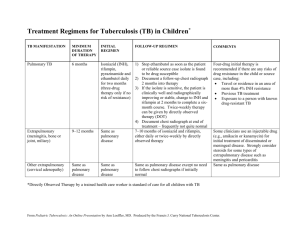
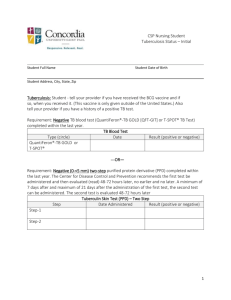
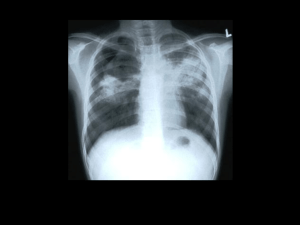
2. While registering the child to the school Mantus test was made to
advertisement

2. While registering the child to the school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed. Test result is negative. What does this test result mean? Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus 3. Study of bacteriological sputum specimens stained by the Ziel-Neelsen method revealed some bright-red acid-resistant bacilli that were found in groups or singularly. When they were inoculated onto the nutrient media, the signs of their growth show up on the 10-15 day. These bacteria relate to the following family: Micobacterium tuberculosis Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Histoplasma dubrosii Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis Coxiella burnettii 4. Autopsy of a 17 year old girl who died from pulmonary failure revealed a small area of caseous necrosis in the inferior lobe of the right lung, and occurences of caseous necrosis in the bronchopulmonary, bronchial and bifurcational lymph nodes. What is the most probable postmortem diagnosis? Primary tuberculosis Hematogenous progression of primary tuberculosis Hematogenous tuberculosis with predominant lung affection Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia under secondary tuberculosis 5. A patient ill with tuberculosis died from progressing cardiopulmonary decompensation. Autopsy in the area of the right lung apex revealed a cavity 5 cm in diameter communicating with lumen of a segmental bronchus. On the inside cavity walls are covered with caseous masses with epithelioid and Langhans cells beneath them. What morphological form of tuberculosis is it? Acute cavernous tuberculosis Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia Infiltrative tuberculosis Acute focal tuberculosis 7. While enrolling a child to school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed. The test result is negative. What does this test result mean? Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus 8. While enrolling a child to school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed. The test result is negative. What does this test result mean? Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis 9. Autopsy of a 17 year old girl who died from pulmonary failure revealed a small area of caseous necrosis in the inferior lobe of the right lung, and occurences of caseous necrosis in the bronchopulmonary, bronchial and bifurcational lymph nodes. What is the most probable postmortem diagnosis? Hematogenous progression of primary tuberculosis Hematogenous tuberculosis with predominant lung affection Caseous pneumonia under secondary tuberculosis Tuberculoma Primary tuberculosis 11. Microscopic analysis of tissue sampling from patients skin reveals granulomas that consist of epithelioid cells surrounded mostly by T-lymphocytes. Among epithelioid cells there are solitary giant multinuclear cells of Pirogov-Langhans typ. In the centre of some granulomas there are areas of caseous necrosis. Blood vessels are absent. What disease are the described granulomas typical for? Tuberculosis Syphilis Leprosy Rhinoscleroma Glanders 12. Microscopic analysis of tissue sampling from patients skin reveals granulomas that consist of epithelioid cells surrounded mostly by T-lymphocytes. Among epithelioid cells there are solitary giant multinuclear cells of Pirogov-Langhans type. In the centre of some granulomas there are areas of caseous necrosis. Blood vessels are absent. What disease are the described granulomas typical for? Tuberculosis Syphilis Leprosy Rhinoscleroma Glanders 13. Autopsy of a man, who died from acute posthaemorrhagic anaemia resulting from pulmonary haemorrhage, revealed the following: macroscopically - lung apexes were deformed, their section showed multiple whitish-grey foci 10-15 mm in diameter and multiple pathological cavities up to 15 mm in diameter with dense walls. Microscopically: the cavity walls presented proliferation of the connective tissue infiltrated by epithelioid cells, multicellular giant cells and lymphocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis? Progressing tuberculosis complex Hematogenic disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis Hematogenic miliary pulmonary tuberculosis Secondary fibrocavernous tuberculosis Primary tuberculosis without signs of progress 14. Autopsy of a man, who died from acute posthaemorrhagic anaemia resulting from pulmonary haemorrhage, revealed the following: macroscopically - lung apexes were deformed, their section showed multiple whitish-grey foci 10-15 mm in diameter and multiple pathological cavities up to 15 mm in diameter with dense walls. Microscopically: the cavity walls presented proliferation of the connective