontinuance Evaluation Process Initial Considerations This procedure will be used to review the continuance, modification, or discontinuance of programs. For purposes of this process, a Program is defined as an organized sequence or grouping of courses or other educational activities leading to a defined objective such as a major, degree, certificate, career certificate, job career goal, license, the acquisition of selected knowledge or skills, or transfer to another institution of higher education. The term Program also applies to Library Services, Health Services, and Student Services as defined above. The scope of the program under consideration will be clearly delineated at the outset of this process. Vocational or occupational programs shall be reviewed every two years by Management Information Systems data (Cal. Educ. Code § 78016) and every three years by Departments in a formal written review (i.e., Program Review). All other programs shall be reviewed every three years with an annual program update. 12 Peralta Community College District Role of Curriculum Committee. The Curriculum Committee, a committee of the Academic Senate, must have a fundamental and integral role in any discussion or appraisal of program continuance, consolidation or discontinuance, recognizing the district’s policy to rely primarily on the Academic Senate in academic matters as set forth in Title 5 Section 53200(C) and Section 53203. In addition, there are local college policies and procedures in this and all areas of curriculum management. For example, Laney College’s Curriculum Website at http://www.laney.edu/wp/curriculum-committee/ outlines both general curriculum procedures as well as those unique to Laney. Consult your college’s curriculum chair for more information. Conditions for Discontinuance. The following conditions may cause a program to be recommended to the Curriculum Committee for discontinuance (based on quantitative and qualitative data) or to be considered for consolidation. Program Review and analysis trends Degree and Certificate completion Changes in demand in the workforce Changes in requirements from transfer institutions Availability of human resources Budget concerns and lack of sufficient funding. Initiating a Discussion on Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation Program discontinuance or consolidation discussions can be initiated by administration or the affected divisions and departments. The instructor(s) and the department chair of the program being considered for discontinuance or consolidation should be given the semester in which they are notified to do research and provide documentation related to the reasons and conditions that were provided for consideration of discontinuance or consolidation of their program and what action, if any, should be taken. The Academic Senate in and through the Curriculum Committee, must have a fundamental and integral role in any discussion of program discontinuance or consolidation, recognizing the district’s policy to rely primarily on the Academic Senate’s advice in academic matters. The instructor(s) and the department chair of the program being considered will have the opportunity to present the program’s relevance at the college council level. Discussion Criteria For each affected Program, both qualitative and quantitative factors shall be discussed in order to have a fair and complete review leading to an eventual decision to continue, continue with qualification, discontinue or consolidate a program. Qualitative factors are based on the mission, values, and goals of the institution and access and equity for students. These factors include but are not limited to: a. Quality of the program and how it is perceived by students, faculty, articulating universities, local business and industry, and the community b. Ability of students to complete their educational goals of obtaining a certificate or degree, or transferring c. Balance of college curriculum (for example, ensuring the non-elimination of all of one type of program, such as all foreign languages) d. Effect on students of modifying, discontinuing, or consolidation of the program e. Uniqueness of the program f. Replication of programs in the surrounding area and their efficacy g. Potential for a disproportionate impact on diversity at the college h. Necessity of the program in order to maintain the mission of the College i. Source of funding for the program (outside vs. general funds) 13 Peralta Community College District j. k. l. Impact on other programs, including transfer, if the program is modified or closed Student Learning Outcomes assessment data Requirements by federal/state/accreditation or other areas (e.g. Title IX) for the program. If there are any, these must be identified. m. Impact on articulated programs Quantitative factors are based primarily on the Program Review where applicable. Factors that may be considered include, but are not limited to, Program Review results showing: a. A sustained downward trend in FTES generated, load, enrollment, number and composition of sections offered, productivity, FTES composition, retention, and persistence b. Sustained increase in expense or annual cost/FTES c. Changes in demands in the workforce, transfer rates, job-outs, completers and graduates, and non-completers d. Projected demand for the program in the future e. Frequency of course section offerings f. Availability of human resources g. FTES generated/FTEF h. Enrollment trends i. Operating cost per FTES j. Student Learning Outcomes Assessment data k. Capital outlay costs/year l. Labor market demand m. Data from the PCCD Course Ranking Index tool Discussion Guidelines Discussion of program appraisal/ discontinuance or consolidation shall include all parties potentially affected by the decision. These include faculty, staff, administrators, students, the employing business and industry, and the community (i.e., CTE Community Advisory Committee). These discussions will be conducted in public, open meetings. The dates, times and locations of these meetings will be published using all means of college communications including in print and electronically. Discussions will be conducted using the best practices for meeting facilitation, including agreed upon ground rules, and recording and publishing outcomes of discussions. Discussions will include both qualitative and quantitative indicators. Sources of data for all indicators will be referenced and cited. Deliberations and conclusions shall rely primarily on the advice of the Academic Senate in and through the Curriculum Committee per district policy. Possible Outcomes of Program Discontinuance/ Program Consolidation Discussion There are three potential outcomes of the Program Discontinuance process. A program may be recommended to continue, to continue with qualification, or to discontinue. Recommendation to Continue A program recommended to continue will do so when, after full and open consideration, it is decided that it is in the best interest of the college, its students, and the larger community to do so. The conclusions resulting in this recommendation will be documented in writing, maintained by the Academic Senate and the Curriculum Committee and forwarded to the Vice President of Instruction or Vice President of Student Services as information. No further action is required. Recommendation to Continue with Qualifications A program may be recommended to continue with qualifications. These qualifications may include specific interventions designed to improve the viability and responsiveness of the program. A specific timeline will be provided during which these interventions will occur and expected outcomes will be outlined in advance. All interventions and timelines will be published in writing, maintained by the Academic Senate and the Curriculum Committee and forwarded to the Vice 14 Peralta Community College District President of Instruction or Student Services as information. After the specified qualification period is completed the program will be reviewed again. Recommendation to Discontinue A recommendation to discontinue a program will occur when, after a full and open discussion, it is concluded that the program falls outside the college’s mission, values, and strategic goals and/or the department’s goals and objectives. Any recommendation for program discontinuance will include the following. The criteria used to arrive at the recommendation, verified by an agreed upon neutral party. A detailed plan and timeline for phasing out the program with the least impact to students, faculty, staff, and the community. Due consideration will be given to approaches to allow currently enrolled students to complete their programs of study. Students’ catalog rights will be maintained and accounted for in allowing them to finish the program. A plan for the implementation of all requirements of collective bargaining for faculty and staff, including application of policies for reduction in force and opportunities to retrain. This recommendation and discontinuance plan will be documented in writing and will include the signatures of the College President, Vice President of Instruction or Student Services (dependent on the program), department chair, Dean, the Curriculum Committee Chair, and the Academic Senate President. The final recommendation will be maintained locally by the Academic Senate and documented by the Curriculum Committee, forwarded to the Council on Planning, Instruction, and Development (CIPD), and presented to the Board of Trustees for approval as a curriculum action. After Board approval, appropriate documentation will be submitted to the State Chancellor’s office (CCCCO). Recommendation for Consolidation A recommendation for Program Consolidation, provided there has been a full and open discussion, may occur when it has been determined that the program falls within the College’s mission, values, and strategic goals, as well as the department’s goals and objectives, but because of cuts in class sections and a reduction in faculty, the program is no longer viable at that college. When this occurs, consideration should be given to consolidating class sections form two or more colleges at one college in order to preserve the program or major and in so doing to meet student needs. References: Administrative Procedure 4021-- Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation Program Discontinuance: A Faculty Perspective. ASCCC, adopted Spring 1998 Title 5 Section 55130, Approval of Credit Programs Title 5 Section 51022, Program Discontinuance Title 5 Section 53200, 53203, Role of the Academic Senate Title 5 Section 55000(g), Definition of educational program Education Code Section 78016, Review of program: Termination CCCCO Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH) (5th edition) ACCJC Standard II.A.6.b Education Code Sections 70901(b), 70902(b), and 78016; California Code of Administrative Regulations Sections 51000, 51022, 55100, 55130 and 55150 Accreditation Standard II.A U.S. Department of Education regulations on the Integrity of Federal Student Financial Aid Programs under Title IV of the Higher Education Act of 196 15 Peralta Community College District Program Goal – Degree or Certificate Degree and certificate programs may have the following specified program goals. • • • • Career Technical Education (CTE) Transfer Career Technical Education (CTE) and Transfer Other – Designed to meet community needs Career Technical Education (CTE) Program Goal A degree or certificate with a program goal of CTE prepares students for employment immediately upon completing the program and/or upgrades employment skills. Pursuant to Title 5, section 51006, CTE programs cannot be designed exclusively for individuals already employed by a particular employer or in a particular industry, unless the college also makes the program available to other interested students or makes available a parallel or comparable program which would enable a student who is not already employed by that employer or in that industry to obtain entry-level employment. Required documentation includes labor market information and analysis, an employer survey, and an explanation of employer relationship. Justification of the need for the new CTE program is specifically required through a job market study, pursuant to Education Code section 78015. In addition to recommendation for approval from their CTE Advisory Committee, a new CTE program proposal must also include a recommendation for approval from the Bay Area Community College Consortium (BACCC). The BACCC is comprised of vocational education and economic development administrators, faculty, and staff from each college in the region. Their activities are funded by the Chancellor’s Office from federal Carl D. Perkins Career Technical Education Act (Perkins) and Economic Development funds, and their charge is to increase collaboration among colleges, encourage regional planning, offer professional development opportunities, and promote marketing of community college CTE programs. The BACCC meets monthly during the regular school year. It is important to consider the lead time for their approvals of new CTE programs or substantive revisions to existing CTE programs in addition to the normal review time. For more information and a calendar of their meeting dates, see their website at http://www.baccc.net/. The Chancellor’s Office requires the recommendation of the BACCC in order to ascertain the need for the proposed program in regard to other community colleges in the area, as specified by Title 5, section 55130 (b)(8)(E). The Chancellor’s Office relies on the advice of the BACCC when reviewing the approval criterion of need, especially in comparing the proposed program to others that are offered by other community colleges in the region. BACCC approval also assures program originators that the design of their program curriculum is along the lines of current good practice as judged by their professional peers. The requirement for a recommendation from BACCC is not absolute. If a program has been refused a recommendation for approval by BACCC, and the college feels the refusal was unjustified or unfair, the college may submit the program to the Chancellor’s Office without a regional recommendation for approval. The burden of justification will be on the college to show why the proposal must be approved without a positive recommendation. Education Code section 78016 requires review of all occupational programs every two years. Title 5, section 55003, requires review of prerequisites, corequisites, and advisory courses at least once every two years. Transfer Goal A degree or certificate with a program goal of transfer prepares students to continue study in the same or similar area at a baccalaureate-granting institution. 16 Peralta Community College District Required documentation includes articulation information (must show that required courses fulfill the majority of lower-division requirements for the baccalaureate major to major) and/or evidence that transfer agreements exist between the community college and baccalaureate institutions to which students may transfer. Required documentation may be obtained at the ASSIST web site (www.assist.org). The documentation must show a good-faith effort on the part of the college to assure that, to the extent possible, students will not have to repeat courses completed at the community college after they transfer. The Chancellor’s Office will review each transfer program proposal to determine if at least 75 percent of courses required for the certificate or major or area of emphasis have course-to-course articulation. Other Goal A degree or certificate with a program goal of “other” is used to develop degree majors or areas of emphasis designed to meet community needs and reflect the educational philosophy of the faculty in a discipline or disciplines. Evidence of need for program proposals is required. Required documentation can be in the form of survey results, letters of support from community agencies, or other regional data in support of the need. This goal is also an appropriate choice for programs that are transferable only to a single university campus, because proposals for transfer programs are required to prove articulation with three university campuses. This type of proposal may have a broad area of emphasis, such as Social Sciences, or a theme-based area of emphasis that consists of an interdisciplinary grouping of courses, such as American Studies, International Business, or Multicultural Studies. The required courses may not align with requirements for transfer, but nevertheless represent a cohesive packaging of courses. If the area of emphasis is designed to prepare students for transfer, all of the required courses must be transferable and must prepare students for a designated field of study at a baccalaureate institution. The intent of such degrees must be clearly expressed in the narrative portion of the proposal. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 17 Peralta Community College District Philosophy and Criteria for the Associate Degree and General Education Philosophy The programs of the District are consistent with the institutional mission, purposes, demographics, and economics of the community. Board of Governors Policies For all associate degrees, it is important to maintain the philosophy that the associate degree represents more than an accumulation of units. As outlined in the policy of the Board of Governors the associate degree symbolizes a successful attempt to lead students through patterns of learning experiences and learning outcomes designed to develop certain capabilities and insight, including: thinking and communicating clearly and effectively, both orally and in writing using mathematics understanding the modes of inquiry of the major disciplines being aware of other cultures and times achieving insights gained through experience in thinking about ethical problems developing the capacity for self-understanding developing the capacity to participate responsibly in a democratic and environmentally sustainable society General Education Criteria Title 5, section 55061, describes the completion of General Education, one component of the degree, as a learning experience that demonstrates: The ability to think and to communicate clearly and effectively both orally and in writing; to use mathematics; to understand the modes of inquiry of the major disciplines; to be aware of other cultures and times; to achieve insights gained through experience in thinking about ethical problems; and to develop the capacity for self-understanding. General Education transfer patterns do not satisfy the requirement for a major or an area of emphasis. In other words, an associate degree cannot consist solely of CSU – General Education – Breadth (CSU-GE-Breadth), IGETC, or the local General Education pattern with the remaining units (to reach 60) in other General Education courses or electives, selected at the student's discretion. Students intending to transfer must be required to complete the CSU-GE-Breadth, IGETC pattern, or General Education pattern for a four-year institution in an adjacent state to fulfill General Education, 18 or more semester units (or 27 quarter units) in a major or area of emphasis, and the balance of units (to reach 60) in transferable courses in order to receive an associate degree. There may also be additional graduation requirements at individual colleges, such as physical education. Some students who intend to transfer will complete more than 60 units in order to meet all requirements for the associate degree. When an associate degree is developed for students who do not intend to transfer, a local General Education pattern of a minimum of 18 semester or 27 quarter units may be required. However, colleges should strongly recommend or require that a student select the appropriate General Education pattern for his or her intended goal with advice from a counselor. General Education is designed to introduce students to the variety of means through which people comprehend the modern world. General Education introduces the content and methodology of the major areas of knowledge including the humanities and fine arts, the natural sciences, and the social sciences, and provides an opportunity for students to develop intellectual skills, information technology facility, affective and creative capabilities, social attitudes, an appreciation for cultural diversity, and a recognition of what it means to be an ethical human being and effective citizen. The General Education patterns applicable to the Associate of Arts for Transfer (AA-T) and the Associate of Science for Transfer (AS-T) are either the CSU GE Breadth Requirements or the IGETC requirements. 18 Peralta Community College District There are high-unit baccalaureate majors, such as engineering and architecture, which require a large number of lower division major preparation courses. Students who intend to transfer into such programs at a baccalaureate institution may complete fewer units of General Education at the community college than the number required in CSU-GE-Breadth and IGETC patterns. They may need to complete a local General Education pattern consisting of 18 or more units and complete any remaining General Education requirements after they transfer. The catalog description for an associate degree must provide an overview of the knowledge and skills that students who complete the requirements must demonstrate. If the degree is designed for students who intend to transfer, then the appropriate baccalaureate major or related majors or areas of emphasis must be identified. If the degree is designed for employment preparation, a list of potential careers must be included. In addition, all prerequisite skills or enrollment limitations must be described. Section 66055.8 of the California Education Code creates an exception to the requirements for the associate degree. To obtain an associate degree in nursing, students who have baccalaureate or higher degrees are only required to complete the course work required for completion of the registered nursing program, including prerequisites and nursing course work. These students are not to be required to complete any other courses required by the college for an associate degree. Procedure Courses proposed for General Education are reviewed annually by the General Education Subcommittee of the Council on Instruction, Planning and Development (CIPD) and recommendations are forwarded to CIPD for action. Academic departments review and propose new courses and revisions to current courses, certificates, programs, and/or majors based on changing industry standards and practices, baccalaureate transfer requirements, newly added associate degree standards, and/or recommendations from the State Chancellor’s Office. The Curriculum Committee evaluates the content of every new and revised course, certificate, program, or major submitted for consideration. Program Definition An educational program is defined in Title 5, section 55000(g), as "an organized sequence of courses leading to a defined objective, a degree, a certificate, a diploma, a license, or transfer to another institution of higher education." In practice, however, the Chancellor’s Office approves only associate degrees and those credit certificates that community colleges wish to award to students and which will be listed on transcripts. In addition, all noncredit programs require Chancellor’s Office approval. Types of Educational programs that must be submitted to the Chancellor’s Office for approval Credit Programs Associate Degrees – traditional AA or AS and AA-T/AS-T Certificates of Achievement that require 18 or more semester units (or 27 or more quarter units) Certificates of Achievement that require 12 to fewer than 18 or more semester units (or 18 to fewer than 27 quarter units) Noncredit Programs All noncredit programs that receive state funding must be submitted to the Chancellor’s Office for approval. These include Course sequences in Career Development and College Preparation (CDCP) that lead to Certificates of Completion or Certificates of Competency for which enhanced funding as enacted by SB 361 is requested Adult High School Diploma (including courses for which enhanced funding as enacted by SB 361 may be requested) 19 Peralta Community College District References: Administrative Procedure 4025--Philosophy and Criteria for the Associate Degree and General Education Title 5 Section 55061 and ACCJC Accreditation Standard II.A.3 Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum. aspx. 20 Peralta Community College District Major or Area of Emphasis In 2007, Title 5, section 55063(a), was modified to allow colleges to develop associate degrees requiring 18 or more semester (27 or more quarter) units in a major or “area of emphasis.” A major may be defined by the lower-division requirements of a specific major at the UC or CSU or a minimum of 18 semester (27 quarter) units in a field or related fields selected by the community college. The requirements for a major must consist of courses that all students are expected to complete for a specific number of units. A small number of the required units may be completed by selecting courses from a list of restricted electives. An area of emphasis is considered to be a broader group of courses and may be defined as 18 or more semester (27 or more quarter) units in related fields intended to prepare the student for a particular major or related majors at a baccalaureate institution or to prepare a student for a particular field as defined by the community college. Such a degree may be similar to patterns of learning that a student undertakes in the first two years of attendance at a baccalaureate institution in order to prepare for a major/area field of study. The requirements for an area of emphasis must specify the number of units that students will select from a list of courses that prepare students for a specific academic or professional goal. Each area of emphasis will be awarded as a separate degree and assigned a separate program control number. The area of emphasis might be as broad as Social Sciences, or a college could design a theme-based area of emphasis that consists of an interdisciplinary grouping of courses, such as American Studies, International Business, or Multicultural Studies. However, if the area of emphasis is designed to prepare students for transfer, all of the required courses for the area of emphasis must be transferable and must prepare students for a field of study offered at a baccalaureate institution. Proposed majors or areas of emphasis may meet community needs and reflect the educational philosophy of the faculty in those discipline(s). These degrees can represent a cohesive packaging of courses that are not accepted for transfer at baccalaureate institutions. When seeking approval for such degrees, the intent must be clearly expressed in the narrative portion of the proposal. Documentation of need can include letters of support, survey results, or anything that provides evidence that the degree fulfills a need of the community. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 21 Peralta Community College District Certificates of Achievement Title 5, section 55070, defines Certificate of Achievement as any credit certificate that may appear by name on a student transcript, diploma, or completion award and which requires 18 or more semester units or 27 or more quarter units of degree-applicable coursework. Chancellor’s Office approval is required. The college can develop and propose a Certificate of Achievement that includes coursework taken to satisfy transfer patterns established by the University of California, the California State University, or accredited public postsecondary institutions in adjacent states. Community colleges are encouraged to develop and seek approval of Certificates of Achievement in CSU-GE-Breadth and IGETC. The college may also request approval from the Chancellor’s Office for certificate programs that require fewer units in order to list these certificates on student transcripts. In order to be approved, the proposed certificate must require 12 or more semester units (or 18 or more quarter units) of degree-applicable credit coursework and must represent a well-defined pattern of learning experiences designed to develop certain capabilities that may be oriented to career or General Education. After Chancellor’s Office approval, they must be called Certificates of Achievement and may be listed on student transcripts. The proposals for these proposed certificates will demonstrate the same levels of need and academic rigor that is required for certificates requiring 18 or more semester (27 or more quarter) units. The proposal requires the same narrative and documentation required for all Certificates of Achievement. Community colleges may also award certificates for fewer than 18 semester or 27 quarter units without Chancellor’s Office approval, but must call such certificates something other than “certificate of achievement.” At Peralta Community College District, these certificates are called “Certificate of Proficiency.” Any group of credit courses in the same four-digit TOP code that totals 18 or more semester units and that are linked to one another by prerequisites or corequisites, are defined as an "educational program" that requires Chancellor’s Office approval. The college must submit this sequence of courses for approval as a Certificate of Achievement. When a college creates a sequence of certificates in a single four-digit TOP code, arranged such that a student must complete one level before taking another level and the set or sequence as a whole requires 18 semester or 27 quarter units or more, then the entire certificate sequence requires Chancellor’s Office approval. For example, if a college creates the low-unit certificates listed below but then makes the Level I low-unit certificate prerequisite to Level II, the college has essentially created an 18-unit program. Multimedia Arts, Basic (or Level I) – 9 units Multimedia Arts, Advanced (or Level II) – requires completion of Level I or equivalent skills and knowledge plus an additional 9 units As such, the college needs to submit the entire 18 units for approval as a Certificate of Achievement. However, Chancellor’s Office approval of these two certificates would not be necessary if the Basic (Level I) certificate is not required for the Advanced (Level II) because each certificate requires fewer than 12 semester units. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 22 Peralta Community College District Associate Degrees for Transfer (ADT) to the California State University System Associate in Arts for Transfer (AA-T) and Associate in Science for Transfer (AS-T) SB 1440 establishes the Student Transfer Achievement Reform (STAR) Act. SB 1440 requires a community college district to grant an ADT to a student in that student’s field of study once a student has met degree and transfer requirements for a particular major. Upon completion of the ADT, the student is eligible for transfer with junior standing into the California State University (CSU) system. Students will be given priority consideration when applying to a particular program that is similar to the student’s community college area of emphasis. Community colleges are required by Senate Bill (SB) 1440 (Padilla) and California Education Code section 66746(a) to develop and offer ADTs that require students to meet both of the following requirements. (1) Completion of 60 semester units or 90 quarter units that are eligible for transfer to the California State University, including both of the following: (A) The Intersegmental General Education Transfer Curriculum (IGETC) or the California State University General Education – Breadth Requirements. (B) A minimum of 18 semester units or 27 quarter units in a major or area of emphasis, as determined by the community college district. (2) Obtainment of a minimum grade point average of 2.0. Title 5, section 55063(a), also requires that students must earn a C or better in all courses required for the major or area of emphasis. In addition, Education Code section 66746 subdivision (b) prohibits a community college district from adding any additional local course requirements for a student to be eligible for the ADT, and subdivision (e) prohibits allowing remedial non-collegiate level coursework to be counted toward the units required for the ADT. Title 5, section 55002(b), describes such courses as “nondegree-applicable credit courses.” SB 1440 also prohibits the CSU from requiring a transferring student to repeat courses similar to those taken at the community college that counted toward their ADT. AA-Ts and AS-Ts - Why create them? Increase students’ ability to transfer to a local CSU Increase students’ ability to finish a 4-year degree in 4 years Ensure our students have the background they need to be successful CSUs will consider these degrees as part of their admission decision The benefit for students completing these ADTs is that the CSU system is required by Education Code section 66747 to “guarantee admission with junior status to any community college student who meets all of the requirements” for the ADT. CSU is required to grant priority admission for a student with this associate degree “to his or her local [CSU] campus and to a program or major that is similar to his or her community college major or area of emphasis, as determined by the [CSU] campus to which the student is admitted.” In addition, section 66747 states that “a student admitted under this article shall receive priority over all other community college transfer students, excluding community college students who have entered into a transfer agreement between a community college and the California State University prior to the fall term of the 2012/13 academic years.” When an ADT is approved by the CCC Chancellor’s Office, the CSU Chancellor’s Office will be notified so that the approved associate degree and its similar CSU baccalaureate degrees may be identified. These 23 Peralta Community College District data will be used to identify eligible students who apply to the CSU for admission as described in Education Code section 66747. The ultimate advantage for students completing these associate degrees is that the associate degree may not require more than 60 semester (or 90 quarter) units; and after transferring into the appropriate program at the CSU, the baccalaureate degree may not require more than 60 additional semester units, for a total of 120 semester (or 180 quarter) units required for the baccalaureate degree (pursuant to Education Code section 66748). Section 66748(b) allows an exception for the maximum units required at the CSU when the Chancellors of the CSU and the CCC systems, and their respective Academic Senates, specify high-unit majors that require more than 120 semester (or 180 quarter) units for the baccalaureate degree. The CSU is prohibited by Education Code section 66748(c) from requiring a transferring student with this associate degree to repeat courses that are similar to those taken at the community college that counted toward the ADT. For up-to-date, detailed information about all aspects of these ADTs, see SB 1440 -- Associate Degrees for Transfer, http://sb1440.org. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 24 Peralta Community College District Transfer Model Curriculum (TMC) In the implementation process for SB 1440 and Education Code section 66746, the ASCCC, in collaboration with the CSU Academic Senate, has developed a Transfer Model Curriculum (TMC) for certain majors that have been identified for students who transfer from a California community college to CSU. Each TMC represents a structure developed by intersegmental faculty for establishing the major component of a California community college Associate Degree for Transfer (ADT). According to Title 5, section 55063, and Education Code, section 66746, the ADT must include a major or area of emphasis consisting of a minimum of 18 semester units. TMCs are being developed as a means of facilitating a statewide response to the mandate that all California community colleges offer Associate Degrees for Transfer (ADT). Draft TMCs are developed by intersegmental faculty (CCC and CSU, primarily) in the discipline and then made available for vetting at www.c-id.net. Once a TMC template is finalized, CCC faculty has the option of developing degrees that align with the TMC. The designators for these ADTs aligned with the TMCs are Associate in Arts for Transfer (AA-T) and Associate in Science for Transfer (AS.-T). The approved TMC templates are located on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division (www.cccco.edu/aad) website under the Transfer Model Curriculum section. 25 Peralta Community College District Course Identification Numbering System (C-ID) The Course Identification Numbering System (C-ID) is a statewide numbering system that is different from the course numbers assigned by individual California Community Colleges. C-ID is a supranumber, a faculty-driven system to assign numbers to significant transfer courses, and a response to needs of transfer partners and their transfer initiatives. Each C-ID number identifies a lower-division, transferable course commonly articulated between the California Community Colleges and universities (including Universities of California, the California State Universities, as well as with many of California's independent colleges and universities). The C-ID number is a designation that ties that course to a specific course “descriptor” that was developed by intersegmental discipline faculty and reviewed statewide. It provides information for students, staff and faculty who must identify which community college courses best meet the expectations transfer partners have for courses that contribute to transfer into a major at specific universities or fulfill general education requirements. The C-ID descriptor also provides information for ongoing curriculum development and revision of lower division courses. The C-ID Numbering System is particularly useful for students attending more than one California Community College since C-ID Designators are often applied to courses students need to prepare for transfer. Once the descriptor for a course has undergone wide discipline review, it is posted for general viewing. Individual college courses are compared to the minimum requirements set by these descriptors. Any community college course that bears the C-ID supranumber conveys that faculty have determined it meets the published course content, rigor, and student learning outcomes. The C-ID descriptor also means that any other course elsewhere, bearing the same number will be accepted by the institution. A C-ID Designator next to a course means that the course is comparable in content and scope to a similar course offered by participating California colleges and universities. Thus, if a catalog lists a C-ID Designator for a course, students can be assured that the course will be accepted at another California Community College that offers a course with the same C-ID Designator. Remember that the content, objectives, and pre and co-requisites of all C-ID descriptors reflect the minimum standards expected in a college's Course Outline of Record (COR). While the COR must meet all of these standards as included in the C-ID descriptor, colleges may certainly go beyond the descriptor and include additional content or higher requirements. Likewise, the specific course title on the C-ID descriptor is advisory, and courses may be approved as meeting the descriptor if they have different but relevant titles. In addition, although colleges may require more units than is required by a descriptor, unit restrictions based on SB 1440 will still apply if the course is included in a TMC-aligned degree. If a TMC for an AD-T has any courses with C-ID Designators, the college must send their course for approval through the C-ID process and receive an approved C-ID designator for their courses prior to submitting their AD-T approval request. Note: The TMC templates and C-ID descriptors are subject to change within the initial vetting process and sometimes after being finalized due to changes in the academic field. Check both the Chancellor’s Office web site http://www.sb1440.org/Curriculum.aspx and the C-ID web site http://www.c-id.net/ to ensure your degrees are in compliance. References: C-ID Final Descriptor Website, http://www.c-id.net/view_final.html Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 26 Peralta Community College District Guidelines for Associate Degree-Applicable Credit Courses For any course that will apply toward the associate degree, Title 5, section 55002(a), requires that the curriculum committee determine that the coursework is truly at a college level and that the course incorporates critical thinking, among other standards. Only courses that are included in the following categories may be offered for degree-applicable credit. All lower division courses accepted toward the baccalaureate degree by the California State University (CSU) or University of California (UC) systems or designed to be offered for transfer Courses that apply to a major or an area of emphasis in CTE fields, defined by the Chancellor’s Office to mean courses within a TOP code designated as vocational English composition or reading courses not more than one level below the first transfer level course in these areas All mathematics courses that fall into the above categories and Elementary Algebra Credit courses in English and mathematics taught in or on behalf of other departments and which, as determined by the local governing board, are comparable to required skills at a level equivalent to those necessary for degree-applicable English and mathematics courses Degree-applicable credit courses must be appropriate to the associate degree and recommended by the College Curriculum Committee. The curriculum committee approves degree-applicable credit courses based on the following standards. Grading policy, based on uniform standards pursuant to Title 5, section 55023, that demonstrates proficiency in subject matter by means of written communication, problem solving, and/or skills demonstrations, as appropriate to the course content Units, based on a relationship specified by the governing board in compliance with Title 5, section 55002.5, which requires a minimum of 48 hours of lecture, laboratory, out-of-class assignments, or other types of study for one unit of credit. For each hour of lecture, the course requires two hours of study and/or laboratory and/or assigned activity. Laboratory courses, however, may require minimal work outside of class scheduled meeting time. Intensity and rigor, as evidenced by the outline of course topics, course objectives, assignments, assessments, and reading materials identified in the Course Outline of Record (COR). Achieving the objectives of degree-applicable credit courses must require students to study independently outside of class time. There is an expectation that students will spend two hours outside of class for each hour of lecture. Required preparation for success in the course, such as prerequisite or corequisite courses, as determined by the curriculum committee in compliance with Title 5, section 55003. Basic skills prerequisites for success in the degree-applicable course that are dependent on communication and/or computation skills. These requirements may include eligibility to enroll in specific English and/or mathematics courses, as determined by an approved assessment method using multiple measures. Course Outline of Record (COR). The course is described in a COR that shall be maintained in the District’s curriculum management system (CurricUNET). A detailed description of the COR is included in this manual. Conduct of Course. Each section of the course is to be taught by a qualified instructor in accordance with a set of objectives and with other specifications defined in the COR. The Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used within Peralta to distinguish various course levels. See the Course Numbering System section of this manual for more information. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 27 Peralta Community College District Guidelines for Nondegree-Applicable Credit Courses The category of nondegree-applicable credit courses was created by regulatory amendments adopted by the Board of Governors in 1986. There were two primary purposes: to allow community college students to receive "workload credit" (which would apply toward maintaining the unit load necessary to receive financial aid) for precollegiate basic skills courses to safeguard the integrity of the associate degree by ensuring that such courses were not counted within the degree Title 5, section 55002(b), requires that nondegree-applicable credit courses be approved by the College Curriculum Committee and district governing board. There are four types of nondegree-applicable credit courses: Nondegree-applicable basic skills courses (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, §55000(j)). Courses designed to prepare students to succeed in degree-applicable credit courses that integrate basic skills instruction throughout the curriculum and assign grades partly upon demonstrated mastery of basic skills. Examples of such courses include college orientation and guidance courses and discipline specific courses such as biology, history, business, etc. Precollegiate career technical preparation courses that provide foundation skills for enrollment in degree-applicable Career Technical Education (CTE) programs. Career technical courses for which meeting the standards for degree-applicable credit courses is neither necessary nor required. The College Curriculum Committee is responsible for recommending approval of nondegree-applicable credit courses based on the following standards. Grading policy, based on uniform standards pursuant to Title 5, section 55023, that demonstrates proficiency in subject matter by means of written communication, problem solving, and/or skills demonstrations, as appropriate to the course content. Units, based on a relationship specified by the governing board in compliance with Title 5, section 55002.5, which requires a minimum of 48 hours of lecture, laboratory, out-of-class assignments, or other types of study for one unit of credit. Intensity, as evidenced by the Course Outline of Record (COR). Nondegree-applicable credit courses must provide instruction in critical thinking, prepare students to study independently outside of class time, include reading and writing assignments, and prepare students to succeed in degree-applicable credit courses. Required preparation for success in the course, such as prerequisite or corequisite courses, as determined by the curriculum committee and in compliance with Title 5, section 55003. Difficulty and level, as determined by the curriculum committee, which ensure that the course requires critical thinking, learning skills, and vocabulary appropriate for a college-level course. The Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used within Peralta to distinguish various course levels. See the Course Numbering section of this manual for more information. References: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 28 Peralta Community College District Transferable Courses Community college courses may be transferable to baccalaureate institutions for three different purposes: elective credit, General Education, and/or lower-division preparation for a baccalaureate major. Faculty, curriculum committees, and articulation officers share responsibility for determining and ensuring the transferable status of courses. The predominant transfer-receiving institutions for California community colleges are the California State University (CSU) and the University of California (UC) systems. Under Executive Order No. 167, the CSU Chancellor has delegated responsibility, since 1973, to the community colleges to determine which courses shall be considered baccalaureate-level for elective transfer credit. By contrast, the UC Office of the President reviews the determination of transferability course-by-course for that system; transferability for elective credit requires that the community college course be essentially equivalent to a course already offered for baccalaureate credit on at least one UC campus. Challenges may be raised at CSU campuses to particular courses that are certified by a community college as transferable, but such challenges do not often occur. Transferability of elective credit, however, does not create any presumption of acceptance for General Education or credit to the major or area of emphasis. Decisions on transferability of individual courses required as part of a university major are made by departmental faculty and committees at each university campus. Major-specific articulation information for most campuses can be found in the database of the Articulation System Stimulating Interinstitutional Student Transfer (ASSIST), online at www.assist.org. The baccalaureate public segments (CSU and UC) have extensive requirements for General Education. Identifying those community college courses that will be accepted by CSU or UC as satisfying their General Education requirements is very important to the success of transfer students. For the UC, the acceptability of a course for General Education is predicated on the acceptability of the equivalent UC course, since each course transferred to UC has been identified, by staff review at the Office of the President, as essentially equivalent to an existing UC course. General Education requirements vary greatly from campus to campus in the UC system. The CSU General Education requirements are standardized through statewide regulations. Procedures for certifying community college courses as meeting CSU’s General Education requirements are set forth in the CSU Chancellor’s Executive Order 1065, which is available online at www.calstate.edu. Since 1993, new courses intended for General Education transfer have been reviewed for acceptability by CSU Chancellor’s Office staff and a subcommittee of the CSU General Education Advisory Committee. This same subcommittee, with the addition of UC representatives, reviews the acceptability of community college courses for the Intersegmental General Education Transfer Curriculum (IGETC), which is accepted by both UC and CSU systems as an alternative pattern for satisfying lower-division General Education requirements. In Spring 2000, the Intersegmental Committee of Academic Senates (ICAS) concluded in a report based on a study of the use, effectiveness, and awareness of IGETC that this General Education pattern is useful and preferred by students who intend to transfer. The paper, titled “Use, Effectiveness, and Awareness of the Intersegmental General Education Transfer Curriculum (IGETC) an Evaluation,” is available on the website of the ASCCC at www.asccc.org. Determining the eligibility of a particular course for university transfer for all these purposes—elective credit, major or area of emphasis requirements, and General Education—is an essential part of the process of local course approval by the curriculum committee, generally with the assistance of a college articulation officer. For CORs submitted to the Chancellor’s Office, evidence of transferability is a quality criterion that is reviewed for all programs and courses in traditionally or potentially transferable disciplines. Guidelines for Transfer Level Courses The course shall: 29 Peralta Community College District Be aimed more at understanding theory and concepts which are grounded in the fundamental academic disciplines rather than at the acquisition of immediate technical skills Treat subject matter with an intensity and pace that establishes an expectation for significantly greater learner independence than that required at the secondary level Enhance understanding of intellectual, scientific, and cultural concepts and traditions Not be of remedial or college preparatory level Move the student toward acquiring competencies expected of university graduates at its completion. The Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used within Peralta to distinguish various course levels. See the Course Numbering System section of this manual for more information. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 30 Peralta Community College District Relationship of Hours to Units Title 5, section 55002.5, establishes the minimum expected time on task (lecture, study, and/or lab work) that is necessary to award one unit of credit. A minimum of 48 hours on the semester system (or 33 hours on the quarter system) of lecture, study, or lab work is required for one unit of credit regardless of term length. In practice, the number of hours varies among institutions, but is generally within the range of 4854 hours per unit for colleges on the semester system. For each hour of lecture, it is assumed that students will be required to spend an additional two hours of study outside of class. The number of units awarded for laboratory courses is generally based on the number of hours of laboratory work, presuming that students complete most required work in class. Because California finance laws assume that primary terms average 17½ weeks on the semester system and 11⅔ weeks on the quarter system (the two semesters or three quarters equal the traditional 35-week academic year), and because student attendance and related apportionment state compliance auditing is based on the units and student contact hours delineated in the official COR, the Chancellor’s Office strongly recommends that colleges use the 18-week semester or 12-week quarter as the basis for the student contact hour calculation used in the COR, even if a college has been approved to use a compressed academic calendar. The 18-week semester or 12-week quarter primary term provides the greatest flexibility in terms of contact hours, and colleges do not risk an audit finding for excessive apportionment claims such as they might experience using a 16-week semester basis for the contacthour calculation. Additionally, it is also important to note the flexible calendar program is designed around the 35-week traditional academic calendar, so basing contact hour targets around an 18-week semester assures that instructional hours lost to “flex” activities will not result in the district not providing the minimum number of hours required by Title 5, section 55002.5, to award a unit of credit. The guidelines provided below are all predicated on an 18-week semester or 12-week quarter term. In determining the number of units to be awarded for courses, colleges must consider total lecture, outside study, and/or laboratory hours. We refer to the combination of these hours as “student learning hours.” Note: For example, a course for which three units is awarded may meet four hours a week over a semester and still be in compliance with these regulations if it is assumed that the increased classroom time serves to decrease outside study time. Thus, a course that seemingly meets for more hours per week than the units awarded may be in compliance, as opposed to a course that simply requires an excess of total classroom hours for the units awarded. A specific example at Peralta is Math 201, Elementary Algebra, a 4 unit course requiring 5 hours of lecture. For lab units, it has not traditionally been expected that the student will study outside the classroom. Therefore, the number of units granted is generally based entirely on the number of hours performed on campus under the immediate supervision and control of a qualified academic employee. For example, 52.5 hours of chemistry laboratory (three hours per week over 18-weeks) would grant one semester unit of credit, whereas 52.5 hours of chemistry lecture would grant three units. The following examples apply to semester units, as outlined in Peralta policy. Lecture or Lab Only Courses One-unit lecture course = 17.5 hours in-class lecture plus 35 hours out-of-class study One-unit laboratory course = 52.5 hours in-class laboratory Lecture and Lab Combined Three units (2 units of lecture and 1 unit of lab) = 35 hours in-class lecture, 52.5 hours inclass laboratory, plus 70 hours out-of-class study Check these again! Some community colleges have assigned a unit of lab credit for fewer than three hours a week of supervised activity in certain courses where it is expected that students will do some homework, but not as much as in a traditional lecture course. For example, in a computer applications course, there may be a certain amount of reading or additional practice required outside of class. The college may award one unit of lab credit for only two hours per week of hands-on computer instruction/activity, as long as the instructor assigns one hour per week of out-of-class study. There is no prohibition against this practice; however, it must be used with caution, particularly in regard to transferable laboratory courses. In the 31 Peralta Community College District natural sciences, it is standard university practice to base the number of units awarded only on the inclass lecture and laboratory hours. Students wishing to transfer a course that includes two hours of lab and one hour of homework for one unit may not earn the same amount of transfer credit for major or General Education purposes as that awarded at baccalaureate institutions. When the combination of lecture and out-of-class study plus laboratory work reaches 108 student learning hours on the semester system or 72 student learning hours on the quarter system, or twice the number of hours required for one unit, students must earn at least two units of credit. Note that a college may not offer two units of credit unless total hours of lecture and out-of-class study plus laboratory work reaches a minimum of 96 student learning hours on the semester system or 66 student learning hours on the quarter system. This regulation may affect the number of units awarded in some disciplines that offer courses with a high number of contact hours, such as courses mandated by professional certification requirements in law enforcement and fire technology. For credit courses, a district may choose to award units of credit in increments of one half or smaller. However, it is not permissible to approve a credit course with zero units of credit. Given that some colleges begin with total student contact hours in order to derive the appropriate units to assign to a course, the following examples are provided. All examples use semester hours. 27 lecture contact hours: a college must offer 1.5 units of credit under the assumption that there are 54 hours of out-of-class study for a total of 81 student learning hours. A college may not offer 2 units of credit, since the minimum of 96 student learning hours (per Title 5) has not been attained. 18 lecture contact hours and 36 lab contact hours: a college may offer 1.5 units of credit under the assumption that the lecture hours entail 36 hours of out-of-class study, resulting in a total of 90 student learning hours; if a college presumes that each lab contact hour also entails half an hour of out-of-class work, then the total hours would equal 108 student learning hours, requiring the college to offer 2 units of credit. Given the variety in calculation of total student contact hours, colleges must make explicit in the COR not only the total units for the course, but the lecture/lab breakdown of the units, the term length being used for the total student contact hour calculation, and the total student contact hours. Accreditation standards require a minimum of 48 student learning hours for the award of a unit of credit. Although Title 5, section 58023, defines an hour of classroom or laboratory time as 50 minutes, when calculating out-of-class study time, an hour retains its ordinary meaning of 60 minutes. Thus, for a one-unit semester lecture course, the minimum hours would be as follows. 16 hours of classroom time + 32 hours of homework 48 hours total student learning time The minimum number of hours expected for a three-unit semester lecture course would be as follows. 48 hours of classroom time + 96 hours of homework 144 hours total student learning time Colleges must take into account holidays and flex days when constructing the academic calendar in order to ensure that all courses can meet the 48-student-learning-hour minimum for each unit of credit awarded. In addition, it is impossible to predict exactly how long it will take for any individual student to complete a given amount of assigned study or homework; therefore, these ratios will not hold true for every individual taking the course. Nevertheless, instructors are required to follow the COR and assign an amount of homework that is consistent with the time it would take the average student to complete the coursework. When a term is more or less than 16 weeks, then the class time and assignments for a one-unit course must be adjusted to meet the required credit hours. For instance, suppose a college schedules a one-unit 32 Peralta Community College District lecture course in a compressed time frame that meets every weekday for two weeks. The minimum hours would be as follows. 1.6 hours of lecture each day + 3.2 hours of homework each day 4.8 hours of student learning each day It is not appropriate to offer courses in a compressed time frame that, by their design, would not permit the student to complete the amount of out-of-class homework required to meet the hours-to-units relationship mandated by Title 5. For example, consider a one-unit lecture course in Library and Information Science – Research Strategies that is normally scheduled for 16 hours, or 2 hours per week for eight weeks. This course cannot be offered as a one-day Saturday class since students would have to complete 16 hours of class time in one day and the students would not have enough time to fulfill their 32 hours of required, outside homework. It is feasible that the class could be scheduled on Saturdays over several weeks, as long as doing so would allow adequate time for students to complete the course requirements. In the spring of 2006, the Peralta DAS passed the following resolution. In the fall of 2006, the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges essentially passed the same resolution. Whereas, With the move to compressed calendars and due to enrollment pressures, a number of colleges are scheduling three-, four-, and even five-unit courses in shortened time frames of fewer than six weeks; and Whereas, There are pedagogical considerations that need to be reviewed by the discipline faculty member who is offering the course and the curriculum committee; Resolved, That the District Academic Senate recommends that when a course of three or more units is to be offered in a time frame of fewer than six (6) weeks, the local curriculum committee engage the discipline faculty in a review of the course for the following: academic integrity and rigor, the method for meeting Carnegie units, the ability for students to complete and for faculty to evaluate outside assignments, and the appropriateness of the method of delivery. Such a course can only be offered in the shortened time frame after it has received curriculum committee approval. The DAS is aware of the college FTES targets and the motivation to meet those targets. They also are aware that students will sign up for very short term classes because the classes move quickly and are over in no time. However there is concern with academic rigor, academic integrity, and whether the same student learning outcomes can be achieved in a 12 - 15 day course compared to when the course is offered in six weeks or 18 weeks. Federal Financial Eligibility For purposes of federal financial eligibility, a “credit hour” shall be not less than: One hour of classroom or direct faculty instruction and a minimum of two hours of out of class student work each week for approximately 15 weeks for one semester, or the equivalent amount of work over a different amount of time or At least an equivalent amount of work as required in the paragraph above of this definition for other academic activities as established by the institution including laboratory work, internships, practica, studio work, and other academic work leading to the award of credit hours Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 33 Peralta Community College District To Be Arranged (TBA) Hours Compliance Advice Pursuant to Legal Advisory 08-02, TBA has been defined as follows. Some courses with regularly scheduled hours of instruction have ‘hours to be arranged’ (TBA) as part of the total contact hours for the course. The TBA portion of the course uses an alternate method for regularly scheduling a credit course for purposes of applying either the Weekly or Daily Census Attendance Accounting Procedures. This is a specialized situation when an exception to normal scheduling is required in certain disciplines. The use of TBA hours must be defined in the Course Outline of Record (COR) when the course is developed. The use of TBA is very restricted. Consult with the College Curriculum Committee chair prior to proposing such a course. The procedures which must be followed for the TBA hours are described in the Legal Advisory. In some situations the entire course might be on TBA, and in that case the course would follow the same rules. Note: The Student Attendance Accounting Manual, page 3.3, refers to TBA hours or “hours to be arranged,” which for purposes of this advisory have the same meaning as ‘HBA’ or ‘hours by arrangement’ or any other local term used to designate these hours. For more information, refer to the Chancellor’s Office website (www.cccco.edu) Legal Affairs Division, Legal Advisory 08-02. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 34 Peralta Community College District Open Courses Every community college is required, as a minimum condition of state aid, to place a statement on open courses in its catalog and class schedules. Title 5, section 51006, requires colleges to publish a statement in the official catalog and schedule of classes that all course sections or classes for which state aid is awarded are open to enrollment and participation by any person admitted to the college. The college may only restrict enrollment in a course when the restriction is specifically required by statute or legislation. This section also allows colleges to require that students meet prerequisites that have been established pursuant to Title 5, section 55003. Situations where enrollment limitation may be allowed are discussed more specifically in Title 5, section 58106. These sections allow the college to restrict students from enrolling in a course when: • Prerequisites, corequisites, or other advisories on recommended preparation have been established for the course. • Health and safety considerations, facility limitations, faculty availability, funding limitations, or other constraints have been imposed by statutes, regulations, or contracts. The college can limit enrollment only through one or more of the following approaches. • Enrolling on a “first-come, first-served” basis or other non-evaluative selection technique • Offering special registration assistance to the handicapped or disadvantaged student • Enrolling in accordance with a priority system established by the local board • Allocating available seats to students who have been judged most qualified in the case of intercollegiate competition, honors courses, or public performance courses • Limiting enrollment to a cohort of students enrolled in two or more courses, provided, however, that a reasonable percentage of all sections of the course do not have such restrictions • Restricting enrollment of a student on probation or subject to dismissal to a total number of units or to selected courses or of a student who is required to follow a prescribed educational plan The open course concept means that no course may be offered for apportionment if it is restricted to a particular group, such as employees of a particular company or organization, students concurrently enrolled in a neighboring university, persons of a particular ethnicity, or any other narrowly defined group. Furthermore, although a course may be designed primarily for individuals in a particular group (for example, individuals already employed in a particular occupation), it may not be offered for apportionment unless it is open to, and designed in such a way that it could also be of benefit to, other students. Thus, a course may be primarily intended for skills upgrading of individuals already experienced in a particular occupation, but it must also be possible for a student in training for that occupation to take and benefit from the course, subject to legally established prerequisites. Certain narrow exceptions to the open course rule are specified in law. These include enrollment preference for fire service personnel (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 58051(d)) and law enforcement trainees (Penal Code, § 832.3[c]), courses conducted in a jail or federal prison (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 58051.6), students who are part of a cohort concurrently enrolled in another specified course (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 58106), and apprentices in “related and supplemental instruction” courses (Labor Code, § 3076.3). Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 35 Peralta Community College District Prerequisites, Co-requisites, and Advisories Prerequisites, co-requisites, advisories, and limitations are necessary to ensure that students succeed in their coursework and have access to the courses they require. It is important to have prerequisites in place where they are a vital factor in maintaining academic standards. It is also necessary to ensure that prerequisites, co-requisites, advisories, and limitations do not constitute unjustifiable obstacles to student access and success. Therefore, to foster the appropriate balance between these two concerns, the Education Code requires that prerequisites, co-requisites, advisories, and limitations be established based solely on content review or content review with statistical validation. Title 5, section 55002, requires, for degree-applicable credit courses, that the campus curriculum committee determine whether prerequisites or corequisites are necessary for student success in a course, including prerequisite English or math levels. This section also states that curriculum committees may establish prerequisites or corequisites for nondegree-applicable credit courses. However, Title 5, section 55003, through local district polices, requires with certain limited exceptions, that prerequisites must be carefully scrutinized before they are established, to be certain that they are necessary and not discriminatory. The review of prerequisites and corequisites is part of the curriculum review conducted by the College Curriculum Committee. In accordance with Title 5, section 55003, prerequisites and corequisites can only be established if they are determined to be necessary, appropriate, and non-discriminatory, or required by regulation or statute. Prerequisites that are met by assessment must conform to the matriculation assessment process found in Title 5, section 55500. Title 5, section 55003, also requires that prerequisites and corequisites be affirmed through a process of "content review" at least once every six years, except for prerequisites and corequisites for CTE courses or programs, which must be reviewed every two years. Terms used in Title 5, section 55003, are defined as follows: Advisory on recommended preparation means a condition of enrollment that a student is advised, but not required, to meet before or in conjunction with enrollment in a course or educational program. Corequisite means a condition of enrollment consisting of a course in which a student is required to enroll in order to succeed in another course. The student acquires the necessary skills, concepts, and/or information in the corequisite course that supports success in the target course. Since the corequisite course provides skills or knowledge necessary for successful completion of another course, it is highly unlikely that the student can achieve a satisfactory grade in the course for which the corequisite is being established without the skills and knowledge provided in the corequisite course. For example, a course in Medical Transcription may require an Introduction to Medical Terminology course as corequisite. The student’s familiarity with medical terms will enable the student to succeed in medical transcription. Prerequisite means a condition of enrollment that a student is required to meet in order to demonstrate current readiness for enrollment in a course or educational program. Meeting the prerequisite provides assurance that the student has the skills, concepts, and/or information to succeed in the target course. The prerequisite ensures that students possess the skills or knowledge necessary for success in a program or course. For example a course might establish completion of an English course (or placement into English at a specific level) as a prerequisite before the student may enroll in a Philosophy course that requires high-level reading and writing skills. A prerequisite or corequisite may be required by statute or regulation, or may ensure the health and safety of students in the course for which the prerequisite or corequisite is established. For example, a college might require that students complete a course in Food Safety as a corequisite to an Introduction to Culinary Arts course. The knowledge of food safety is required by health regulations and also ensures the safety of students in the laboratory portion of the Culinary Arts course. 36 Peralta Community College District A course may be established as a prerequisite or a corequisite. If established as a prerequisite, a student must enroll in the course prior to enrollment in the target course. If established as a corequisite, the student may enroll in the corequisite prior to enrolling in the target course or simultaneously with the target course. The Guidelines for Title 5, section 55003: Policies, Prerequisites, Advisories on Recommended Preparation document was released February 2012 and is available on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website (www.cccco.edu/aad). Information in the Catalog and Schedule of Courses The college shall provide the following explanations both in the college catalog and in the schedule of courses. Definitions of prerequisites, co-requisites, and limitations on enrollment including the differences among them and the specific prerequisites, co-requisites, and limitations on enrollment that have been established Procedures for a student to challenge prerequisites, co-requisites, and limitations on enrollment and circumstances under which a student is encouraged to make such a challenge. The information about challenges must include, at a minimum, the specific process including any deadlines, the various types of challenge that are established in law, and any additional types of challenge permitted by the college. Definitions of advisories on recommended preparation, the right of a student to choose to take a course without meeting the advisory, and circumstances under which a student is encouraged to exercise that right Challenge Process Any student who does not meet a prerequisite or co-requisite or who is not permitted to enroll due to a limitation on enrollment but who provides satisfactory evidence may seek entry into the course as follows. If space is available in a course when a student files a challenge to the prerequisite or corequisite, the District shall reserve a seat for the student and resolve the challenge within five (5) working days. If the challenge is upheld or the District fails to resolve the challenge within the five (5) working-day period, the student shall be allowed to enroll in the course. If no space is available in the course when a challenge is filed, the challenge shall be resolved prior to the beginning of registration for the next term and, if the challenge is upheld, the student shall be permitted to enroll if space is available when the students registers for that subsequent term. Grounds for challenge shall include the following. Those grounds for challenge specified in Title 5 Section 55201(f) The student seeks to enroll and has not been allowed to enroll due to a limitation on enrollment established for a course that involves intercollegiate competition or public performance, or one or more of the courses for which enrollment has been limited to a cohort of students. The student shall be allowed to enroll in such a course if otherwise he or she would be delayed by a semester or more in attaining the degree or certificate specified in his or her educational plan. The student seeks to enroll in a course that has a prerequisite established to protect health and safety, and the student demonstrates that he/she does not pose a threat to himself/herself or others. The student has the obligation to provide satisfactory evidence that the challenge should be upheld. However, where facts essential to a determination of whether the student's challenge should be upheld are or ought to be in the college's own records, then the college has the obligation to produce that information. Curriculum Review Process Faculty may suggest prerequisites, co-requisites, and advisories on recommended preparation (advisories) when they submit a new or modified course to the work flow. 37 Peralta Community College District The faculty in the discipline or, if the college has no faculty member in the discipline, the faculty in the department should follow the steps below. Approve the course; and, As a separate action, approve any prerequisite or co-requisite, only if: The prerequisite or co-requisite is an appropriate and rational measure of a student's readiness to enter the course or program as demonstrated by a content review including, at a minimum, all of the following. involvement of faculty with appropriate expertise; consideration of course objectives set by relevant department(s). The curriculum review process should be done in a manner that is in accordance with accreditation standards. be based on a detailed course syllabus and outline of record, tests, related instructional materials, course format, type and number of examinations, and grading criteria; specification of the body of knowledge and/or skills which are deemed necessary at entry and/or concurrent with enrollment; identification and review of the prerequisite or co-requisite which develops the body of knowledge and/or measures skills identified under iv. matching of the knowledge and skills in the targeted course and those developed or measured by the prerequisite or co-requisite (i.e., the course or assessment) maintain documentation that the above steps were taken. Approve any limitation on enrollment that is being established for an honors course or section, for a course that includes intercollegiate competition or public performance, or so that a cohort of students will be enrolled in two or more courses, and, in a separate action, specify which. Approve that the course meets the academic standards required for degree applicable courses, non-degree applicable courses, non-credit courses, or community service respectively. Review the course outline to determine if a student would be highly unlikely to receive a satisfactory grade unless the student had knowledge or skills not taught in the course. If the student would need knowledge or skills not taught in the course itself, then the course may be approved for degree applicable credit only if all requirements for establishing the appropriate prerequisite have been met excepting only approval by the curriculum committee. Review the course outline to determine whether receiving a satisfactory grade is dependent on skills in communication or computation. If receiving a satisfactory grade is sufficiently dependent on such skills, then the course may be approved for degree applicable credit only if all requirements have been met for establishing a prerequisite or co-requisite of not less than eligibility for enrollment to a degree-applicable course in English or mathematics, respectively. The academic senate has the responsibility for the final approval of prerequisites, co-requisites, and advisories on recommended preparation (advisories) except that the academic senate may delegate this task to the curriculum committee without forfeiting its rights or responsibilities under Title 5 Sections 53200-53204 and within the limits set forth in Title 5 Section 55003. Certain limitations on enrollment must be established in the same manner. The curriculum committee also reviews the course and prerequisite in a manner that meets each of the requirements specified above. If the District chooses to use content review as defined in Title 5 of the Code of California Regulations section 55000(c) to define prerequisites and co-requisites in reading, written expression, or mathematics for courses that are degree applicable and are not in a sequence, it must adopt a plan consistent with Title 5 of the Code of California Regulations section 550039(c). 38 Peralta Community College District Program Review: Regular Review of Prerequisites and Co-requisites The college shall periodically review each prerequisite, co-requisite, or advisory to establish that each is still supported by the faculty in the discipline or department and by the Curriculum Committee and is still in compliance with all other provisions of this policy and with the law. This review shall occur as a regular part of the program review process. Career Technical Education (CTE) courses or programs shall be reviewed every two years. All other courses and programs at least every six years. Implementing Prerequisites, Co-requisites, and Limitations on Enrollment Implementation of prerequisites, co-requisites, and limitations on enrollment must be done in a consistent manner and not left exclusively to the classroom instructor. Every attempt shall be made to enforce all conditions a student must meet to be enrolled in the course through the registration process so that a student is not permitted to enroll unless he/she has met all the conditions or has met all except those for which he/she has a pending challenge or for which further information is needed before final determination is possible of whether the student has met the condition. Instructor's Formal Agreement to Teach the Course as Described Each college shall establish a procedure so that courses for which prerequisites or co-requisites are established will be taught in accordance with the course outline, particularly those aspects of the course outline that are the basis for justifying the establishment of the prerequisite or co-requisite. The process shall be established by consulting collegially with the local academic senate and, if appropriate, the local bargaining unit. Courses Exempt from Content Review Title 5 subdivision (e) of section 55003 specifies the conditions under which a prerequisite or co- requisite does not need to be subject to either content review or content review with statistical validation: It is required by statute or regulation; or It is part of a closely-related lecture-laboratory course pairing within a discipline; or It is required by four-year institutions; or Baccalaureate institutions will not grant credit for a course unless it has the particular communication or computation skill prerequisite. Review of Individual Courses If the student's enrollment in a course or program is to be contingent on his or her having met the proposed prerequisite(s) or co-requisite(s), then such a prerequisite or co-requisite must be established as described. If enrollment is not blocked, then what is being established is not a prerequisite or corequisite but, rather, an advisory on recommended preparation and must be identified as such in the schedule and catalog. Advisories or Recommended Preparation The college may recommend that a student meet a standard of readiness at entry only if recommended by the faculty in the discipline or department and by the Curriculum Committee as provided above. This process is required for such recommendations described by the college in its catalog or schedule as "prerequisites," or "recommended," or by any other term. Limitations on Enrollment The types of limitation on enrollment specified below may only be established through the curriculum review process by the discipline or department faculty and the curriculum committee specified above including the requirement to review them again at least every six years; for example, as part of program review. The following requirements must also be met in order to establish these particular limitations on enrollment. 39 Peralta Community College District Performance Courses The college may establish audition or try-out as a limitation on enrollment for courses that include public performance or intercollegiate competition such as but not limited to band, orchestra, theater, competitive speech, chorus, journalism, dance, and intercollegiate athletics provided that: For any certificate or associate degree requirement which can be met by taking this course, there is another course or courses which satisfy the same requirement; and The college includes in the Course Outline of Record (COR) a list of each certificate or associate degree requirement that the course meets and of the other course or courses which meet the same requirement. Limitations on enrollment established as provided for performance courses shall be reviewed during program review or at least every six years to determine whether the audition or try-out process is having a disproportionate impact on any historically under-represented group and, if so, a plan shall be adopted to seek to remedy the disproportionate impact. If disproportionate impact has been found, the limitation on enrollment may not be printed in subsequent catalogs or schedules nor enforced in any subsequent term until such a plan has been endorsed by the department and the college administration and put into effect. Honors Courses A limitation on enrollment for an honors course or an honors section of a course may be established if, in addition to the review by the faculty in the discipline or department and by the curriculum committee as provided above, there is another section or another course or courses at the college which satisfy the same requirements. If the limitation is for an honors course and not only for an honors section, the college must also include in the COR a list of each certificate or associate degree requirement that the course meets and of the other course or courses which meet the same associate degree or certificate requirement. Blocks of Courses or Sections Blocks of courses or blocks of sections of courses are two or more courses or sections for which enrollment is limited in order to create a cohort of students. Such a limitation on enrollment may be established if, in addition to review by the faculty in the discipline or department and by the curriculum committee as provided above, there is another section or another course or courses that satisfy the same requirement. If the cohort is created through limitations on enrollment in the courses rather than limitations on specific sections of courses, then the college must include in the COR a list of each certificate or associate degree requirement that the course meets and of the other course or courses which satisfy the same associate degree or certificate requirement. Prerequisites and Recommended Preparation in C-ID Descriptors Remember that the content, objectives, and pre and co-requisites of all C-ID descriptors reflect the minimum standards expected in a college's Course Outline of Record (COR). While the COR must meet all of these standards as included in the C-ID descriptor, colleges may certainly go beyond the descriptor and include additional content or higher requirements. References: Administrative Procedure 4260 Prerequisites, Co-requisites, and Advisories Title 5 Section 55003 Title 5 Sections 55000 et seq. Guidelines for Title 5 Regulations Section 55003, Policies for Prerequisites, Co-requisites and Advisories on Recommended Preparation (CCCCO, February 2012) http://extranet.cccco.edu/Portals/1/AA/Credit/Prerequisites_Guidelines_55003%20Final.pdf C-ID Final Descriptor Website, http://www.c-id.net/view_final.html Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 40 Peralta Community College District Stand-Alone Credit Courses When a credit course is not part of an approved program, it is “not degree-applicable” or commonly referred to as a stand-alone credit course. This term also refers to credit courses that are required for a certificate of fewer than 18 semester or 27 quarter units that has not been approved by the Chancellor’s Office as a Certificate of Achievement. Effective Fall 2007, districts were delegated authority to approve stand-alone credit courses that are offered for credit, if the college where the courses will be offered is certified for local approval pursuant to Title 5, section 55100. The approved course must be reported to the Chancellor’s Office in order to assign a unique course control number. This number is required when submitting enrollment data via the Chancellor’s Office Management Information Systems (MIS). Title 5, section 55100, requires the district to annually certify that all faculty and staff who are involved in the curriculum approval process have received training from the Chancellor’s Office in the policies and procedures related to the curriculum review and approval process. Annually, training is available from the Chancellor’s Office for Chief Instructional Officers and curriculum committee chairs, who are then responsible for training all persons who are involved in the curriculum approval process. Colleges are required to complete the training annually to be certified. Documentation of training completion at each college is required by September 30th of each year to the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division. Training materials are available on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website (www.cccco.edu/aad). If a college is not certified to locally approve stand-alone credit courses, then approval from the Chancellor’s Office is required. The college may not approve a stand-alone credit course that was previously denied approval by the Chancellor’s Office, unless the course is modified to adequately address the reasons for denial. When a college offers a group of stand-alone credit courses in the same Taxonomy of Programs (TOP) code that total 18 semester units or 27 quarter units and that are linked to one another as prerequisites or corequisites, the courses are no longer considered stand-alone and Chancellor’s Office program approval is required. The college must submit this sequence of courses for approval as a Certificate of Achievement. This is intended to guard against creating a group of stand-alone courses that are linked into a sequence of courses. For example, the college could approve three stand-alone credit courses that are prerequisite to each other, such as ACCT 100 Introduction to Accounting, ACCT 110 Principles of Accounting, and ACCT 120 Computer Applications for Accounting. ACCT 100 is prerequisite to ACCT 110, which is prerequisite to ACCT 120. These three stand-alone credit courses are required for a 10-unit Skills Certificate in Accounting. At this point, the college is in compliance and can offer these courses and award the certificate without Chancellor’s Office approval. Two years later, however, the college approves some new stand-alone courses in Tax Studies, including ACCT 200 Introduction to Tax Law (3 units), ACCT 201 Tax Preparation (3 units), and ACCT 202 Tax Planning (3 units). The course ACCT 120 is a prerequisite to ACCT 200, which is prerequisite to ACCT 201 and corequisite to ACCT 202. The 19 units of stand-credit alone courses are linked together by prerequisites and corequisites and approval is needed. The status of these courses changes from standalone credit courses to program-applicable. In order to fulfill requirements for a certificate or degree major or area of emphasis, students cannot count 18 or more semester units (or 27 or more quarter units) of courses that have been approved as standalone credit courses. This requirement may limit the number of stand-alone credit courses that students may choose to complete to fulfill requirements for an award. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 41 Peralta Community College District Selected Topics (Experimental Course) Policy One type of stand-alone credit course that colleges have locally approved, even before local approval of stand-alone courses was delegated, is the “experimental” course or the course that covers “special topics” in a specific discipline. In general, an experimental course is one for which full information on some approval criterion, such as feasibility or need, cannot be determined until the course is actually offered on a pilot basis. A special topics course is one which employs a consistent disciplinary framework, but for which the specific focus may change from term to term. An example is a Special Topics in Political Science or Current Events in Political Science course in which the content will be different in each term. If a particular topic is addressed regularly, it must be approved as a regular course. At some colleges, special topics may not be defined as narrowly as this. Some colleges may use the terminology “special topics” in lieu of “experimental.” These terms are not defined in Title 5 and may be interpreted in district policy in either way. Peralta has identified these Special Topics as Selected Topics or Experimental Courses. New courses may be designated as Selected Topics with the exception of courses requiring outside agency licensing (RN, LVN, Radiologic Technology, Aviation Operations and Maintenance, Dental Assisting, Cosmetology, Child Development, Nursing Assistant). The course numbering system for Selected Topics is as follows. 48 UA – ZZ associate degree; transferable Berkeley City College 48 AA – FZ associate degree; transferable College of Alameda 48 GA – MZ associate degree; transferable Laney College 48 NA – TZ associate degree; transferable Merritt College 248 UA – ZZ associate degree; non-transferable Berkeley City College 248 AA – FZ associate degree; non-transferable College of Alameda 248 GA – MZ associate degree; non-transferable Laney College 248 NA – TZ associate degree; non-transferable Merritt College 348 UA – ZZ non-associate degree Berkeley City College 348 AA – FZ non-associate degree College of Alameda 348 GA – MZ non-associate degree Laney College 348 NA – TZ non-associate degree Merritt College 448 UA – ZZ Apprenticeship and Cooperative Education Berkeley City College 448 AA – FZ Apprenticeship and Cooperative Education College of Alameda 448 GA – MZ Apprenticeship and Cooperative Education Laney College 448 NA – TZ Apprenticeship and Cooperative Education Merritt College 548 UA – ZZ Non-credit Courses Berkeley City College 548 AA – FZ Non-credit Courses College of Alameda 548 GA – MZ Non-credit Courses Laney College 548 NA – TZ Non-credit Courses Merritt College 648 UA – ZZ Non-credit Courses Berkeley City College 648 AA – FZ Non-credit Courses College of Alameda 648 GA – MZ Non-credit Courses Laney College 648 NA – TZ Non-credit Courses Merritt College Experimental/selected topic courses will be processed through the regular new course work flow at the college and submitted to CIPD as an informational item. 42 Peralta Community College District Liberal Arts Selected Topics courses numbered 48 AA – ZZ, 248 AA – ZZ, and 348 AA – ZZ may be offered for ½ - 5 semester units. Career Technical Education (CTE) Selected Topics courses numbered 48 AA – ZZ, 248 AA – ZZ and 348 AA – ZZ may be offered for ½ - 9 semester units. The number of Selected Topics courses offered at any one time in each liberal arts department is six; the number of Selected Topics courses offered at any one time in each CTE department is eight. Each Selected Topics course can be offered for a maximum of two times. After the second time the course is offered, the department should decide if it wants the course to be a permanent offering, also known as institutionalizing the course. If so, the department resubmits the course through the work flow as a new course, assigning it a permanent number. If not, the course must be retired. Experimental/selected topic courses, while offered and included in the colleges’ schedules of classes, are not considered to be regular catalog entries. At such time as these courses receive permanent status they can be added to the college catalog. New courses may be proposed as experimental/selected topics or as a permanent course. Contact your curriculum chair for an appropriate number. The timing to approve a selected topics course is the same as for all other courses. They are not on an expedited approval schedule. Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. See Part II, Processing New and Revised Courses and Programs for more details. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 43 Peralta Community College District Community Service (Fee-Based) Courses Per the provision of Education Code Section 78300, the colleges of the Peralta Community College District may offer Community Service courses (fee based courses). Community service courses shall be open for admission of adults and of minors who can benefit from the courses. Community Service classes and activities are those instructional and enrichment offerings, not supported by state apportionment, designed for the physical, mental, moral, economic, or civic development of persons in attendance. These activities which exist in various formats extend the regular and traditional educational services of the District for broader community and individual benefits. Community Service courses are not to be confused with any “service learning” or “civic engagement” activities that may be incorporated into regular class offerings supported by state apportionment. No General Fund monies may be expended to establish or maintain community service courses. Students involved in community service courses shall be charged a fee not to exceed the cost of maintaining the courses. Community Service (Fee Based) applies to courses outside the credit and non-credit programs of the District and therefore do not require state approval. These courses are offered for zero units. Within the PCCD these Liberal Arts and Occupational Education courses are numbered 848 AA – ZZ and 948 AA – ZZ. As of February 6, 2012, the following approval process for fee based courses was approved by CIPD. The colleges will submit fee based courses through their College Curriculum Committees in CurricUNET. Approved courses will be forwarded to the district for inclusion in the monthly curriculum report submitted to the board for approval, using this format. CIPD approval is not required. Fee Based Courses Monthly Curriculum Report Subject Catalog Number, Course Title Total number of hours Course description. Example: Fee Based Courses Monthly Curriculum Report BIOL 801, Biology of Growing Food 12 Hours Basics of growing edible plants for household production: Design and layout, composting, soil preparation, planting, maintenance, and harvesting. Intended for students with no or limited previous gardening experience. Fee Based Courses are not input into PeopleSoft. PeopleSoft is not used to schedule or enroll fee based students. Each college will determine its own practice for class scheduling and enrolling fee based students. Each college must develop information for the schedule of classes to inform students of the fee based offerings. For additional information, refer to the California Community Colleges Guidelines for Community Services Offering, available under Resources, on the Chancellor’s Website at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. It is also available at the Peralta District Curriculum Website at http://web.peralta.edu/curriculum/. Reference: 44 Peralta Community College District Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 45 Peralta Community College District Contract Education The District/Colleges may contract for instructional classes to be offered at the request of public or private agencies or groups. These courses shall be provided to such organizations on a contract basis as the need arises. Instructional courses shall be consistent with the goals of the District/Colleges, and responsive to the educational requirements of the respective public or private agencies or groups requesting them. These programs are normally closed to the general public and are therefore not eligible for apportionment in accordance with the Education Code. Courses offered through contract education must be approved by the College Curriculum Committee. They may be credit courses, non-credit courses, or community service (fee-based) courses. If the course is created specifically for contract education purposes and it is a non-credit course, it should be numbered using the 700 series. References: Board Policy 4400 Community Service Programs Education Code Section 78300 Administrative Procedure 4104 Contract Education Title 5 Section 55170 46 Peralta Community College District Non-Credit Courses Noncredit instruction is one of several educational options authorized by the California Education Code to be offered within the California Community Colleges. Students are offered access to a variety of courses at no cost to assist them in reaching their personal, academic, and professional goals. Currently, 10 categories of noncredit courses are eligible for state funding and are listed below. Noncredit courses often serve as a first point of entry for those who are underserved, as well as a transition point to prepare students for credit instruction. Noncredit instruction is especially important for students who are the first in their family to attend college, for those who are underprepared for college-level coursework, and for those who are not native English speakers, among others. The California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office website (www.cccco.edu) provides links to resources that can assist with the development of noncredit courses and programs as required by the California Education Code and applicable portions of the California Code of Regulations (referred to as Title 5 in this Handbook). This section draws information from several publications and sources, which can be found in the noncredit section of the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website (www.cccco.edu/aad). Chancellor’s Office approval is required for all noncredit courses that receive state funds. A document that can be useful to curriculum committees in carrying out their responsibilities for course development and approval is the Academic Senate Paper, “The Course Outline of Record: A Curriculum Reference Guide.” It can be downloaded from the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges (ASCCC) website at www.asccc.org. Course Outlines of Record (CORs) for noncredit courses are completed in the same format as those for credit courses, with a few exceptions. No units are listed. Advisories are optional. Methods of evaluation are indicated, but grades are optional. Most noncredit courses are identified as Pass/No Pass. Out of class assignments are optional. Courses should be numbered using the 500 or 600 series. Taken together, the content of the course, methods of instruction, assignments, and methods of evaluation must be described in the COR in a manner that is integrated and leads to the achievement of the course objectives. The 10 noncredit categories (CB22) classify a noncredit course in accordance with its primary objective. The classifications of noncredit courses are eligible for state apportionment in accordance with Education Code sections 84757(a) and 84760.5, and Title 5, section 58160. The table below aligns CB22 with applicable TOP codes for each Noncredit Eligibility Category, as described in the Taxonomy of Programs Manual, 6th Edition available under Resources on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. Noncredit Category – These 10 categories of noncredit courses are eligible for state apportionment as noted above Noncredit: A = English as a Second Language B = Immigrant Education C = Elementary and Secondary Basic Skills D = Health and Safety Education E = Education Programs for Persons with Substantial Disabilities F = Parenting Education G = Family and Consumer Sciences H = Education Programs for Older Adults 47 Peralta Community College District I = Short-term Vocational Programs with High Employment Potential J = Workforce Preparation The Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used within Peralta to distinguish various course levels. See the Course Numbering System section of this manual for more information. For more details refer to California Community Colleges, Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH) available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. Section 4: Noncredit Curriculum in that handbook describes the standards and criteria for noncredit program and course development, approval procedures for noncredit programs and courses, and instructions for completing applications for approval of noncredit programs and courses by the Chancellor’s Office. 48 Peralta Community College District Distance Education Definition Distance education is covered by Title 5, Chapter 6, Subchapter 3, starting with section 55200. Both credit and noncredit courses may be offered through distance education, which is defined as “instruction in which the instructor and student are separated by distance and interact through the assistance of communication technology.” Distance education regulations refer to all courses that are developed with the intent that individual classes or sections, or any portion of the course, may be scheduled as distance education instead of traditional, face-to-face instruction. This includes courses referred to as “hybrid” which combine traditional, face-to-face instruction and distance education with either synchronous or asynchronous instructor-student interaction through communication technology. Title 5 regulations specify that course quality standards apply to distance education in the same manner as for traditionally delivered courses and that each course designed for delivery via distance education must be separately approved by the College Curriculum Committee. In addition, the regulations require regular contact between instructors and students. Course Approval Each proposed or existing course offered by distance education shall be reviewed and approved separately by the local College Curriculum Committee. Separate approval is mandatory if any portion of the instruction in a course or a course section is designed to be provided through distance education. The review and approval of new and existing distance education courses shall follow the curriculum approval procedures outlined in Administrative Procedure 4020 Program and Curriculum Development. Distance education courses shall be approved under the same conditions and criteria as all other courses, using the District’s curriculum management system, CurricUNET. Distance education proposals are sent to the Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) for district-level review. Certification When approving distance education courses, the department proposing the course and the College Curriculum Committee will certify the following: Course Quality Standards: The same standards of course quality are applied to the distance education courses as are applied to traditional classroom courses. Course Quality Determinations: Determinations and judgments about the quality of the distance education course were made with the full involvement of the College Curriculum Committee approval procedures. Instructor Contact: Each section of the course that is delivered through distance education will include regular effective contact between instructor and students. Duration of Approval: All distance education courses approved under this procedure will continue to be in effect unless there are substantive changes of the course outline. Federal Financial Aid Eligibility: Consistent with federal regulations pertaining to federal financial aid eligibility, the District/Colleges authenticate or verify that the student who registers in a distance education course is the same student who participates in and completes the course and receives the academic credit. 49 Peralta Community College District The District/College will provide to each student at the time of registration, a statement of the process in place to protect student privacy and estimated additional charges associated with verification of student identity, if any. The colleges shall utilize one or more of these methods to authenticate or verify the student’s identity: Secure credentialing/login and password Proctored examinations New or other technologies and practices that are effective in verifying student identification Scheduling Instructors for Distance Education classes. The instructor must use or commit to using a recognized CMS/LMS (course or learning management system) to deliver course content, which adheres to the following standards: Welcome/Orientation Organizational components Instructional modalities Assessment practices and expectations Instructor must have the following three elements in place prior to being assigned an online course: Has received training in the use of at least one course management system (such as WebCT, Blackboard, ETUDES-NG, MOODLE) Has successfully completed a course in how to teach online, such as “Teaching an Online Course” (offered by PCCD/Merritt College, @One, another community college, another appropriate external entity or UC extensions course) Uses the Peralta email system (with a peralta.edu email address) and has a Peralta webpage on the college website that hosts the online course. This webpage will provide a link to the CMS/LMS (course/learning management system) website. Recommended preparation includes that the instructor: Has enrolled in an online course of some kind Has worked with a mentor who is an experienced online instructor Recommended ongoing instructor preparation should include maintaining currency in online education such as: Technologies Pedagogy Collaborating with other online instructors Ongoing assessment of student learning outcomes Complete a certificate in online education (at least 3 and as many as 8 courses in online education for certification as an online instructor) References: Administrative Procedure 4105 Distance Education Title 5 Sections 55200 et seq 42 U.S. Code Sections 12100 et.seq 29 U.S. Code Section 794d ACCJC Guide to Evaluating Distance Education and Correspondence Education 34 Code of Federal Regulations Part 602.17 U.S. Department of Education regulations on the Integrity of Federal Student Financial Aid Programs under Title IV of the Higher Education Act of 1965, as amended Distance Education Regulations and Guidelines (2008 Omnibus Version) available on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website 50 Peralta Community College District (http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/InstructionalProgramsandServicesUnit/Dista nceEducation.aspx) Distance Education Regulations and Guidelines for Students with Disabilities (January 2011) available on the Chancellor’s Office Academic Affairs Division website (http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/InstructionalProgramsandServicesUnit/Dista nceEducation.aspx) 51 Peralta Community College District Independent Study Independent study is a mode of instruction in which students are not required to be under the immediate supervision and control of a qualified academic employee. This must not be confused with the requirement in Title 5, section 55002, that all courses offered for credit must require students to study independently outside of class. Instead, this discussion of independent study refers to a course that is not regularly scheduled, but for which it is expected that the student will interact directly with the instructor on an individual basis. All colleges may offer locally approved independent study courses. Title 5, section 58009, was revised in 2006 in order to address disparity in apportionment for laboratory independent study courses and traditional courses. Apportionment for independent study laboratory courses is now calculated based on the student contact hours rather than on units. Independent Study permits a student to explore an area of study or project of his/her choice not covered by regular catalog offerings. Such study may include directed field experience, research, or development of skills and competence. Conditions for Independent Study The student must have completed 12 semester units at the college. The student must be concurrently enrolled in at least one other class at the college. The student can enroll in one (1) Independent Study course in any given semester which cannot exceed five (5) units. The student can only earn a maximum of five (5) units in any one discipline, regardless of the number of repeats. Approval Process for Independent Study The student must demonstrate that his or her background is adequate for the proposed course of study and must have prior successful academic experience in the particular discipline of study. The student must submit the required Independent Study form, with a written request, including an outline of the project to the instructor (contract full-time instructor) and obtain written approval prior to the end of the second week of the semester. The student must have approval of the department chair. The student must have the approval of the Office of Instruction. Independent Study Course Characteristics Independent Study courses are conducted by full-time instructional faculty and are graded in a manner consistent to other course offerings. Students must have access to the instructor during the instructor’s office hours or at other times with the instructor’s consent. These courses may count as electives and generally do not fulfill specific Associate degree requirements. Transfer credit for Independent Study (49’s) is contingent upon an evaluation of the course by the receiving University of California. Independent Study (49’s) transfers as elective credit to the CSU system. Course number 49 is designated for Independent Study. Only subject matter not offered within the District shall be considered appropriate. Courses may be offered for ½ - 5 semester units. References: Administrative Procedure 4101 Independent Study Title 5 Sections 55230 et seq. 52 Peralta Community College District Course Repetition and Repeatability Policy The Peralta Community College District Administrative Procedure 4225 provides detail regarding course repetition and course repeatability and should be referenced. This procedure follows state regulations in Title 5. Following is a summary and is not intended to replace or change Administrative Procedure 4225. A. Students may petition to repeat a course for one of the following reasons: 1. To alleviate substandard academic work (“D,” “F,” “FW,” and/or “NP”) or because a “W” was earned. (Two repeats permitted; thus can only take the course three times). 2. To meet a “legally mandated training requirement as a condition of continued paid or volunteer employment” (documentation required). 3. To address a “significant change in industry or licensure standards which is necessary for a student’s employment or licensure” (documentation required). 4. Because of “extenuating circumstances” including verified cases of accidents, illness, or other circumstances beyond the student’s control. 5. Because “another institution of higher education to which the student seeks to transfer has established a recency requirement which the student will not be able to satisfy without repeating the course in question” (documentation required). 6. Because of a “significant lapse of time” (no less than 36 months) and “there is a properly established recency prerequisite for the course or program pursuant to Title 5 section 55003.” B. Students can repeat courses for one of the following reasons and a petition is not required. 1. A student is permitted to enroll in a variable unit open-entry/open-exit course as many times as necessary to complete the entire curriculum of the course once. 2. A student may repeat Cooperative Work Experience for a total of 16 semester units, with a maximum of 6 semester credit hours during one enrollment period in general work experience and a maximum of 8 semester credit hours during one enrollment period in occupational work experience. 3. A student may repeat a course which is designated as repeatable because repetition of that course is required by CSU and/or UC for completion of a bachelor’s degree. 4. A student may repeat a course for purposes of Intercollegiate Athletics (350 contact hours per year per sport and 175 contact hours in courses that focus on conditioning and skill development) OR participation for up to four (4) semester enrollments in that course. 5. A student may repeat courses that are designed specifically for participation in non-athletic competitive events between students from different colleges and the event is sanctioned by a formal collegiate or industry governing board. 6. A student may enroll in active participatory courses in physical education, visual or performing arts that are related in content for no more than four (4) courses in each content area (even if a “W” is received). C. A student with a disability may repeat a special class for students with disabilities any number of times based on an individualized determination that such repetition is required as a disabilityrelated accommodation for that particular student for one of the reasons specified in Title 5 section 56029. References: Administrative Procedure 4225 Course Repetition and Course Repeatability Credit Course Repetition Guidelines, July 2013. It is available under Guidelines at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx 53 Peralta Community College District Cooperative Work Experience Education Purpose The purpose of Occupational Work Experience (Cooperative Education/COPED) is to provide for on the job experiences for students whereby they will gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between classroom theory and practical application, be an active participant in an actual workplace environment, and improve their employment opportunities. In keeping with the educational philosophy of the District/Colleges, which maintain that occupational education is a vital and inseparable segment of the total educational program of the Colleges, the Colleges of the Peralta Community College district are committed to the development and expansion, as appropriate, of the effective program of work experience education. Work Experience courses (COPED) are submitted for review and approval to the local College Curriculum Committee and forwarded to the Council on Instruction, Planning and Development (CIPD) for final approval. Cooperative work experience education is an exception to the usual requirement that state-reimbursed community college education be under the immediate supervision of a qualified academic employee. Resources and information about cooperative work experience education can be found on the Chancellor’s Office website (www.cccco.edu) under the Economic Development and Workforce Education Division in the CTE section. The Work-Based Learning Handbook is an online reference to topics and issues central to the effective implementation and operation of cooperative work experience education and work-based learning programs. The regulations for cooperative work experience are covered in Title 5, Chapter 6, Subchapter 3, Article 4, beginning with section 55250. A college that offers cooperative work experience must provide certain services, including supervision by a qualified instructor or coordinator, written evaluation of students' progress, consultation with employers, and other elements. Units of work experience must be earned in certain patterns described in regulations. There are two types of cooperative work experience education. General work experience education is supervised employment intended to assist students in acquiring desirable work habits, attitudes, and career awareness. The work experience does need not be related to the student's specific educational goals. Occupational work experience education is supervised employment where on-the-job learning relates to the student's specific educational or occupational goal. Work experience, in conjunction with a program of instruction, makes it possible for a student to obtain college credit for paid or volunteer experience. Title 5, section 55253, states that a maximum of 16 units can be granted for occupational work experience or a combination of general and occupational work experience education. Students may enroll in no more than four (4) units of cooperative Work Experience education per semester, on the basis of 75 hours of paid work experience per semester per each unit of credit, or 60 hours of unpaid or volunteer work experience per semester per each unit of credit. The student’s plan of work and study must have the approval of the college work experience supervisor/coordinator. When work experience education is reported in the Chancellor’s Office Management Information Systems, the Taxonomy of Programs (TOP) code 4932.00 must be used for general work experience education. Occupational work experience must be reported in the same TOP code as the program of which it is a part. For example, occupational work experience in the area of automotive technology must be reported in TOP code 0948.00. The Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used within Peralta to distinguish various course levels. See the Course Numbering System section of this manual for more information. References: 54 Peralta Community College District Administrative Procedure 4103 Work Experience Title 5 Sections 55250 et seq. Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 55 Peralta Community College District American Cultures (AC) Requirement The American Cultures Center at University of California, Berkeley, works with California Community Colleges to develop courses which meet the American Cultures Requirement on the UC Berkeley campus. The American Cultures Center focuses its attention on creating courses which provide integrative and comparative analysis of race, ethnicity and culture in the United States. As courses are developed they recommend considering: the transnational effects on the making and meaning of American cultures the ways in which digital content as both cultural practice and teaching tools are being integrated the intersection of studies of genetic ideas, practices, race and science the ways in which students and faculty engage with the interests and questions set by local communities As faculty developing courses to meet the AC requirement, the materials created by UC Berkeley faculty are fully available. Contact the AC Center to schedule a visit with a faculty member, attend any of the campus events which the AC Center sponsors, or to talk about ideas for new courses or initiatives. Additional information is available at the American Cultures Website http://americancultures.berkeley.edu. 56 Peralta Community College District Credit By Examination Credit by Examination may be obtained by one of the following external examination methods. Achievement of a score of 3, 4, or 5 on an Advanced Placement Examination administered by the College Entrance Examination Board. Achievement of a score that qualifies for credit by examination in the College Level Examination Program. Achievement of a score that qualifies for credit by examination in the International Baccalaureate Program. Details regarding each examination process are to be published in the college catalogs and are reviewed by the college Articulation Officers. Rules for Credit by Examination through a College Administered Examination Credit by examination can also be obtained through satisfactory completion of an examination administered by the college in lieu of completion of a course in the college catalog. The student must be currently registered in the college and have completed 12 units at the college for residency purposes. The student must have a minimum cumulative grade point average (GPA) of 2.0. The student must be in good standing and have no financial obligations owed to the Peralta Community College District. The course is listed in the college catalog as having a credit-by-exam option. A grade of incomplete (I) may not be assigned for Credit by Examination. The student’s grade shall be recorded on his/her academic record, even if it is substandard. The student will not have the option of rejecting a substandard grade. Credit by Examination counts as enrollment for repeatability purposes. The student may make only one attempt of Credit by Examination per course. The student may not earn more than 12 units of Credit by Examination for an associate degree and 6 units toward a certificate of achievement. The student must pay the fees equal to the enrollment fee cost of the course (BOGFW does not cover this fee). Although the University of California and the California State University accept, with certain limitations, appropriate credits obtained by examination, there is no guarantee that other institutions will do so. The grade obtained through Credit by Examination will be recorded on the transcript (academic record) with a descriptor CE (Credit by Examination). Basic Skills courses, laboratory courses, physical education activity courses, and basic courses in the student’s native language are excluded from Credit by Examination consideration. Credit by Examination is not available where: the student already has completed a more advanced course in the discipline. the student previously has received an evaluative symbol grade (A, B, C, D, F, W, FW, CR, P, NC or NP) for a course taken at one of the Peralta colleges. the student has failed a Credit by Examination test (cannot petition to retake the course by Credit by Examination) Grades issued upon completion of Credit by Examination will be included in the calculation of the student’s grade point average for determining scholarship awards. 57 Peralta Community College District Credit by Examination only shall be available in Fall and Spring semesters. The student must be enrolled at the college or enrolled in an approved CTE/high school articulated program during the semester in which the Credit by Examination is attempted. The petition for Credit by Examination must be completed and submitted to the Office of Instruction by the beginning of the fifth (5th) week of the semester and the examination must be completed before the end of the semester. Credits acquired by examination are not applicable to meeting of such unit load requirements as Selective Service deferment, Veteran's, Social Security benefits, athletics, or residency for financial aid. Credits acquired by examination shall not be counted in determining the 12 semester hours of credit in residence required for an Associate degree. Credit by Examination Procedure Student obtains a Petition for Credit by Examination from the Office of Instruction or from a counselor. Student completes the Student Information section of the petition and submits it to a counselor for Verification of Eligibility as noted below. Currently enrolled at the college in the semester in which the exam is to be taken In good academic standing Has less than 15 units earned through Credit by Examination Not currently enrolled in the course to be challenged through Credit by Examination Grade Basis selected (as appropriate to the course) Once the Verification of Eligibility has been completed, the student picks up the petition from the counselor. Student meets with the department chair of the discipline to receive approval for the petition. If approved, a full-time instructor is assigned to administer the examination and the student makes arrangements to take the examination. Student takes approved petition to the Cashier’s Office (Bursar’s Office) for payment of fees and receipt. Fees are non-refundable regardless of the outcome of the exam. BOGFW cannot be used for payment of Credit by Examination fees. Fees must be paid after department approval is granted and before the examination is administered. Student submits approved petition to the instructor administering the examination. The instructor will record the date of the exam and the grade received, attach the examination materials, and forward the completed petition to the department chair. The department chair will review and sign the petition, and forward it to the Office of Instruction. Completed examination materials must remain on file in the Office of Instruction for three years. The Office of Instruction will assign a class number for the examination and forward the petition to the Office of Admissions and Records to be processed. The Office of Admissions and Records will post the course and assigned grade to the student’s academic record (transcript). The petition will be retained in the Office of Admissions and Records. Reference: Administrative Procedure 4235 Credit by Examination Title 5 Section 55050 58 Peralta Community College District Advanced Placement (AP) Equivalency Best Practices Checklist for Determining Advanced Placement (AP) Equivalency 1. Identify college courses for AP course equivalency consideration Typically the articulation officer and/or counselors identify courses for AP course equivalency consideration and request the discipline faculty to make a determination. 2. Determine AP course equivalency by discipline faculty (in consultation with the articulation officer) Determination based on: College Board AP course and examination information http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/Controller.jpf Corresponding AP course equivalency information from 4-year feeder institutions Articulation agreements equated with the 4-year AP course equivalency 3. Submit AP course equivalency to the Curriculum committee When the discipline faculty have determined the AP cut score for course equivalency it is submitted to the curriculum committee for review. 4. Submit AP course equivalency to the Board of Trustees a. After the curriculum committee reviews the AP course equivalency it is submitted to the Board of Trustees for final approval and adoption as district policy. 5. AP course equivalency credit noted on student transcripts Reference: Title 5 § 55052. Advanced Placement Examinations. The governing board of a community college district may adopt policies to grant credit for satisfactory completion of advanced placement examinations typically recognized by colleges and universities as measuring competencies comparable to those achieved in baccalaureate level courses. The faculty in the appropriate discipline must approve advanced placement examinations, scores deemed to constitute satisfactory performance, courses offered by the college for which credit will be granted, and requirements that may be met by such examinations in accordance with policies and procedures approved by the curriculum committee established pursuant to section 55002. The student's academic record shall be clearly annotated to reflect that credit was earned through an advanced placement examination. 59 Peralta Community College District Grading Policy: Pass/No Pass or Grade Courses may be offered as follows. Grade only Grade or Pass/No Pass Pass/No Pass only Courses with Pass/No Pass options may be established in either or both of the following categories: Courses in which all students are evaluated on a pass/no pass basis. Courses in which each student may elect on registration, or prior to the fourth week of instruction (30% of instruction for summer session or short-term classes), to take the course on a pass/no pass basis. A student electing to be evaluated on the pass/no pass basis will receive both course credit and unit credit upon satisfactory completion of the course. In computing a student's grade-point average, grades of pass/no pass are omitted. A pass grade is granted for performance that is equivalent to the letter grade of "C" or better. A student who fails to perform satisfactorily will be assigned a "no pass" grade. The student is held responsible for all assignments and examinations required in the course. The standards of evaluation are identical for all students in the course. Reference: Administrative Procedure 4232 Pass/No Pass Title 5 Section 55022 60 Peralta Community College District The Taxonomy of Programs The Taxonomy of Programs (TOP) is a system of numerical codes used at the system level to collect and report system-wide information on programs and courses that have similar outcomes. Local program titles, however, differ substantially from college to college. For example, one college may offer a program titled Mechanized Agriculture, another college may offer a program titled Agriculture Engineering Technology, and a third college may offer a program with the title Agriculture Equipment Operations and Maintenance, all under TOP code 0116.00. Although the TOP was originally designed to aggregate information about programs, the use of TOP codes has been extended to courses as well. Each program and course must be assigned a TOP code that is consistent with its content. TOP codes and titles serve a variety of purposes at the system level and are used in the following ways. • • • • The CCC Curriculum Inventory, to identify the particular types of curriculum throughout the state The MIS database, to collect and report information on student awards (degrees and certificates) granted for particular types of programs, enrollment, and full-time equivalent students (FTES) in courses within particular curriculum categories Career Technical Education (CTE) accountability reports on program completions and course success in particular types of occupational programs The reporting of noncredit programs and courses for each noncredit eligibility category and for determining eligibility for enhanced funding The Taxonomy of Programs, 6th Edition includes a list of TOP codes currently in use and is available under Resources on the Chancellor's Office Academic Affairs Division website http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. 61 Peralta Community College District Open-Entry/Open-Exit Title 5, section 58164, defines open-entry/open-exit as credit or noncredit courses in which students enroll at different times and complete at various times or at varying paces within a defined time period, such as a semester or quarter. When an open-entry/open-exit course provides supplemental learning assistance (pursuant to Title 5, section 58172) in support of another course or courses, the COR for the supplemental open-entry/openexit course must identify the course or courses it supports, as well as the specific learning objectives the student is to pursue. Determination of student contact hours must be based on a maximum number of hours that the curriculum committee considers reasonably necessary to achieve the learning objectives of the primary course or courses being supplemented. Thus, the supplemental course outline must be prepared in light of the primary course objectives, but the hours for the supplemental outline will then be based on the objectives and related assignments specified in the supplemental course outline. Open-entry/open-exit courses must be designed in such a way that most students who are appropriately placed in the course would be able to master the objectives and successfully complete the course in about 48–54 hours per unit of credit. Some students may need more hours to complete the course and may need greater assistance from faculty and staff. Some students may need fewer hours to do the same and need little or no assistance. Regardless of the number of hours the student needs to complete the course, the number of units earned will be the same and the number of hours needed by most students to complete the course as approved by the curriculum committee will be recorded in the outline of record. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 62 Peralta Community College District Instructional Material Fees The Student Fee Handbook is published by the Legal Affairs Division in the Chancellor’s Office and is available on the Chancellor’s Office website (www.cccco.edu) under the Legal Affairs Division. Title 5, section 51012, allows the district governing board to establish only mandatory student fees that are expressly authorized by law. In all cases, the district policy must provide financial assistance or waiver of these fees for qualifying students. Instructional Materials Fees The President of each college is authorized to require students to provide instructional and other materials required for a credit or non-credit course, as necessary. Such materials shall be of continuing value to a student outside of the classroom setting and shall not be solely or exclusively available from the District. Required instructional materials shall not include materials used or designed primarily for administrative purposes, class management, course management, or supervision. Where instructional materials are available to a student temporarily through a license or access fee, the student shall be provided options at the time of purchase to maintain full access to the instructional materials for varying periods of time ranging from the length of the class up to at least two years. The terms of the license or access fee shall be provided to the student in a clear and understandable manner prior to purchase. Prior to the approval of any new instructional materials fee, the President shall ensure that the fee meets the guidelines as published by the State Chancellor’s Office in “Student Fee Handbook,” Section 5, “Instructional Materials.” Definitions. "Instructional and other materials" means any tangible personal property which is owned or primarily controlled by an individual student and are of continuing value outside of the classroom. “Tangible personal property” includes electronic data that the student may access during the class and store for personal use after the class in a manner comparable to the use available during the class. "Required instructional and other materials" means any instructional and other materials which a student must procure or possess as a condition of registration, enrollment or entry into a class; or any such material which is necessary to achieve those required objectives of a course which are to be accomplished under the supervision of an instructor during class hours. "Solely or exclusively available from the District" means that the material is not available except through the District, or that the District requires that the material be purchased or procured from it. A material shall not be considered to be solely or exclusively available from the District if it is provided to the student at the District's actual cost; and 1) The material is otherwise generally available, but is provided solely or exclusively by the District for health and safety reasons; or 2) The material is provided in lieu of other generally available but more expensive material which would otherwise be required. "Continuing value outside of the classroom setting" are materials which can be taken from the classroom setting and which are not wholly consumed, used up, or rendered valueless as they are applied in achieving the required objectives of a course to be accomplished under the supervision of an instructor during class hours. References: Administrative Procedure 5031 Instructional Materials Fees Education Code Section 76365; Title 5 Sections 59400 et seq. 63 Peralta Community College District Scheduling Courses in Shortened Time Frames In 2006, the District Academic Senate (DAS) and the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges (ASCCC) passed the following resolution. This resolution outlined a process for determining which courses could be offered in a three week time frame. This process is intended to address articulation issues related to short-term courses as well as to ensure all the elements necessary to meet the Carnegie unit could be met (lecture hours, lab hours and out of classroom assignment hours). Students are inclined to sign up for very short term classes because the classes move quickly and are over in no time. However there is concern with academic rigor, academic integrity, and whether the same student learning outcomes can be achieved in a 12 - 15 day course compared to when the course is offered in six weeks or 18 weeks. That resolution is as follows: "Whereas, With the move of many colleges to compressed calendars and study abroad programs and due to enrollment pressures, a number of colleges are scheduling three-, four-, and even five-unit courses in shortened time frames of fewer than six weeks; and Whereas, There are pedagogical considerations that need to be reviewed by both the faculty within the disciplines of courses proposed under such time frames as well as the curriculum committees of colleges using such compressed calendars; Resolved, That the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges recommends that when a course of three or more semester or equivalent quarter units is to be offered in a time frame of fewer than six weeks, the local curriculum committee, as part of the curriculum approval process, engage the discipline faculty in a separate review of the course for the following: academic integrity and rigor, the method for meeting Carnegie units, the ability for students to complete and for faculty to evaluate assignments, including those done outside of class, and the appropriateness of the method of delivery, to determine whether the course should be offered in a specific shortened time frame.” 64 Peralta Community College District Program and Course Review Title 5, section 55130, authorizes the Chancellor’s Office to review established programs periodically and to terminate approval of a program. The Chancellor’s Office collects information from all colleges on the processes for and/or the results of locally conducted program reviews as required by Title 5, section 51022. In addition, Education Code section 78016 specifically requires that colleges review the effectiveness of CTE programs every two years. The minimum requirements for this periodic review must demonstrate that the program: • continues to meet a documented labor market demand • does not represent unnecessary duplication of other manpower training programs in the college’s service area • is of demonstrated effectiveness as measured by the employment and completion success of its students Review of instructional programs on a regular basis and according to a regular procedure is also mandated by the standards of the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges of the Western Association of Schools and Colleges. Several accrediting standards speak to institutional planning, research, and design of instructional programs; however, the most direct requirement for program review is Standard II A.2 (e). IIA.2 (e) The institution evaluates all courses and programs through an on-going systematic review of their relevance, appropriateness, achievement of learning outcomes, currency, and future needs and plans. The most direct implication of the accreditation standards is the need to review each Course Outline of Record (COR) on a regular basis, at least within the 6-year accreditation cycle. Good practice for occupational programs is to review the program to the standards required by Education Code every two years and then do a course by course review for curriculum standards every six years. At present there is no standard model(s) officially recommended for conducting program review in the California community college system. There is an imperative, however, that every college must conduct an effective review of its instructional programs on a regular basis. Working with the District Academic Senate, the Peralta District incorporated the review of curriculum into the Instructional Program Review process. Each college establishes a calendar of all programs to ensure that all instructional programs and student services are reviewed within the six-year accreditation cycle. Each college in the Peralta system has developed its own procedures for Program Review. For more information, refer to the college Curriculum Committee website, the college Curriculum Chair, and/or the Vice President of Instruction. Reference: Program and Course Approval Handbook (PCAH). It is available under Resources at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.asp x. 65 Peralta Community College District Part II Processing New and Revised Courses and Programs 66 Peralta Community College District Initiating New Course or Revision Full and part-time faculty members may develop and/or revise courses. This process begins at the department level with discussion on the reasons for the course proposal. If the course is interdisciplinary, all involved departments participate in each step of the procedure. Reasons for proposing a new or revised course may include, but are not limited to: • maintaining discipline currency • responding to business or industry needs • developing curriculum pattern for major • enhancing student’s knowledge of the discipline New courses may be proposed as experimental/selected topics or as a permanent course. Contact your curriculum chair for an appropriate number. Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. Substantive Change A substantive change to an existing course is processed in CurricUNET as Course Changes in Catalog. Therefore, any change to any information shown in the college catalog is considered a substantive change. Substantive changes are submitted to CIPD and the Board of Trustees after being processed by the College Curriculum Committee. The following items involve substantive changes. Discipline name and/or abbreviation Course number Course title Course description Pre/corequisite/advisories Hours Units Grading basis Course repeatability TOP Code Credit Status Though not technically in the college catalog, the following items are processed as substantive changes. Credit by Exam Basic Skills Status SAM Code Prior to College Level (CB21) Funding Agency Category Distance Education Changes need to go to CIPD for information only Substantive Changes to Courses under Uniform Course Numbering (UCN) For any substantive change to an existing course which is part of the District’s UCN system, consensus must be obtained from all colleges offering the course using the consultation process outlined in section “Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues” in this manual. All colleges should coordinate in order to bring the changes to CIPD for action at the same meeting. Non-Substantive Change 67 Peralta Community College District A non-substantive change to an existing course is processed in CurricUNET as Course Changes only in Non-Catalog Information. Any changes to items not listed above as substantive changes are considered non-substantive changes. Non-substantive changes are final after being processed by the College Curriculum Committee and the date of implementation is the College Curriculum Committee approval date. When a Course Change Requires a New Course Number In most cases, changes to a course do not require a new course number. However, when the units and hours increase/decrease or a lecture or lab component is added or deleted, a new course number is generally required. For example, if SCIEN 85 is 4 units, 3 hours lecture and 3 hours lab and the department wants to change it to two courses, one 3 hours lecture and a separate lab of 3 hours, a new number is required, since without the lab hours, SCIEN 85 is no longer the same course. 68 Peralta Community College District Course Outline of Record (COR) It is the responsibility of the course originator to complete the COR on CurricUNET. If the course originator does not have access to CurricUNET or needs help getting started, the faculty member should contact the college curriculum chair. Course originators should review the information in this section under “Completing Course Outline of Record” for detailed information about the contents of each item required in developing or revising a course. The Curriculum Committee uses the following criteria to evaluate course proposals. Appropriateness to mission of college, department, and discipline Need as justified by department Curriculum standards Appropriateness of course content Adequate resources Compliance CTE departments’ advisory board support Departmental faculty support. Consultation with other disciplines or colleges Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. The COR documents the course requirements for faculty, administration, students, and the public. All faculty teaching a particular course should access the current COR and ensure the course is taught within the guidelines. All active CORs are available on CurricUNET. No log in is necessary. Go to http://www.curricunet.com/pccd/ and Search Course. An additional resource regarding CORs is The Course Outline of Record: A Curriculum Reference Guide adopted Spring 2008 by the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges. It is available at www.asccc.org. 69 Peralta Community College District Completing the Course Outline of Record (COR) Following are descriptions of the elements in the COR that must be completed as part of the course development process. All items in the CurricUNET Course Checklist must be completed, saved, and finished before the system will allow you to submit it to the work flow. To use CurricUNET for the first time, contact the College Curriculum Committee chair. This section of the manual only covers the content elements of the COR; it does not explain how to get to the data entry screens in CurricUNET. Faculty who teach at more than one college should have a different CurricUNET login and password for each college. More details about using CurricUNET can be found in the Help Section on the CurricUNET Home Page and in the Peralta District Guide to CurricUNET (under development). In addition, each college has a Curriculum Web Page; Laney’s has been well developed to provide good support for the system. Finally, the College Curriculum Committee chair is an excellent resource. Course Checklist Cover □ College: The correct college should be listed. □ Discipline: The drop down menu allows selection of the appropriate discipline for the course. □ Number: If this is a new course, contact the College Curriculum Committee chair for an appropriate number. If that person is not immediately available, use 9999 until they have been contacted. For explanation of the course numbering system, see section “Course Numbering System” in this manual If the course is being borrowed from another college, use the same number. More information is available in “Program Curriculum and Course Development/ Work Flow/Consultation” and “Uniform Course Numbering” in this manual. In most cases, changes to a course do not require a new course number. However, when the units and hours increase/decrease or a lecture or lab component is added or deleted, a new course number is generally required. For example, if SCIEN 85 is 4 units, 3 hours lecture and 3 hours lab and the department wants to change it to two courses, one 3 hours lecture and a separate lab of 3 hours, a new number is required, since without the lab hours, SCIEN 85 is no longer the same course. □ □ □ Full Course Title: The title should be clear and concise. Review course titles in the college catalogs for ideas. Cross Listing Course: If a course is going to be taught in more than one discipline this requires that it be cross listed. A second outline must be created in the other discipline. All elements of the outline (except the Discipline and perhaps the Number) must be identical for both courses. When either of the courses is offered, the instructor of record must have the qualifications to teach in that discipline. For example, if a POSCI and a HIST course are cross listed, but offered this semester as POSCI, the instructor must be qualified in POSCI. If both POSCI and HIST are offered concurrently as one course with one instructor, the instructor must be qualified in BOTH POSCI and HIST. Students should be notified they are not able to take both cross listed courses. At the end of the Catalog Course Description, the following notation should be included for each course. “Not open for credit to students who have completed or are currently enrolled in (the cross listed course number, e.g. BUS 32). Catalog Course Description: 70 Peralta Community College District □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ The course description is NOT an outline of the course. It is an overview or summary of key ideas and concepts. It is generally less than 50 words. There is a standard format used by all Peralta Colleges; review the college catalog to see examples of existing descriptions. General Guidelines: Start with an adjective or noun; do not use “a”, “an” or “the course”. After the first general phrase, put a colon and start the next word with a capital letter. Use mostly descriptive terms, no verbs, and very few articles. There should be congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives and the student learning outcomes. Justification: If this is a new course, explain the purpose the course will serve in the department, discipline, and/or college curriculum. If this course is being modified, update this as necessary. In most cases, the original justification will not be deleted. Proposed Start: For new courses, enter the semester and year the course will first be offered. For course modifications, enter the semester and year the changes will become effective. For course deactivations, enter the semester and year the course will no longer be offered and will be removed from the catalog. Since all new and modified courses take time to go through the work flow, these dates will never be the current semester. In most cases, plan two to three semesters ahead. Open-Entry/Open-Exit: Most courses are not open-entry/open-exit. See the section “Open-Entry/Open-Exit” in this manual for more information. Required for Degree/Certificate: If a course is required for a degree or certificate, click yes and the next box will open. If it is not required for a degree or certificate, it is a stand-alone course. See the section “Stand-Alone Courses” in this manual for more information. Required for Degree/Certificate (specify): If Yes was clicked in the previous item, this box will open and you should enter the names of all degrees and/or certificates for which this course is required. Modular: Most courses are not modular. For modular courses, at the end of the Catalog Course Description, the following notation should be included for each course. “Not open for credit to students who have completed or are currently enrolled in Subject Crse #. “ See the section “Modularization” in this manual for more information. Credit by Exam: The department may identify this course as eligible for Credit by Exam. If they choose to do so, they must prepare a representative exam and present it to the Curriculum Committee at the time the course is reviewed. See the section “Credit by Exam” in this manual for more information. Assignments at College Level: Most courses will be college level. See section “College Level Courses” in this Manual. Readings at College Level: Most courses will be college level. See section “College Level Courses” in this Manual. List of Changes For a new course, enter “New Course.” For a course modification, list all areas from the course checklist which were modified. If necessary, explain the reasons for the modifications. For example, “general update of COR” or “revision of COR for Articulation purposes.” Units/Hours When the units and hours increase/decrease or a lecture or lab component is added or deleted, a new course number is generally required. For example, if SCIEN 85 is 4 units, 3 hours lecture and 3 hours lab and the department wants to change it to two courses, one 3 hours lecture and a separate lab of 3 hours, a new number is required, since without the lab hours, SCIEN 85 is no longer the same course. 