tissue infiltrated by epithelioid cells, multicellular giant cells and lymphocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis? Secondary fibrocavernous tuberculosis Primary tuberculosis without signs of progress Progressing tuberculosis complex Hematogenic disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis Hematogenic miliary pulmonary tuberculosis 15. Microscopic analysis of tissue sampling from patients skin reveals granulomas that consist of epithelioid cells surrounded mostly by T-lymphocytes. Among epithelioid cells there are solitary giant multinuclear cells of Pirogov-Langhans type. In the centre of some granulomas there are areas of caseous necrosis. Blood vessels are absent. What disease are the described granulomas typical for? Tuberculosis Syphilis Leprosy Rhinoscleroma Glanders 19. A patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of occasional pains at the bottom of abdomen that get worse during menses, weakness, indisposition, nervousness, some dark bloody discharges from vagina on the day before and the day after menses. Bimanual examination results: body of womb is enlarged, appendages cannot be determined, posterior fornix has tuberous surface. Laparoscopy results: ovaries, peritoneum of rectouterine pouches and pararectal fat are covered with "cyanotic spots". What is the most probable diagnosis? Polycystic ovaries Chronic salpingitis Genital organs tuberculosis Widespread form of endometriosis Ovarian cystoma 20. A 3 year old child has been suffering from fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis for 4 days. He has been taking sulfadimethoxine. Today it has fever up to 39oC and maculopapular rash on its face. Except of rash the childs skin has no changes. What is your diagnosis? Scarlet fever Rubella Pseudotuberculosis Measles Allergic rash 21. During an operation for presumed appendicitis the appendix was found to be normal; however, the terminal ileum is evidently thickened and feels rubbery, its serosa is covered with grayish-white exudate, and several loops of apparently normal small intestine are adherent to it. The most likely diagnosis is: Acute ileitis Ileocecal tuberculosis Crohns disease of the terminal ileum Perforated Meckels diverticulum Ulcerative colitis 22. A patient consulted a nurse about attacks of morning cough with lots of sputum, often with a foul smell. What disease are these symptoms typical for? Cancer of lungs Pneumonia Pulmonary tuberculosis Multiple bronchiectasis Chronic bronchitis 25. A patient is 50 years old, works as a builder with 20 years of service recor d. He was admitted to the hospital for chest pain, dry cough, minor dyspnea. Objectively: sallow skin, acrocyanosis, asbestos warts on the hands. In lungs - rough respiration, diffuse dry rales. The x-ray picture shows intensification of pulmonary pattern, signs of pulmonary emphysema. What is the most likely diagnosis? Lung cancer Chronic obstructive bronchitis Tuberculosis Asbestosis Pneumonia 26. A 50-year-old male suburbanite underwent treatment in rural outpatient clinic for pneumonia. The treatment didnt have effect and the disease got complicated by exudative pleuritis. What prevention and treatment facility should the patient be referred to for further aid? Phthisio-pulmonological dispensary Tuberculosis dispensary Central district hospital Municipal hospital Regional hospital 27. A 15-year-old child presents with puffiness in the region of the mandible branch; enlarged, dense and painless lymph nodes adhering to the surrounding tissues. X-ray picture of mandible branch shows a well-defined bone resorption area containing small sequestra. After Mantoux test a 12 mm papule was noted. What is the most likely diagnosis? Tuberculosis of mandible branch Mandibular actinomycosis Chronic osteomyelitis of mandible branch Acute mandibular osteomyelitis Ewings sarcoma 28. A 58 year old patient applied to an oral surgeon and complained about painful ulcer on the lateral surface of his tongue. Objectively: left lateral surface of tongue has a roundish ulcer with undermined soft overhanging edges, palpatory painful, ulcer floor is slightly bleeding and covered with yellowish nodules. What is the most probable diagnosis? Tuberculosis Syphilis Traumatic ulcer Actinomycosis Trophic ulcer 29. Fluorography of a 45 y.o. man revealed some little intensive foci with indistinct outlines on the top of his right lung for the first time. The patient doesnt feel worse. He has been smoking for many years. Objectively: pulmonary sound above lungs on percussion, respiration is vesicular, no rales. Blood count is unchanged. What is the most probable diagnosis? Focal pulmonary tuberculosis Peripheral cancer of lung Eosinophilic pneumonia Bronchopneumonia Disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis 30. A 5-year-old boy was progressively getting worse compared to the previous 2 months. A chest x-ray has shown right middle lobe collapse. A tuberculin skin test was strongly positive. What is the most characteristic finding in primary tuberculosis? Hematogenous dissemination leading to extrapulmonary tuberculosis Atelectasis with obstructive pneumonia Miliary tuberculosis Hilar or paratracheal lymph node enlargement Cavity formation 31. While registering the child to the school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed test result is negative. What does this result of the test mean? Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis 32. Autopsy of a 48 y.o. man revealed a round formation 5 cm in diameter with clearcut outlines in the region of the 1st segment of his right lung. This formation was encircled with a thin layer of connective tissue full of white brittle masses. Make a diagnosis of the secondary tuberculosis form: Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis Tuberculoma Acute focal tuberculosis Caseous pneumonia Acute cavernous tuberculosis 35. A 15-year-old child presents with puffiness in the region of the mandible branch; enlarged, dense and painless lymph nodes adhering to the surrounding tissues. X-ray picture of mandible branch shows a well-defined bone resorption area containing small sequestra. After Mantoux test a 12 mm papule was noted. What is the most likely diagnosis? Tuberculosis of mandible branch Mandibular actinomycosis Chronic osteomyelitis of mandible branch Acute mandibular osteomyelitis Ewings sarcoma 36. A 39-year-old patient complains of some soft ulcers and tubercles on the oral mucosa, gingival haemorrhage, pain and loosening of teeth. Objectively: mucous membrane of tongue and gums presents single ulcers with soft, swollen, slightly painful edges, covered with a yellow film. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged, soft, painless, not adherent to the surrounding tissues. What is your provisional diagnosis? Lupus tuberculosis Lepra Tertiary syphilis Scrofuloderma Suttons aphthae 37. A 58 year old patient applied to an oral surgeon and complained about painful ulcer on the lateral surface of his tongue. Objectively: left lateral surface of tongue has a roundish ulcer with undermined soft overhanging edges, palpatory painful, ulcer floor is slightly bleeding and covered with yellowish nodules. What is the most probable diagnosis? Tuberculosis Syphilis Traumatic ulcer Actinomycosis Trophic ulcer 38. While registering the child to the school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed test result is negative. What does this result of the test mean? Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus 39. Study of bacteriological sputum specimens stained by the Ziel-Neelsen method revealed some bright-red acid-resistant bacilli that were found in groups or singularly. When inoculated onto the nutrient media, the signs of their growth show up on the 10-15 day. These bacteria relate to the following family: Micobacterium tuberculosis Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Histoplasma dubrosii Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis Coxiella burnettii 40. Autopsy of a 17 year old girl who died from pulmonary failure revealed a small area of caseous necrosis in the inferior lobe of the right lung, and occurences of caseous necrosis in the bronchopulmonary, bronchial and bifurcational lymph nodes. What is the most probable postmortem diagnosis? Primary tuberculosis Hematogenous progression of primary tuberculosis Hematogenous tuberculosis with predominant lung affection Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia under secondary tuberculosis 41. A patient ill with tuberculosis died from progressing cardiopulmonary decompensation. Autopsy in the area of the right lung apex revealed a cavity 5 cm in diameter communicating with lumen of a segmental bronchus. On the inside cavity walls are covered with caseous masses with epithelioid and Langhans cells beneath them. What morphological form of tuberculosis is it? Acute cavernous tuberculosis Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia Infiltrative tuberculosis Acute focal tuberculosis 42. Autopsy of a man who had tuberculosis revealed a 3x2 cm large cavity in the superior lobe of the right lung. The cavity was interconnected with a bronchus, its wall was dense and consisted of three layers: the internal layer was pyogenic, the middle layer was made by tuberculous granulation tissue and the external one was made by connective tissue. What is the most likely diagnosis? Fibrous focal tuberculosis Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis Tuberculoma Acute cavernous tuberculosis Acute focal tuberculosis 43. Autopsy of a man who had tuberculosis revealed a 3x2 cm large cavity in the superior lobe of the right lung. The cavity was interconnected with a bronchus, its wall was dense and