71 Peralta Community College District □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Variable Units: If yes is selected, a box will open to allow minimum and maximum units to be entered. Units: Enter the number of units. See section “Relationship of Hours to Units” in this manual. Lecture Hours: Enter the number of lecture hours. See section “Relationship of Hours to Units” in this manual. Lab/Studio/Activity Hours: Enter the number of hours. See section “Relationship of Hours to Units” in this manual. TBA Hours: In the rare instances when TBA Hours are used, consult a college dean and the section “To Be Arranged (TBA) Hours Compliance Advice” in this manual. Repeatability: Most courses are NOT repeatable. See section “Course Repetition Policy” in this manual. Previously Offered as a Selected Topic: If the purpose of this proposal is to institutionalize (make permanent) a course previously offered as a selective topic/experimental course, select yes. Additional boxes will appear. □ Enrollment Max Average Enter the maximum number of students enrolled when the course was offered as a selected topic. Also enter the average (if the course was offered more than once). □ # Times Offered Enter the number of times the course was offered as a selected topic. For more information see section “Selected Topics (Experimental Course) Policy” in this manual. Grading Policy: Courses may be established with one of three grading policies. There are specific advantages and disadvantages to students’ transcript for each. Consult the department chair, college dean, articulation officer and/or the section “Grading Policy: Pass/No Pass or Grade” in this manual for more information. Degree/Transfer □ Designation: Specify the course classification: Degree credit, Non-Degree credit (stand-alone), NonCredit, Community Services (Fee-Based). See other sections of this manual for more information: “Guidelines for Associate DegreeApplicable Credit Courses”; “Guidelines for Nondegree-Applicable Credit Courses”; “Stand-Alone Courses”; and “Community Service (Fee-Based) Courses”. □ Meets GE/Transfer requirements (specify): This section should only be completed by the Articulation Officer or under the guidance of the Articulation Officer. Lecture Content List major topics to be covered. This section must be more than listing chapter headings from a textbook. Outline the course content, including essential topics, major subdivisions, and supporting details. It should include enough information so that a faculty member from any institution will have a clear understanding of the material taught in the course and the approximate length of time devoted to each. List percent of time spent on each topic; ensure percentages total 100%. There should be congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes. Lab Content This heading will only show if there are lab hours listed in the Units/Hours section. List major topics in the appropriate sequence. This section must be more than listing chapter headings from a textbook. It should include enough information so that a faculty member from any institution will have a clear understanding of the material taught in the lab and the 72 Peralta Community College District approximate length of time devoted to each. List percent of time spent on each topic; ensure percentages total 100%. There should be congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes. Student Performance Objectives List student performance objectives (exit skills) required of students. There should be at least one objective for each major topic in the content section. Objectives should be measurable and should use verbs requiring cognitive outcomes. See section “Bloom’s Taxonomy” in this manual for ideas. There are also links to Bloom’s Taxonomy in the CurricUNET system. There should be congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) Each SLO consists of an Outcome Text (drawn from the performance objectives) which will be measured during the regular assessment process, a mapping to an appropriate Institutional Outcome, and an Assessment Method. There should be congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes. It is essential that every course have SLOs for assessment and accreditation purposes. Board Policy 4210 and Administrative Procedure 4210, Student Learning Outcomes, affirm that student learning outcomes represent the knowledge, skills, abilities, attitudes, values, and behaviors that a student has attained at the end (or as a result) of his or her engagement in a particular set of collegiate experiences. The use of learning outcomes assessment results stimulates discussion and directs activities that can improve instructional delivery, curricula, programs, and/or services and will be used in institutional planning and resource allocation. Each college manages their SLOs slightly differently. See the college assessment coordinator for additional information. Methods of Instruction Check all that apply. If this course is also being proposed as a Distance Education Course, be sure to check that box. That action will open the next two items, Distance Ed and Instructor Student Contact. If it is not being proposed for Distance Education, those two items will remain grey and not accessible. Distance Education A distance education course is defined as instruction in which the instructor and student are separated by distance and interact through the assistance of communication technology. When a course is proposed to be offered in distance education mode, additional review and documentation is required. See “Distance Education” section of this manual for more information. □ □ □ Delivery Methods There are three types of Distance Education Courses. If a class never meets in person, it is 100% Internet Based. A hybrid class meets part of the time face to face and part of the time using communication technology. A hybrid may be offered 51% or more online or less than 51% online. When identifying these delivery methods, consider the overall requirements of the course, not necessarily limiting the course to only one of the methods. If it is likely that this course could be offered in any of the methods, check all so that there would not be a need to submit a course change in the future. The College Curriculum Committee will seriously question whether the course and/or discipline lends itself to Distance Education, so it is important to be able to justify the request. The most difficult to justify is usually 100% internet based. Recommended Maximum Student Enrollment Distance Education courses may or may not have a different maximum student enrollment. The administration of each college, together with the department chair, establishes the maximums. Need/Justification 73 Peralta Community College District □ □ □ □ Clearly explain the purpose of offering the course by distance education. This might include allowing a wider range of students, including those with logistical, physical or geographical barriers, to take the course; allowing for an increase in the amount of reading and writing assigned; and allowing students to work at their own pace. Do the following sections of the COR differ by offering this course via Distance Education? If Performance Objectives, Assignments, or Assessments differ when the course is offered via distance education, the changes should be indicated and explained. If Performance Objectives are different, it becomes a new course and requires a new outline. In other words, the course content, the performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes must be the same whether a course is offered face to face or via distance education. Technical Issues Identify any equipment and staff necessary to support the course for students and instructors. Identify the contingency plans available if access to the delivery system is interrupted. An LMS (Learning Management System) is necessary to support this class. Each college may have various LMS systems available to instructors and students, such as Moodle, WebCT, Blackboard, ETUDES-NG, MOODLE. If access to the LMS is interrupted, e-mail list and a back-up server are usually available. Accommodations for Students with Disabilities Distance education courses, resources, and materials must be designed and delivered in such a way that the level of communication and course-taking experience is the same for students with or without disabilities. If this course is not designed to meet these requirements, it will not be approved. Additional Resources Identify any additional resources or clerical support needed or anticipated. These will be reviewed by the department chair, curriculum committee, and administration. Instructor-Student Contact It is critical to ensure adequate contact between instructor and student for distance education courses. Identify for the curriculum committee all planned types of regular Instructor-Student Contacts using the drop down menu. Be sure to indicate the frequency for each contact, e.g. weekly, daily, as needed. Assignments List all out-of-class assignments, including library assignments. Achieving the objectives of degree-applicable credit courses must require students to study independently outside of class time. There is an expectation that students will spend two hours of independent work outside of class for each hour of lecture. The outside class hours should be calculated automatically by CurricUNET, but double check them before moving on. Outside assignments are not required for lab-only courses, although they can be given. Student Assessment Indicate how students will be assessed, i.e., what the grades will be based on. Typical classroom assessment techniques include, but are not limited to, essays, computational problem solving, non-computational problem solving in which critical thinking should be demonstrated by solving unfamiliar problems via various strategies, skill demonstration, or multiple choice. Check as many boxes as are applicable. For degree applicable credit courses, at least one of the following must be indicated: essays, computational problem solving, or non-computational problem solving. If "ESSAY" is not checked, an explanation must be given or it cannot be a degree applicable course. Essay assignments include "blue book" exams and any written assignment of sufficient length and complexity to require students to select and organize ideas, to explain and support the ideas, and to demonstrate critical thinking skills. Requisites Identify any pre-requisite, co-requisite, recommended preparation, or other advisory. See section “Prerequisites, Co-requisites, and Advisories” in this manual. The requisites must be consistent for all colleges if the course is taught on other campuses in the district. 74 Peralta Community College District When assigning a co-requisite, keep in mind that students must remain enrolled in the corequisite course for the entire semester. The enrollment system will cross check for attempted drops. A student who completed a co-requisite in a previous semester will be allowed to take the course. □ □ □ Choose type of requisite. A pull down menu will appear from which you will pick the requisite course or add additional information. Are subject course and pre/corequisite sequential or adjunctive? Check appropriate box. Communications, computational, non-sequential pre/corequisite: (In the following space, explain how the need for the pre/corequisite was validated.) Indicate the method used to scrutinize the validity of the requisite. Sequential courses can be validated using content review (see below). Some courses are validated by citing the four year schools and their requirements for a similar course for which ours might be articulated. Other courses are validated with statistical research. Any documentation to support any validation other than content review should be included as an attached file in CurricUNET. The next part of assigning a requisite is to do content review. Content Review Content review is the process of validating or justifying the requisite by comparing one of the following. the performance objectives/exit skills of the requisite course to the performance objectives of the course being developed or modified the performance objectives of the requisite course to the lecture content of the course being developed or modified the lecture content of the requisite course to the lecture content of the course being developed or modified the lecture content of the requisite course to the performance objectives of the course being developed or modified Identify the items in the new/modified course that can only be accomplished if the student achieved a corresponding item in the requisite course. Texts, Readings, and Materials Texts and instructional materials should be completely referenced. List text(s) that the department has evaluated and determined to be representative of the college level materials appropriate for the course. Date of publication is critical; transfer institutions require texts to have current publication date(s) within 5 years of outline addition/update. If any text entered is older than five years, CurricUNET requires a rationale or justification for its use. Sample rationale or justification: “Our piano faculty continually examine new texts as they become available. It is our collective opinion that the Mastering Music Series is the most appropriate for our beginning piano classes. Its pedagogy is up to date.” Textbooks need to be current for transferability, as well as for effective teaching. New faculty consult the COR to determine which texts have been identified as representative before they choose a text. The main text plays a remarkably strong role in articulation of a course. It should be clearly recognized by those in the discipline at other institutions as a major work which presents the fundamental theories and practices of the subject. Library When developing a proposal, faculty should consult with the college librarian to ensure library resources and services are adequate to support the course or program. This section of the COR should be completed by the librarian or under the guidance of the librarian. Attached Files 75 Peralta Community College District If there are additional documents that should be archived with the COR, they can be attached here. This might include, but is not limited to: Letters of support from Advisory Committees Minutes from Advisory Committee meetings C-ID Descriptors Sample Course Syllabus Documentation to support any validation process for prerequisites, co-requisites, and/or recommended preparation Records of consultation with other colleges, if any issues need to be documented for future reference CSU catalog documentation for repeatable courses Approval letters from CCCCO 76 Peralta Community College District Creating a Fee Based Course The COR for a fee based course has fewer requirements than CORs for other courses. The explanations of the required data are similar to the regular COR described above. Fee based courses are approved by the College Curriculum Committee and sent directly to the Board of Trustees; CIPD approval is not required. See section “Community Service (Fee-Based) Courses” in this manual for more information. 77 Peralta Community College District Deactivating a Course or Program Reasons for deactivating a course or program may include, but are not limited to: maintaining discipline currency responding to business or industry needs removing courses from the catalog which have not been offered in the past two to five years and are not expected to be offered in the foreseeable future removing programs from the catalog which are no longer meeting students’ needs Deactivating a course requires the faculty member and department chair to complete the appropriate CurricUNET work flow. □ Proposed Start: Enter the semester and year the course will no longer be offered and will be removed from the catalog. Since deactivations take time to go through the work flow, these dates will never be the current semester. In most cases, plan two to three semesters ahead. □ List of Changes The List of Changes field on the course checklist should clearly explain why the course will no longer be in the college catalog. When deactivating a course, always cross check to be sure it is not listed in any active program. If it is, and you still wish to deactivate the course, you must also submit the changes in the program to the College Curriculum Committee at the same time the course deactivation is presented. After the approval by the Curriculum Committee, the request goes to CIPD and the Board of Trustees. Once the deactivation is finalized, two blue historical work flows for the course will show in CurricUNET. Berkeley City College TRAV 048UA-ZZ Selected Topics in Travel Industry *Historical* **BCC New Course** Linda Balko Effective Date: Spring 2008 Berkeley City College TRAV 048UA-ZZ Selected Topics in Travel Industry *Historical* **BCC Deactivate Course** Jayne Matthews Effective Date: Summer 2011 Deactivation of a program requires the faculty member and department chair to complete the appropriate CurricUNET work flow. Since deactivations take time to go through the work flow, the effective date will never be the current semester. In most cases, plan two to three semesters ahead. For additional details about the program deactivation process see the section “Program Discontinuance or Program Consolidation” in this manual. 78 Peralta Community College District Reactivating a Course or Program A course or program that has been previously deactivated and is shown in CurricUNET as historical must be processed as a new course or program to ensure all elements are reviewed for currency. Generally a reactivated course uses the original course number. The Curriculum Chair can clone the historical course or program to allow the originator to begin the process. Since all new courses and programs take time to go through the work flow, these dates will never be the current semester. In most cases, plan two to three semesters ahead. 79 Peralta Community College District Course Numbering System Assigning Course Numbers for all Courses Prior to assigning a course number, the originator should answer the following questions. 1. Is this course transfer level? Will it transfer to a four year school? If yes, is it also degree applicable? 2. If not a transfer course, is it nevertheless a college level course? If yes, is it also degree applicable? 3. If not a transfer level or college level course, is it a basic skills course? If yes, how many levels below transfer is the material in the course? If yes, remember a basic skills course cannot be degree applicable. Having gathered this information, you can now use the information below to determine the range in which to assign the course number. The Curriculum Chair should be consulted to ensure no duplication of numbers occurs. 001 – 199 Transfer and Associate Degree applicable courses, including Selected Topics for liberal arts and vocational disciplines (48s) Degree credit courses in approved programs LRNRE Resources (LRNRE) courses numbered below 200, while transferable to CSU and/or UC, are not degree applicable, i.e., they are not required for a degree or certificate and do not satisfy General Education requirements. 200 – 249 Associate Degree applicable courses, including Selected Topics for liberal arts and vocational disciplines (248s) Not transferable Degree credit courses in approved programs 250 – 299; 348 Non Associate Degree applicable courses 400 – 499 Credit Apprenticeship and Cooperative Education/Work Experience Education courses Apprenticeship courses are non-degree applicable and non-transfer Cooperative Education courses are degree applicable and transferable, with the exception of Apprentice Work Experience courses. 500 – 599 Non-credit, general, apprenticeship, and older adult courses (non-credit courses that require state approval) 600 – 699 Non-credit, courses specifically for the disabled (non-credit courses that require state approval) 700 – 799 Not-for-credit courses for contract education. 800 – 999 Community Services (fee-based) courses. Uniform Course Numbering 80 Peralta Community College District When one or more Peralta Colleges offer the same course using the same catalog information, the Uniform Course Numbering system (UCN) is used. If one college wants to begin offering a UCN course (borrow a course) or if a college proposes any substantive change in a UCN course, the consultation process outlined in section “Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues” in this manual should be followed. 81 Peralta Community College District When a Course Change Requires a New Course Number The following substantive changes make such a significant change to the course that it is actually a new course. Therefore, a new number must be assigned to the course. Discipline name and/or abbreviation Course number Hours Units TOP Code Credit Status Basic Skills Status SAM Code Prior to College Level (CB21) Funding Agency Category In most cases, changes to a course do not require a new course number. However, when the units and hours increase/decrease or a lecture or lab component is added or deleted, a new course number is generally required. For example, if SCIEN 85 is 4 units, 3 hours lecture and 3 hours lab and the department wants to change it to two courses, one 3 hours lecture and a separate lab of 3 hours, a new number is required, since without the lab hours, SCIEN 85 is no longer the same course. Reusing Course Numbers Course numbers of historical or inactive courses cannot be reused. Reusing a number can cause confusion on student transcripts when one number identifies two substantially different courses. 82 Peralta Community College District Modularization Modularization involves breaking an existing course into two or more sections. For example, one college may offer CIS 42 as a 3 unit course. Another college may choose to offer the same CIS 42 course as CIS 42A and CIS42B, each a 1.5 unit course. Since this is actually creating two new courses, new course outlines must be initiated in CurricUNET for both courses. They will then be processed through the college and district work flows like any other new course. If the modularization involves a UCN course, consultation must occur as outlined in section “Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues” in this manual. For modular courses, at the end of the Catalog Course Description, the following notation should be included for each course. “Not open for credit to students who have completed or are currently enrolled in Subject Crse #. “ 83 Peralta Community College District Bloom’s Taxonomy When writing performance objectives and student learning outcomes, use verbs requiring cognitive outcomes. Bloom’s Taxonomy is one resource to help identify these verbs. Bloom’s Taxonomy Verb List Cognitive Domain Knowledge Cite Define Describe Draw Enumerate Identify Index Indicate Label List Match Meet Name Outline Point Quote Read Recall Recite Recognize Record Repeat Reproduce Review Select State Study Tabulate Trace Write Comprehension Add Approximate Articulate Associate Characterize Clarify Classify Compare Compute Contrast Convert Defend Describe Detail Differentiate Discuss Distinguish Elaborate Estimate Example Explain Express Extend Extrapolate Factor Generalize Give Infer Interact Interpolate Interpret Observe Paraphrase Picture graphically Predict Review Rewrite Subtract Summarize Translate Visualize Application Acquire Adapt Allocate Alphabetize Apply Ascertain Assign Attain Avoid Back up Calculate Capture Change Classify Complete Compute Construct Customize Demonstrate Depreciate Derive Determine Diminish Discover Draw Employ Examine Exercise Explore Expose Express Factor Figure Graph Handle Illustrate Interconvert Investigate Manipulate Modify Operate Personalize Plot Practice Predict Prepare Price Analysis Analyze Audit Blueprint Breadboard Break down Characterize Classify Compare Confirm Contrast Correlate Detect Diagnose Diagram Differentiate Discriminate Dissect Distinguish Document Ensure Examine Explain Explore Figure out File Group Identify Illustrate Infer Interrupt Inventory Investigate Layout Manage Maximize Minimize Optimize Order Outline Point out Prioritize Proofread Query Relate Select Separate Size p 84 Synthesis Abstract Animate Arrange Assemble Budget Categorize Code Combine Compile Compose Construct Cope Correspond Create cultivate Debug Depict Design Develop Devise Dictate Enhance Explain Facilitate Format Formulate Generalize Generate Handle Import Improve Incorporate Integrate Interface Join Lecture Model Modify Network Organize Outline Overhaul Plan Portray Prepare Prescribe Produce Evaluation Appraise Assess Compare Conclude Contrast Counsel Criticize Critique Defend Determine Discriminate Estimate Evaluate Explain Grade Hire Interpret Judge Justify Measure Predict Prescribe Rank Rate Recommend Release Select Summarize Support Test Validate Verify Peralta Community College District Knowledge Comprehension Application Process Produce Project Provide Relate Round off Sequence Show Simulate Sketch Solve Subscribe Tabulate Transcribe Translate Use Analysis Subdivide Train Transform Synthesis Program Rearrange Reconstruct Relate Reorganize Revise Rewrite Specify Summarize Write Evaluation A group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment. This title draws attention away from the somewhat static notion of “educational objectives” (in Bloom’s original title) and points to a more dynamic conception of classification. The authors of the revised taxonomy underscore this dynamism, using verbs and gerunds to label their categories and subcategories (rather than the nouns of the original taxonomy). These “action words” describe the cognitive processes by which thinkers encounter and work with knowledge: Remember o Recognizing o Recalling Understand o Interpreting o Exemplifying o Classifying o Summarizing o Inferring o Comparing o Explaining Apply o Executing o Implementing Analyze o Differentiating o Organizing o Attributing Evaluate o Checking o Critiquing Create o Generating o Planning o Producing In the revised taxonomy, knowledge is at the basis of these six cognitive processes, but its authors created a separate taxonomy of the types of knowledge used in cognition: 85 Peralta Community College District Factual Knowledge o Knowledge of terminology o Knowledge of specific details and elements Conceptual Knowledge o Knowledge of classifications and categories o Knowledge of principles and generalizations o Knowledge of theories, models, and structures Procedural Knowledge o Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms o Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and methods o Knowledge of criteria for determining when to use appropriate procedures Metacognitive Knowledge o Strategic Knowledge o Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including appropriate contextual and conditional knowledge o Self-knowledge 86 Peralta Community College District Initiating New Programs or Revisions An educational program is defined in Title 5, section 55000(g), as "an organized sequence of courses leading to a defined objective, a degree, a certificate, a diploma, a license, or transfer to another institution of higher education." Full and part-time faculty members may develop and/or revise programs. This process begins at the department level with discussion on the reasons for the program proposal. If the program is interdisciplinary, all involved departments participate in each step of the procedure. All new or revised programs must be submitted to CIPD and the Board of Trustees after approval by the College Curriculum Committee. Reasons for proposing a new or revised program may include, but are not limited to: • maintaining discipline currency • responding to business or industry needs • developing curriculum pattern for major • enhancing student’s knowledge of the discipline For new programs (certificates or degrees) or substantive changes to programs which are similar to any other program in the district or contain similar courses offered at other colleges (whether or not these programs are in the same discipline), consultation must occur as outlined in section “Goals for Consultation among Colleges regarding Curriculum Issues” in this manual. Credit Programs • Associate Degrees (traditional AA or AS) that require 60 units • Associate Degrees for Transfer (AA-T/AS-T) that require 60 units • Certificates of Achievement that require 18 or more semester units • Certificates of Achievement that require 12 to fewer than 18 semester units • Certificates of Proficiency that require no more than 17.5 units Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. 87 Peralta Community College District Program Outline It is the responsibility of the program originator to complete the Program Outline on CurricUNET. If the program originator does not have access to CurricUNET or needs help getting started, the faculty member should contact the college curriculum chair. Program originators should review the information in this section under “Completing the Program Outline” for detailed information about the contents of each item required in developing or revising a course. The Curriculum Committee uses the following criteria to evaluate program proposals. Appropriateness to mission of college, department, and discipline Need as justified by department Curriculum standards Appropriateness of program content Adequate resources Compliance CTE departments’ advisory board support Departmental faculty support Consultation with other disciplines or colleges Completing the Program Outline Following are descriptions of the elements in the program outline that must be completed as part of the program development process. All items in the CurricUNET Degree/Certificate Checklist must be completed, saved, and finished before the system will allow you to submit it to the work flow. To use CurricUNET for the first time, contact the College Curriculum Committee chair. This section of the manual only covers the content elements of the program outline; it does not explain how to get to the data entry screens in CurricUNET. More details about using CurricUNET can be found in the Help Section on the CurricUNET Home Page and in the Peralta District Guide to CurricUNET (under development). In addition, each college has a Curriculum Web Page; Laney’s has been well developed to provide good support for the system. Finally, the College Curriculum Committee chair is an excellent resource. Note: Approval of curriculum is a time-consuming process. Due to the various levels of review required by policy and law within the college and the district, as well as the state requirements to have an approved state control number prior to the courses/programs being offered, new curriculum or changes to existing curriculum should normally be submitted at least two semesters prior to planned implementation. Program Outline Cover □ Program Title Identify the program title as it will be listed in the catalog. □ Discipline Identify the discipline in which the program will be managed. □ Award type Identify which type of degree or certificate is being developed. □ Justification for Proposal If this is a new program, explain the purpose the program will serve in the department, discipline, and/or college curriculum. 88 Peralta Community College District □ The justification should also clearly outline the specific program plan for transfer to four year schools or the specific Career/Technical Education goals for the program. Detailed supporting documentation should also be attached in CurricUNET. If this program is being modified, update this as necessary. In most cases, the original justification should not be deleted. Career Opportunities If this program is in the Career Technical Education areas (CTE), include a brief description of the career opportunities available to the student who completes the program. Program Description This is the description of the program which will be printed in the catalog. It should be clear and concise. Program Outcomes It is essential that every program have Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) for assessment and accreditation purposes. Each PLO consists of an Outcome Text which will be measured during the regular assessment process, a mapping to an appropriate Institutional Learning Outcome, and an Assessment Method. Each college manages their PLOs slightly differently. See the college assessment coordinator for additional information. Course Block Definitions All courses required to be completed for the program must be listed. Attach Files If there are additional documents that should be archived with the program outline, they can be attached here. General attachments might include: Documentation prepared to submit to the California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office (CCCCO) for approval, including program narrative, labor market information (CTE only), ASSIST/Transfer documentation, and signature page. Approval Letters from the CCCCO Transfer Model Curriculum (TMC) Template for Associate Degrees for Transfer (ADT) Documentation of Transfer Plan to four year schools Additional attachments for Career/Technical Education (CTE) programs might include: Letters of Support from Advisory Committees CTE Advisory Council Approval Meeting Minutes Documents for CTE programs approved by the Bay Area Community College Consortium (BACCC) California Division of Apprenticeship Standards (DAS) Approval Letter (Apprenticeship only) Employer Survey (CTE only) 89 Peralta Community College District Part III Additional Related Information 90 Peralta Community College District Curriculum Related Job Duties Curriculum development is a team effort. Some of the participants in the process include faculty originators, department chairs, Student Learning Outcome (SLO) coordinators, articulation officers, librarians, tech review committee members, curriculum committee members, curriculum specialists, curriculum chairs, and Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) members. Outlines of the suggested functions for each of these positions, as they relate to curriculum, follow. Each college may assign these responsibilities differently. It is important to understand that these functions must be completed in a timely manner by someone who understands it is his/her responsibility. This is critical to ensure the timely processing of new and modified courses and programs. Faculty Originator Meet with Department Chair to discuss proposal. Meet with department faculty, deans, tech review faculty, and/or articulation officer as needed. Prepare proposal using CurricUNET. Ensure all elements of the proposal are complete and accurate, using this manual. Consult with librarian regarding resources available to support the course and program. Document consultation in CurricUNET. Submit the proposal to the CurricUNET work flow. Monitor the progress of the proposal in the CurricUNET work flow and review comments made by reviewers. Attend the Curriculum Committee Meeting to present and defend the proposal. Department Chair Approve outlines and programs in the work flow. 1) Meet with the originator of the outline or program and discuss its contents 2) Verify the outline or program fits the educational plans for the discipline/department and was considered during Program Review 3) Discuss the viability of the course. 4) Determine if this course or program requires consultation with other disciplines/departments within the college. 5) Determine if this course or program requires consultation with the other Peralta Colleges. See the section Curriculum Issues which Require Consultation among Colleges section in the Program, Curriculum, and Course Development area of this manual for details. Keep in mind departments may overlap and research areas in related disciplines. 6) Document consultation in List of Changes, Justification, or as attached documents. Review all areas of the work flow prior to approving, including, but not limited to: 1) Are the units realistic for the course? 2) Does the outline meet the criteria established in this manual? 3) Is there congruence among the catalog description, lecture and/or lab content, student performance objectives, and the student learning outcomes? 4) If a course is part of a program, is there congruence between the course and the Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs)? 5) Do the percentages for the lecture/lab content equal 100% and is the content is an accurate reflection of what will be taught? 6) If there are pre-requisites, co-requisites, or recommended preps, are they accurate and was content review completed correctly? 7) Is there a current textbook? 8) Could a new instructor use this COR effectively to develop a syllabus? Ensure that changes to courses and programs are coordinated. 1) If a course is deactivated and is part of a degree program, is the degree program being updated at the same time? 91 Peralta Community College District Prepare all documentation required for submitting new and revised programs to the California Community College Chancellor’s Office (CCCCO). Student Learning Outcome (SLO) Coordinator (pending) Articulation Officer (pending) Librarian Course outlines should be reviewed within one week of notification that outline is awaiting review. Review Steps 1) Review course outline. 2) Based on the contents of the course outlines, determine appropriate subject area(s). 3) Search library online catalog to evaluate coverage of subject area in library’s collection, including print, non-print and electronic titles. Review for depth of coverage, variety of reading levels and currency. 4) Review library database subscriptions to evaluate coverage of subject area. Review for depth of coverage, variety of reading levels and currency. 5) Determine adequacy of collection to support curriculum and check boxes on Library section of Course Checklist, as appropriate. Add note if needed. 6) Review textbook and supplemental reading materials on course outline to determine appropriate acquisitions for general collection (non-textbook titles). Submit to acquisitions librarian for purchase recommendation. 7) Request additional supplemental reading list from originator, if necessary. 8) Select and submit action (approve or recommend changes) as librarian in curriculum approval process. 9) Submit supplemental reading lists to acquisitions librarian for purchase recommendation. 10) Submit any additional recommended titles to acquisitions librarian for purchase recommendation. Tech Review Committee Member (pending) Curriculum Committee Member Attend all scheduled curriculum committee meetings. Review and approve curriculum using CurricUNET. Review proposals for new courses and programs, course and program revisions and deactivations. Participate in the program review and accreditation review processes. Review and recommend changes in the general education and graduation requirements. Review course proposals for alignment with articulation requirements. Review proposals for alignment with Career Technical Education (CTE) goals and requirements. Review proposals for alignment with educational plans and departmental goals as stated in program reviews. Review proposals for appropriateness of course content for a community college. Recommend procedures and policies affecting curriculum. Review and recommend changes to the college catalog. Mediate curriculum disputes at the college that have not been resolved by faculty and administration prior to being placed on the Curriculum Committee agenda. The curriculum committee may approve, deny, or return course proposal to originator and department for further consideration. Curriculum Specialist Schedule Meeting Room for Curriculum Committee Meetings. Work with the Curriculum Chair to prepare and distribute Curriculum Committee Agenda 72 hours in advance (in compliance with the Brown Act). Post to the College or Curriculum Web Site. Review to ensure any changes to degrees or certificates are submitted at the same time as any courses being changed that directly affect the program (e.g., units, titles) 92 Peralta Community College District Prepare minutes from local curriculum committee meetings. Maintain file of approved minutes as well as post approved minutes to the College or Curriculum Web Site. Make corrections to CurricUNET as approved in Curriculum Committee Meetings. Complete appropriate Codes/Dates fields as final approval step in CurricUNET files prior to submission to CIPD. Work with Curriculum Chair to develop agenda for CIPD and ensure it is submitted to CIPD. Work with Curriculum Chair to ensure all approved curriculum is finalized in CurricUNET after CIPD approvals/changes. Finalize and Implement CurricUNET course or program records, after approval at CIPD and the Board of Trustees, including but not limited to documenting approval dates and CB codes on Codes Page of Course Checklist. Support Curriculum Chair in facilitating submission of degrees and certificates by the administration to the State Chancellor’s Office. Curriculum Committee Chair Provide training and consultation to faculty and staff involved in curriculum development and revision. Serve as liaison for CurricUNET training, questions, and issues at the college. Facilitate submission of degrees and certificates by the administration to the State Chancellor’s Office. Support Curriculum Committee o Work with the Curriculum Specialist to prepare and distribute Curriculum Committee Agenda 72 hours in advance (in compliance with the Brown Act). Post to the College or Curriculum Web Site. o Review to ensure all curriculum elements are complete and appropriate. This is a tiny job if Department Chairs and Tech review have done theirs. A big job, if not. o Review to ensure any changes to degrees or certificates are submitted at the same time as any courses being changed that directly affect the program (e.g., units, titles). o Facilitate curriculum committee meetings. o Final edit of minutes from local curriculum committee meetings. Work with Curriculum Specialist to develop agenda for CIPD and ensure it is submitted to CIPD. o Review CIPD agenda sent out by District to ensure proposals are accurate. o Forward CIPD agenda to department chairs who may have an interest in the other college’s agendas. o Schedule guests to attend CIPD to answer questions about proposed curriculum as needed. o Represent the college at CIPD and present the curriculum actions o Work with Curriculum Specialist to ensure all approved curriculum is finalized in CurricUNET. Participate in District Curriculum Chairs Meetings and activities. o Represent the college at the monthly District Curriculum Chairs meetings. o Provide input to District policies and procedures which directly affect curriculum. o Coordinate CurricUNET changes on a district level prior to requests being submitted to CurricUNET 93 Peralta Community College District Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) The primary responsibilities of the Council on Instruction, Planning, and Development (CIPD) are: to advise the district in academic areas and related planning to provide a leadership role in program review and development to review college curriculum additions, deletions, or modifications and submit them to the Board of Trustees for approval Curriculum oversight includes: • Peralta Uniform Course Numbering (UCN) process • Consistent implementation of core curriculum at all colleges • Quality assurance of programs within the district through regularly scheduled review • Uniform compliance with Title 5 regulations regarding curriculum • Guidelines for program and course implementation as it relates to state and federal agencies, other external agencies, and accreditation standards. Membership Each college shall have five voting members: the Vice President of Instruction, one other manager (the Vice President of Student Services or a Division Dean of Instruction), the College Curriculum Committee Chair, the Articulation Officer, and a Faculty Senate appointee. The Vice Chancellor of Educational Services and a faculty member shall co-chair the committee. The Vice Chancellor shall have one vote in case of a tie. Ex-officio Members: PFT President, District Academic Senate President, Associate Vice Chancellor for A&R and Student Services. Process After College Curriculum Committee approvals, the following items are submitted to CIPD for review and/or approval. • • • • • New courses and programs Substantive changes to courses Modifications to programs Selected Topics courses (informational only) Distance Education proposals (informational only) Any CIPD member can place an item on the agenda. CIPD will review, analyze, and make recommendations to the Chancellor or designee who will forward appropriate information to the Board of Trustees. Items for each month’s CIPD agenda must be submitted no later than ten days prior to the meeting. Once items are approved by CIPD, they should not be changed prior to or after going to the Board. Policy/Procedures When CIPD Member Absent Sound action by CIPD depends upon active and dependable participation by all members. Regular attendance is essential. The question arises as to what should occur when a member cannot attend CIPD. Three options are presented for consideration. OPTION I Conduct all CIPD business with members in attendance. OPTION II Alternate appointed for absent member. OPTION III 94 Peralta Community College District Absentee ballot: • Used for agenda items only (this requires that the agenda will be distributed in a timely manner). • Ballot must be in the office of the Vice Chancellor of Educational Services no later than noon of the meeting day. • The ballot must have the item(s) being voted on clearly identified, signed, and dated by the member. • The ballot will be opened by the Vice Chancellor during the CIPD meeting, after the vote of those present has been taken. • Any business which occurs during a meeting and requiring consensus or vote will be acted upon by those present. There will not be a delay of action because of member(s) absent. 95 Peralta Community College District College Level Courses The following criteria will be used in determining if a course is college level. (Not all of these criteria are equally applicable in all fields of study, but they should be taken into consideration to the extent appropriate in approval of degree applicable and transfer courses.) Time Demands Course should conform to time demands of Carnegie units (in lecture courses, 2 hours a week of outside work for each unit of credit; and/or in lab courses, 3 hours of practicum for each unit of credit). Rigor Students should be required to exhibit their understanding of the course materials and concepts as well as such critical thinking skills as finding alternatives, understanding through significant performances including skills demonstrations or substantial written essays. Theory and Application In liberal arts courses, content and text should involve understanding, questioning, and application of concepts and theory through analyses, syntheses, and arguments; CTE courses will emphasize problem solving and application of principles through skills demonstrations. Open-Endedness/Independent Learning Courses should involve some student input into the nature of assignments and projects. Assignments should require independent thinking and judgment; as much as possible, students should define their own problems and organize their own tasks with guidance from instructor, seeking further information on the subject outside of materials presented directly by instructor and text. College-Level Texts and Primary Sources Instructors generally choose to use textbooks. Texts should be supplemented by primary sources or other readings. The texts should be postsecondary in focus, with a significant requirement of independent, critical thinking from the student. 96 Peralta Community College District Critical Thinking Critical thinking is reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do. It involves a number of skills and cognitive processes which can be improved by instruction and conscious effort. A list of critical thinking skills would include the following (different skills tend to be significant in different fields, but all educational areas involve these skills to some degree). Observational Skills: Observe patiently and objectively in order to gain insight. Self-Awareness: Be aware of one's own thought processes, values, and priorities and understand how they influence one's own observations. Reasoning Skills: Reason systematically and logically, recognize and formulate concepts, distinguish facts from inferences, tell reasons from conclusions, recognize and correct faulty reasoning. Questioning Skills: Rationally and systematically question procedures and ideas. Problem-Solving Skills: Pose and solve problems through systematically analyzing alternatives; test, refine, and apply proposed solutions. Presenting Ideas: Present one's position on an issue or solution to a problem using reasoning and evidence while remaining open to other perspectives and new data that might require a revised approach. Find out from Jenny Lowood what BCC’s definitions are and moosh them into this. 97 Peralta Community College District Disabled Students Programs and Services Under federal and State laws, the District and Colleges are required to ensure that academic requirements and practices, facilities, electronic information technology, printed materials, and College services and activities are accessible to individuals with disabilities. The College will make modifications as necessary in order to provide equal access. The role of the Disabled Student Programs and Services (DSP&S) program is to assist the colleges in meeting federal and state obligations to students with disabilities. DSP & S is the primary provider for support programs and services that facilitate equal educational opportunities for students with disabilities who can benefit from instruction as required by federal and State laws. No student with disabilities is required to participate in the DSP&S program. If a student requests accommodations and does not want to register with DSP&S, he/she will need to submit documentation to the College 504/ADA Coordinator. DSP&S will evaluate the disability documentation and discuss the request for accommodations with the student. Each College maintains a plan for the provision of programs and services to students with disabilities designed to assure that they have equal access to College classes and programs. The yearly DSP&S Plan, as required by the State Chancellor’s Office, describes the processes, procedures, and requirements, as well as a full description of the program. Other information regarding the goals and objectives of DSP&S can be found in the DSP&S Program Review document. Academic Accommodations Procedures for Students with Disabilities Pursuant to Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, Title 5, Section 56027, and Board Policy 5.24, the Peralta Community College District has developed the following procedures to respond in a timely manner to requests by students with disabilities for academic accommodations. Pursuant to Title 5, Sections 56000-56088 the District has developed DSP&S at each college to assist students with disabilities in accessing appropriate instruction, programs, academic accommodations and auxiliary aids. The goal of all academic accommodations and auxiliary aids is to minimize the effects of the disability on the educational process. The student with a disability shall be given the opportunity both to acquire information and to be evaluated in a way that allows the student to fully demonstrate his/her knowledge of the subject. The goal is to maintain academic standards by giving the student assignments that are comparable in content, complexity, and quantity. When a student requests disability-related services, the student's disability is verified by the DSP&S professional, according to state-mandated criteria. If the student is deemed ineligible for services, DSP&S shall provide the student with written notice of the denial stating both the reasons for the denial and that the student has a right to appeal the denial through the District Discrimination and Complaint Procedures. Pending the resolution of any dispute regarding an accommodation, the accommodation will be provided. The DSP&S professional (as defined in Title 5 Section 56006, 56048, 56060, 56064 and 56066), in consultation with the student, determines educational limitations based on documentation of the disability and functional limitations and authorizes the use of any appropriate auxiliary aids and/or academic accommodations. These may include but are not limited to: • • • • Auxiliary aids such as a tape recorder, assistive listening device, calculator, computer, taped text or spelling checker used in the classroom and/or in completing class assignments The use in the classroom of a reader, American Sign Language interpreter, note taker, or scribe, or real-time captioner for students who are deaf or hard of hearing or the presence of service animals, mobility assistants, or attendants in the classroom Testing accommodations such as extended time for test taking and distraction-reduced test setting Extending the length of time permitted for course or degree requirements and flexibility in the manner in which specific course content is accessed, based on individual disability 98 Peralta Community College District • • Substitution for specific courses required for the completion of General Education degree requirements, or substitutions or waivers of major or certificate requirements Access to Alternate Media such as Braille, large print, and electronic text (e-text) With the consent of the student, instructors are informed of authorized auxiliary aids and academic accommodations. It is the responsibility of the instructor to allow auxiliary aids to be used in the classroom or to coordinate with the DSP&S professional for the delivery of academic accommodations. It is the responsibility of the DSP&S professional to make arrangements for and facilitate the delivery of academic accommodations with the disabled student in coordination with faculty, as appropriate. The DSP&S professional will assist with providing the appropriate accommodations and appropriate follow up for DSP&S students. An example of appropriate follow up might be a DSP&S Counselor contacting an instructor and DSP&S student to inquire about the effectiveness of an accommodation. Instructors cannot unilaterally deny approved accommodations and students may not be asked or required to negotiate with instructors or staff about the provisions of adjustments or aids that have been approved by the DSP&S. If an instructor receives an accommodation form and does not understand it or disagrees with the accommodation, it is the instructor’s responsibility to contact DSP&S to discuss the issue. Grievance Procedures If a student is denied academic accommodations or the use of auxiliary aids by an instructor and wishes to appeal, she/he should contact the DSP&S professional who will schedule a meeting with the instructor to discuss and resolve the issue. The student may invite the DSP&S professional (i.e., a DSP&S Coordinator, Counselor, Instructor, Acquired Brain Injury ((ABI) Specialist, Learning Disability (LD) Specialist etc.) to attend this meeting. In the case where an unresolved issue becomes a dispute (i.e., an issue that is not resolved informally between the student and the instructor with the assistance of the DSP&S professional), the student may file a complaint through the District’s Harassment and Discrimination Complaint Procedures. Pending the resolution of any dispute regarding an accommodation, the accommodation will be provided. Meeting General Education Degree Requirements: When the severity of the disability of an otherwise qualified student precludes successful completion of a course required for graduation from a college within the Peralta Community College District, despite an earnest effort on the part of the student to complete the course or its prerequisite--if appropriate for the disability as determined by a qualified DSP&S Specialist-and despite the provision of academic adjustments and/or auxiliary aids, the student may request a substitution of the course as an alternative method of meeting General Education degree requirements. The Evaluation Team will consist of the DSP&S Coordinator, the Department chair or instructor from the discipline of the course or major for which a substitution is being requested, and the appropriate Dean of Instruction. The team may consult, as appropriate, with DSP&S professionals, Associate Vice Chancellor for Admissions and Records and Student Services, and the College Vice President of Instruction in order to make a decision. In assessing requests, the Evaluation Team should consider the anticipated exit skills from the course that can be substituted for comparable exit skills in another course. These comparable skills may be found in a discipline different from the discipline of the original course. Meeting Major or Certificate Requirements 99 Peralta Community College District The process for evaluating requests for major or certificate requirements is the same as for General Education Requirements above except that the student may request a substitution or a waiver of the course as an alternative method of meeting major or certificate requirements. A course substitution maintains the standards of academic rigor of degree programs because the student is required to demonstrate comparable skills (when a student completes a comparable course as established by an Evaluation Team). Therefore, requesting a course substitution is the preferred option to meet General Education degree requirements. For major or certificate course requirements, course substitutions and/or waivers may be considered. Course substitutions are applicable for Peralta Community College District and may not be recognized by a transfer college. Evaluation of Substitution/ Waiver Request Documentation The student will complete the Request for Change of Graduation Requirements Form (available in the DSP&S office) and submit it to the DSP&S professional with the following attachments. • Petition for Substitution/Waiver (obtained from the Admissions Office) • Letter (written by the student) addressing the criteria listed in Part B • Evidence from the DSP&S Professional (DSP&S Coordinator, Counselor, Instructor, Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) Specialist, Learning Disability (LD) Specialist, etc.) verifying the disability and how it relates to the student's request • Documentation of the student's academic record, the degree requirements for graduation and information about the course in question regarding whether or not it is essential to the student's course of study, major, transfer goals and/or employment goals as appropriate • Additional supporting documentation can be provided by students Evaluation of Request • The DSP&S professional will review all documents, outline evidence of the use of all appropriate and available services and academic adjustments and indicate that, according to the criteria listed below, the request is appropriate. The DSP&S professional then signs the Request for Change of Graduation Requirements Form and forwards the packet to the DSP&S Coordinator, who will convene an Evaluation Team. • The Evaluation Team consists of the DSP&S Coordinator, the Department Chair (or an Instructor) from the discipline of the course or major for which a substitution is being requested and the Dean of Instruction with responsibility for the Division, which includes the discipline of the course substitution. The Evaluation Team meeting is to be chaired by the Dean of Instruction and should consult with the Associate Vice Chancellor for Admissions and Records and Student Services, DSP&S professionals, and the College Vice President of Instruction as appropriate • The Evaluation Team will assess student requests based on the following criteria. • Documentation of the student's disability with specific test scores, when appropriate, and a description of educationally related functional limitations in the academic area under discussion • Evidence of the student's earnest efforts to meet the graduation requirement, which may include • Consistent and persistent efforts in attempting to meet all graduation requirements 100 Peralta Community College District • • • • • • Evidence that the student has attempted to take the course in question or its prerequisite with accommodations and has been unable to successfully complete course requirements Regular attendance (i.e., meeting the attendance requirements of the course) Completion of all course assignments Use of all appropriate and available services such as tutorial assistance or instructional support classes Use of all appropriate and available academic accommodations such as test accommodations Agreement among the student, DSP&S Counselor and the appropriate Disabilities Specialist that, due to the severity of the disability, the student would not be able to successfully complete the course requirements, even with accommodations • Evidence that the student is otherwise qualified such as: • The student's success in completing other course work requirements for the degree/certificate as indicated by a grade point average of 2.0 or greater in degree applicable classes. • Information about the course in question regarding whether or not it is essential to the student's Course of Study, Major, Transfer Goals or Employment Goals • Information about alternatives to the course in question based on the learning/academic goals of that course Decision Process Meeting General Education Degree Requirements The Evaluation Team's decision will be made by majority vote. If the Team recommends a course substitution, the Team will request the department in which the student is asking for course substitution to provide a list of previously identified appropriate course substitutions. If the department cannot identify an appropriate course substitution or if the Team concludes that a substitute course is inappropriate due to the severity of the disability, as documented by the Verification of Disability and Educational Limitations Form, then the College Vice President of Instruction and the Associate Vice Chancellor for Admissions and Records and Student Services shall be included in the evaluation process to assist with the identification of an appropriate course substitution. To approve recommendations for course substitutions, the Evaluation Team will forward its recommendation to the Vice President of Instruction and then to the Associate Vice Chancellor for Admissions and Records and Student Services. The District Office of Admissions and Records will verify, implement, and notify the student. Meeting Major/Certificate Requirements The process for evaluating requests for major/certificate requirement is the same as those stated above except that the student may request a substitution or a waiver of a course as an alternative method of meeting major or certificate requirement. Complaint Procedure If the student is dissatisfied with the decision of the Evaluation Team, she/he may follow the District’s Harassment and Discrimination Complaint Procedures. The finding may be appealed directly to the District Affirmative Action Officer. Students can obtain the assistance of the District Affirmative Action Office at any point during this process. Equal Access to Electronic and Information Technology Federal and State laws require that all electronic and information technology purchased or used by federal agencies must be accessible for use by persons with disabilities. This regulation applies to the development, procurement, maintenance and/or use of all electronic and information technologies. 101 Peralta Community College District The Information Technology Department will ensure that College employees who purchase or request recommendations about information technology products are informed of the accessibility requirements of Section 508. Grant recipients will be informed of their obligations under Section 508 requirements. The Purchasing Department will ensure that vendors and other contract recipients are informed of their obligations under section 508 requirements. The Colleges and District will ensure that web pages and related links are accessible to individuals with disabilities as defined by World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The Colleges will ensure that video and multimedia products developed by the College and/or housed at the College are equally accessible to individuals with disabilities and comply with Section 508. The Colleges will ensure that faculty who develop web pages, online learning, and other distance learning options for students are informed of their obligations under section 508. The College will ensure that faculty and staff are informed of their obligations under Section 508 requirements as they pertain to enrolled and prospective students. The Colleges will ensure that all staff members are informed of their obligations under Section 508 requirements as they pertain to visitors and events on campus. The Office of Instruction will ensure that all library staff members are informed of their obligations under Section 508 as they pertain to library patrons. References: Administrative Procedure 5140 Disabled Students Programs and Services Education Code Sections 67302, 67310 and 84850; Title 5 Sections 56000 et seq. 42 U.S.C. Section 12101, 34 CFR Sections 104.3 and 104.44; 36 CFR 11135 102 Peralta Community College District Special Classes Students with Disabilities Special classes are instructional activities designed to address the educational limitations of students with disabilities who would be unable to substantially benefit from regular college classes even with appropriate support services or accommodations. Such classes shall be open to enrollment to students who do not have disabilities; however, to qualify for a special class, a majority of those enrolled in the class must be students with disabilities. Special classes may also refer, however, to distinct courses with their own CORs, designed either to meet educational objectives unique to a population with specific disabilities, or to supplement the standard objectives in an otherwise similar course with objectives unique to that population. In both cases, special classes must be primarily instructional in nature and must have objectives that fall within the instructional mission of the California community colleges. Such courses cannot be designed primarily to provide group activities or services (e.g., therapeutic activity, counseling, or assessment testing), but must instead provide systematic instruction in a body of content or skills whose mastery forms the basis of the student grade. Title 5 contains definitions and specific provisions related to approval of courses for students with disabilities. • Courses designed to meet the needs of students with specific functional limitations "shall be open to enrollment of students who do not have disabilities" (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 56028). • The course description published in the college catalog may note that it has been designed for students with specific disabilities, but the college may not restrict enrollment to such students, nor require students to register for classes through the Disabled Student Program and Services (DSPS) program or counselor, nor otherwise violate the open-enrollment provisions of state law (California Code of Regulations, Title 5, § 1006). • California Code of Regulations, Title 5, section 56029, allows extended repetitions of DSPS courses under certain circumstances. In compliance with California Code of Regulations, Title 5, section 56028, the following special class considerations are required when developing a COR pursuant to Title 5, section 55002. • Specify the disability or disabilities the course is designed to address • Describe the objectives the course is to fulfill as they relate to these disabilities • Describe why a special course is needed to meet this need, rather than its being met through accommodation in a regular course • Specify how it will be determined that the objectives have been achieved • Explain what disability-specific instructional methods, materials, equipment, etc., will be used and why Sections of courses in the regular curriculum that are merely adapted to enable students with disabilities to meet the regular course objectives in alternative ways do not require separate Chancellor’s Office approval. 103 Peralta Community College District Peralta Community College Process Chart Curricunet Action Course Change to Catalog Info Purpose Course Deactivation No plans to offer the course in the future Course Reactivation Reinstate course previously deactivated New course, institutionalizing x48 New Course Change something that appears in the catalog, includes DE addendum New Fee Based Course Non-Catalog Course Changes Updating text, content, objectives, New Program New degree or certificate Program Modification Changes to courses, units, title Program Deactivation No plans to offer degree/certificate in immedite future or ever College Action Approve, forward to CIPD CIPD Action Approve, forward to CIPD Approve, forward to CIPD Approve, forward to CIPD Approve, send to Curric Analyst for Board, Implement Approve, Implement Approve, Send to Board Approve, Send to Board Approve, Send to Board NA Approve Approve, forward to CIPD, Submit to State Approve, forward to CIPD, Submit to State Approve, forward to CIPD, Submit to State 104 Approve, Include in Board Rpt Board Action Not Required State Action New CB00 only if the following elements change: TOP code, degree applicability, units, SAM code, levels prior to transfer or noncredit category changes. Yes, Change to Inactive Approve Yes, Change to Active Approve Yes, New CB00 Approve NA NA NA NA Approve, Send to Board Approve Yes, either new program or substantial change Approve, Send to Board Approve Yes, either substantial or non substantial change Approve, Send to Board Approve Yes, either change to Inactive or Delete Peralta Community College District CB Code Listing There are numerous codes used by the California Community College Chancellor’s Office (CCCCO) to identify and analyze curriculum in the system. Some of these codes are assigned at the college level and some are assigned at the District level. In CurricUNET, these codes are only accessible for input by SuperAdmin Users. However, the faculty originator, in consultation with the department chair, the Curriculum Committee Chair, and in some instances, the articulation officer, should determine which codes are appropriate. CB-00 State ID or Control Number Every course has a unique state issued control number. This number is required when submitting enrollment data via the Chancellor’s Office Management Information Systems (MIS). The District Curriculum and Systems Technology Analyst requests this number after the Board of Trustees has approved the course. CB-03 TOP Code The TOP aggregates information about programs and courses. Each program and course must be assigned a TOP code that is consistent with its content. The Taxonomy of Programs, 6th Edition includes a list of TOP codes currently in use and is available under Resources on the Chancellor's Office Academic Affairs Division website http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum.aspx. CB-04 Course Credit Status D = Credit - Degree Applicable C = Credit - Not Degree Applicable N = Noncredit CB-05 Course Transfer Status A = Transferable to both UC and CSU. B = Transferable to CSU only. C = Not transferable CB-08 Course Basic Skill Status (PBS Status) Yes, Course IS a basic skills course = B if CB 22 is C or J No, Course is NOT a basic skills course = N if CB 22 is A, B, D, E, F, G, H, or I CB-09 SAM Code A = Apprenticeship B = Advanced Occupational C = Clearly Occupational D = Possibly Occupational E = Non-occupational CB-10 Course COOP Work Exp-ED N = is not part of a cooperative work experience education program. C = is part of a cooperative work experience education program. G = General Work Experience 105 Peralta Community College District CB-11 California Classification Codes A = Liberal Arts and Sciences B = Developmental Preparatory C = Adult and Secondary Basic Education D = Personal Development and Survival — Student without a Disability E = Courses for Students with Substantial Disabilities F = Parenting and Family Support G = Community and Civic Development H = General and Cultural I = Career-Technical Education J = Workforce Preparation Enhanced Funding K = Other Noncredit Enhanced Funding L = Non-Enhanced Funding CB-13 Special Class Status S = Yes, Approved for Disability N = No, Not Special Class CB-21 Levels Below Transfer (Course Prior to College Level Rubrics) The data element CB 21 indicates course levels in a sequence below the transferable course in Basic Skills English, ESL, mathematics, and reading. These sequences are used to report student progress through sequential basic skills courses statewide, to provide a matrix for the comparison of courses prior to transfer across all 112 community colleges, and to provide a common course level for reporting student placement. Faculty originators and department chairs are responsible for assigning the CB-21 code, with guidance from the Curriculum Chair and Curriculum Committee. It should be entered on the Codes page in CurricUNET prior to submission to the Curriculum Committee. Rubrics to assist faculty originators in assigning the appropriate CB-21 code are available on the CCCO web site at http://extranet.cccco.edu/Divisions/AcademicAffairs/CurriculumandInstructionUnit/Curriculum/CB21Cours ePriortoTransferRubrics.aspx. X= A = 1 level below transfer B = 2 levels below transfer C = 3 levels below transfer Y = Not applicable CB-22 Non Credit Course Category A = English as a Second Language B = Immigrant Education C = Elementary and Secondary Basic Skills D = Health and Safety Education E = Education Programs for Persons with Substantial Disabilities F = Parenting Education G = Family and Consumer Sciences H = Education Programs for Older Adults I = Short-term Vocational Programs with High Employment Potential J = Workforce Preparation Y = Not applicable 106 Peralta Community College District CB-23 Funding Agency Category A = This course was primarily developed using Economic Development funds B = This course was partially developed using Economic Development funds. (Economic Development funds exceed 40% of total development costs) Y = Not applicable CB-24 Program Course Status 1 = Program-applicable 2 = Stand-alone Sheryl: the info above is a combination of CurricUNET and the chart below. Is the chart below needed? Is it current? Identifier Name Values / Examples CB01 Course discipline and number Example: ENGL100 CB02 Course title Limited to 68 characters, including punctuation and spaces CB03 Course T.O.P. code Format: xxxxxx (no decimal) Examples: 010300;490310 CB04 Course Credit Status D = Credit - Degree Applicable C = Credit - Not Degree Applicable N = Noncredit CB05 Course Transfer Status A = Transferable to both UC and CSU. B = Transferable to CSU only. C = Not transferable CB06 Maximum Course Units The maximum number of units of academic credit a student may earn from enrolling in a single section of this course. Example: 03.50; 04.00 CB07 Minimum Course Units The minimum number of units of academic credit a student may earn from enrolling in a single section of this course. This value must be greater than zero. Example: 00.50; 01.00 CB08 Course Basic Skills Status Yes = B if CB 22 is C or J No = N if CB 22 is A, B, D, E, F, G, H, or I CB09 Course SAM Priority Code A = Apprenticeship B = Advanced Occupational C = Clearly Occupational D = Possibly Occupational E = Non-occupational CB10 Course Cooperative Work Experience Education Status This will always be “N” until a new policy is written 107 N = is not part of a cooperative work experience education program. C = is part of a cooperative work experience education program. Peralta Community College District Identifier Name Values / Examples CB11 Course Classification Status CB13 Course Special Class Status S = Yes N = No CB21 Course Prior to Transfer Level Note: Basic skills courses may be coded A-H, but non-basic skills courses are usually Y. Refer to CB21 data element for further information. CB22 Noncredit eligibility category Y = Not applicable (Always Noncredit) A = One level below transfer. B = Two levels below transfer. C = Three levels below transfer. D = Four levels below transfer. E = Five levels below transfer. F = Six levels below transfer. G = Seven levels below transfer. H = Eight levels below transfer. A = English as a Second Language B = Immigrant Education C = Elementary and Secondary Basic Skills D = Health and Safety Education E = Education Programs for Persons with Substantial Disabilities F = Parenting Education G = Family and Consumer Sciences H = Education Programs for Older Adults I = Short-term Vocational Programs with High Employment Potential J = Workforce Preparation CB23 Funding Agency Category A = This course was primarily developed using Economic Development funds B = This course was partially developed using Economic Development funds. (Economic Development funds exceed 40% of total development costs) Y = Not Applicable (Always a “Y”) CB24 Course Program Status 1 = Program-applicable 2 = Stand-alone A = Liberal Arts and Sciences B = Developmental Preparatory C = Adult and Secondary Basic Education D = Personal Development and Survival — Student without a Disability E = Courses for Students with Substantial Disabilities F = Parenting and Family Support G = Community and Civic Development H = General and Cultural I = Career-Technical Education J = Workforce Preparation Enhanced Funding K = Other Noncredit Enhanced Funding L = Non-Enhanced Funding 108 Peralta Community College District Performance Objectives (Exit Skills) vs. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) Performance Objectives, SLOs and the Course Outline of Record (COR) Performance Objectives (Exit Skills) are part of the COR and should closely align with course content. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) appear as a required addendum to the COR. Student learning outcomes, and their corresponding assessment methods, must be approved by the Learning Assessment Coordinator before a curriculum request (e.g. new course, course modification, distance education addendum, etc.) can be approved. There should be a clear distinction between performance objectives and student learning outcomes. However, both should align with the course content. What are performance objectives (exit skills)? Objectives make up the step-by-step learning goals of a course and are directly related to the specific elements of the course content. There will be many individual objectives for any class. Although the number of individual objectives will vary according to course content, a reasonable number of objectives would range from 6 to 20. What are student learning outcomes? Student learning outcomes are broad, overarching statements of what a student will be able to do upon completion of the course. Usually 2-3 outcomes are adequate. *** Suggested Definitions from the Academic Senate for California Community Colleges Objectives. Objectives are small steps that lead toward a goal, for instance the discrete course content that faculty cover within a discipline. Objectives are usually more numerous and create a framework for the overarching Student Learning Outcomes which address synthesizing, evaluating and analyzing many of the objectives. Student Learning Outcomes (SLO). Student learning outcomes (SLOs) are the specific observable or measurable results that are expected subsequent to a learning experience. These outcomes may involve knowledge (cognitive), skills (behavioral), or attitudes (affective) that provide evidence that learning has occurred as a result of a specified course, program activity, or process. An SLO refers to an overarching outcome for a course, program, degree or certificate, or student services area (such as the library). SLOs describe a student’s ability to synthesize many discreet skills using higher level thinking skills and to produce something that asks them to apply what they’ve learned. SLOs usually encompass a gathering together of smaller discrete objectives (see definition above) through analysis, evaluation and synthesis into more sophisticated skills and abilities. Source: SLO Terminology Glossary (Academic Senate for California Community Colleges) 109 Peralta Community College District Glossary of Acronyms Used in the Curriculum World AACRAO: American Association of Collegiate Registrars and Admissions Officers AARTS: Army/American Council on Education Registry Transcript System AA-T/AS-T: Associate Degrees for Transfer (see SB 1440) ACE: American Council on Education ADT: Associate Degree for Transfer (shorthand for AA-T/AS-T) AI: CSU American Institutions Requirement (also known as “Code” Requirement) AICCU: Association of Independent California Colleges and Universities AO: Articulation Officer AP: Advanced Placement ASCCC: Academic Senate for California Community Colleges ASCSU: Academic Senate of the California State University ASSIST: Articulation System Stimulating Interinstitutional Student Transfer BOARS: UC Board of Admissions and Relations with Schools C-ID: Course Identification Numbering System CAN: California Articulation Number System CAP: California Acceleration Project CCC: California Community College(s) CCCCO: California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office CIAC: California Intersegmental Articulation Council CLEP: College-Level Examination Program COR: Course Outline of Record CPEC: California Postsecondary Education Commission CSU: The California State University CSUCO: California State University Chancellor’s Office CSU GE-B: General Education-Breadth pattern for CSU transfers CurricUNET: Curriculum Management System DANTES: Defense Activity for Non-Traditional Education Support DD: Department of Defense (as in Form DD-214 or DD-295) DE: Distance Education DL: Distance Learning DSST: DANTES Subject Standardized Tests EAP: Early Assessment Program ECE: Excelsior College Examinations ECO: Extended Course Outline EM: Executive Memorandum EMOC: Executive Management Oversight Committee EO: Executive Order ESL: English as a Second Language ETS: Ensuring Transfer Success (also: Educational Testing Service, but refers to the former in the articulation community) FAFSA: Free Application for Federal Student Aid FERPA: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act GE: General Education GEAC: General Education Advisory Committee GPA: Grade Point Average ICAS: Intersegmental Committee of Academic Senates IGETC: Intersegmental General Education Transfer Curriculum IMPAC: Intersegmental Major Preparation Articulated Curriculum K12: Kindergarten through 12th Grade LDTP: Lower Division Transfer Patterns LOTE: Language Other Than English (see IGETC) MOOC: Massive Open Online Course MOU: Memorandum of Understanding NCIAC: Northern California Intersegmental Articulation Council OSCAR: Online Services for Curriculum and Articulation Review PLA: Prior Learning Assessment 110 Peralta Community College District RFP: Request for Proposals SB 1440: Senate Bill 1440 (see STAR Act) SCHEC: South Coast Higher Education Council SCIAC: Southern California Intersegmental Articulation Council SCIGETC: Science Intersegmental General Education Transfer Curriculum SOC: Servicemembers Opportunity Colleges STAR Act: Student Transfer Achievement Reform Act (see SB 1440) Statway: A one-year alternative curriculum concentrating on statistical content with requisite arithmetic and algebraic concepts taught and applied in the context of statistics. It is structured especially to serve students planning to transfer and continue further studies in humanities or social sciences. STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math TAG: Transfer Admission Guarantee TAP: Transfer Admission Planner TCA: Transfer Course Agreement (see UC TCA) TCDA: Transfer Center Directors Association TCSU: Transfer-CSU Course Designation (see LDTP) TCW: Transfer Counselor Website Title 5: The part of the California Code of Regulations governing Education TMC: Transfer Model Curriculum (see SB 1440) UC: The University of California UCOP: University of California Office of the President UC TCA: University of California Transferable Course Agreements WASC: Western Association of Schools and Colleges 111 Peralta Community College District Curriculum Review Planning Report This is a sample of the instructions given to faculty at Laney College to assist them in their periodic curriculum review process. Curriculum Review Planning Report - Laney College Name of the Discipline: Date of the Report: List Faculty Involved in Developing this Report: Please complete this evaluation before your presentation date with the curriculum committee. We ask that you use the checklist on the reverse side to let us know where you are in your curriculum updating and your departmental methods for analyzing and evaluating the contents of course and degree/certificate offerings. Let us know what methods you use to maintain the integrity of academic standards and achieve consistency within the instructional program? COURSES 1) List courses in the catalog and the date of the most recent course outline updates: Course Number Course Name Date of Most Recent Update DEGREES & CERTIFICATE PROGRAM 2) List degree and certificate programs offered: Name Degree Certificate Course Verification Checklist Completed □ Yes □ No 112 Date of Most Recent Update Peralta Community College District CURRICULUM REVIEW (COURSE VERIFICATION CHECKLIST) Completed To be accomplished by Please use CurricUNET to review all courses taught in your department and any certificates/degrees offered 113 Peralta Community College District 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 COURSE USE Has the course been offered in the last two years? If not, consider deactivating the course. DESCRIPTION/CATALOG INFORMATION Does the course description accurately describe the course? COURSE ALIGNMENT Does the course content align with course objectives? Do the course objectives align with the overarching student learning outcomes? STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES Does the course/program have up-to-date student learning outcomes and assessment methods LECTURE/LAB CONTENT, METHODS Are course content and teaching methods listed in the COR current, appropriate and effective? To what extent are writing skills and critical thinking reinforced? TEXTBOOK CURRENCY Is the textbook current? (Transfer institutions require textbooks with a publication date that is within the 5 years) COLLEGE LEVEL MATERIALS For degree-applicable courses, are the reading materials college level? REQUISITES Have you completed the Content Review part of the outline? Have you reviewed and revalidated the prerequisites, co-requisites, recommended preparations? (Must be done at least every 6 years) DISTANCE EDUCATION Is there an online option for your courses? If so, is the distance education addendum current and accurate? STAND ALONE COURSES Are any of your courses not degree applicable? TRANSFER COURSES Do transfer level courses meet CSU/UC standards? (Contact Articulation Officer Laura Bollentino (lbollentino@peralta.edu) if you have questions) DEGREES AND CERTIFICATES Are the courses appropriate? Are the units required appropriate? Are the descriptions of degrees/certificates current? 114