consisted of three layers: the internal layer was pyogenic, the middle layer was made by tuberculous granulation tissue and the external one was made by connective tissue. What is the most likely diagnosis? Acute cavernous tuberculosis Acute focal tuberculosis Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis Fibrous focal tuberculosis Tuberculoma 44. Study of bacteriological sputum specimens stained by the Ziel-Neelsen method revealed some bright-red acid-resistant bacilli that were found in groups or singularly. When inoculated onto the nutrient media, the signs of their growth show up on the 10-15 day. These bacteria relate to the following family: Micobacterium tuberculosis Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Histoplasma dubrosii Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis Coxiella burnettii 45. Autopsy of a man, who died from acute posthaemorrhagic anaemia resulting from pulmonary haemorrhage, revealed the following: macroscopically - lung apexes were deformed, their section showed multiple whitish-grey foci 10-15 mm in diameter and multiple pathological cavities up to 15 mm in diameter with dense walls. Microscopically: the cavity walls presented proliferation of the connective tissue infiltrated by epithelioid cells, multicellular giant cells and lymphocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis? Secondary fibrocavernous tuberculosis Primary tuberculosis without signs of progress Progressing tuberculosis complex Hematogenic disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis Hematogenic miliary pulmonary tuberculosis 46. Microscopic analysis of tissue sampling from patients skin reveals granulomas that consist of epithelioid cells surrounded mostly by T-lymphocytes. Among epithelioid cells there are solitary giant multinuclear cells of Pirogov-Langhans type. In the centre of some granulomas there are areas of caseous necrosis. Blood vessels are absent. What disease are the described granulomas typical for? Tuberculosis Syphilis Leprosy Rhinoscleroma Glanders 48. X-ray picture of chest shows a density and an abrupt decrease in the upper lobe of the right lung. The middle and lower lobe of the right lung exhibit significant pneumatization. The right pulmonary hilum comes up to the dense lobe. In the upper and middle parts of the left pulmonary field there are multiple focal shadows. In the basal region of the left pulmonary field there are clear outlines of two annular shadows with quite thick and irregular walls. What disease is this X-ray pattern typical for? Fibro-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis Atelectasis of the right upper lobe Abscessing pneumonia Peripheral cancer Pancoast tumour 49. A 15-year-old child presents with puffiness in the region of the mandible branch; enlarged, dense and painless lymph nodes adhering to the surrounding tissues. X-ray picture of mandible branch shows a well-defined bone resorption area containing small sequestra. After Mantoux test a 12 mm papule was noted. What is the most likely diagnosis? Tuberculosis of mandible branch Mandibular actinomycosis Chronic osteomyelitis of mandible branch Acute mandibular osteomyelitis Ewings sarcoma 50. A 39-year-old patient complains of some soft ulcers and tubercles on the oral mucosa, gingival haemorrhage, pain and loosening of teeth. Objectively: mucous membrane of tongue and gums presents single ulcers with soft, swollen, slightly painful edges, covered with a yellow film. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged, soft, painless, not adherent to the surrounding tissues. What is your provisional diagnosis? Lupus tuberculosis Lepra Tertiary syphilis Scrofuloderma Suttons aphthae 51. A 42-year-old patient complains of a painful ulcer in the mouth that is getting bigger and does not heal over 1,5 months. Objectively: on the buccal mucosa there is a shallow soft ulcer 2 cm in diameter with irregular undermined edges. The ulcer floor is uneven and covered with yellow-gray coating. The ulcer is surrounded by many small yellowish tubercles. Regional lymph nodes are elastic, painful, matted together. Which disease is characterized by such symptoms? Tuberculosis Syphilis Lichen planus Cancer Ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis 52. A 48-year-old patient complains of subfebrile temperature and a growing ulcer on the gingival mucosa around the molars; looseness of teeth in the affected area, cough. Objectively: gingival mucosa in the region of the lower left molars has two superficial, extremely painful ulcers with undermined edges. The ulcers floor is yellowish, granular, covered with yellowish, and sometimes pink granulations. The ulcers are surrounded by the tubercles. Dental cervices are exposed, there is a pathological tooth mobility. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged and make dense matted together groups. What is the most likely diagnosis? Tuberculosis Syphilis Acute aphthous stomatitis Infectious mononucleosis Decubital ulcer 53. A 58 year old patient applied to an oral surgeon and complained about painful ulcer on the lateral surface of his tongue. Objectively: left lateral surface of tongue has a roundish ulcer with undermined soft overhanging edges, palpatory painful, ulcer floor is slightly bleeding and covered with yellowish nodules. What is the most probable diagnosis? Tuberculosis Syphilis Traumatic ulcer Actinomycosis Trophic ulcer 54. While registering the child to the school Mantus test was made to define whether revaccination was needed test result is negative. What does this result of the test mean? Absence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of cell immunity to the tuberculosis Absence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus Absence of antitoxic immunity to the tuberculosis Presence of antibodies for tubercle bacillus 55. Study of bacteriological sputum specimens stained by the Ziel-Neelsen method revealed some bright-red acid-resistant bacilli that were found in groups or singularly. When they were inoculated onto the nutrient media, the signs of their growth show up on the 10-15 day. These bacteria relate to the following family: Micobacterium tuberculosis Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Histoplasma dubrosii Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis Coxiella burnettii 56. Autopsy of a man who had tuberculosis revealed a 3x2 cm large cavity in the superior lobe of the right lung. The cavity was interconnected with a bronchus, its wall was dense and consisted of three layers: the internal layer was pyogenic, the middle layer was made by tuberculous granulation tissue and the external one was made by connective tissue. What is the most likely diagnosis? Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis Fibrous focal tuberculosis Tuberculoma Acute focal tuberculosis Acute cavernous tuberculosis 57. Autopsy of a 17 year old girl who died from pulmonary failure revealed a small area of caseous necrosis in the inferior lobe of the right lung, and occurences of caseous necrosis in the bronchopulmonary, bronchial and bifurcational lymph nodes. What is the most probable postmortem diagnosis? Primary tuberculosis Hematogenous progression of primary tuberculosis Hematogenous tuberculosis with predominant lung affection Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia under secondary tuberculosis 58. A patient ill with tuberculosis died from progressing cardiopulmonary decompensation. Autopsy in the area of the right lung apex revealed a cavity 5 cm in diameter communicating with lumen of a segmental bronchus. On the inside cavity walls are covered with caseous masses with epithelioid and Langhans cells beneath them. What morphological form of tuberculosis is it? Acute cavernous tuberculosis Tuberculoma Caseous pneumonia Infiltrative tuberculosis Acute focal tuberculosis 60. A child entering the school for the first time was given Mantoux test in order to determine if there was a need for revaccination. The reaction was negative. What is the meaning of this test result? No cell-mediated immunity to tuberculosis No anti-toxic immunity to tuberculosis Availability of cell-mediated immunity to tuberculosis No antibodies to the tuberculosis bacteria Presence of antibodies to the tuberculosis bacteria 61. Study of the biopsy material revealed a granuloma consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages with foamy cytoplasm (Mikulicz cells), many hyaline globules. What disease can you think of? Leprosy Syphilis Tuberculosis Rhinoscleroma Actinomycosis 62. Autopsy of a young man revealed some lung cavities with inner walls made up of granulation tissue with varying degrees of maturity; pronounced pneumosclerosis and bronchiectasis. Some cavities had caseation areas. What is your presumptive diagnosis? Infiltrative tuberculosis Acute cavernous tuberculosis Bronchiectasis Caseous pneumonia Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis 63. A 45-year-old patient, a sailor, was hospitalized on the 2nd day of the disease. A week ago he returned from India. Complains of body temperature of 41°C, severe headache, dyspnea, cough with frothy rusty sputum. Objectively: the patient is pale, mucous membranes are cyanotic, breathing rate is 24/min, tachycardia is present. In lungs: diminished breath sounds, moist rales over both lungs, crepitation. What is the most likely diagnosis? Miliary tuberculosis Pneumonic plaque Sepsis Ornithosis Influenza 64. A 40-year-old patient complains of fever up to 39°C, cough with sputum and blood admixtures, dyspnea, weakness, herpetic rash on the lips. Objectively: respiration rate - 32/min. Under the shoulder blade on the right the increased vocal fremitus and dullness of percussion sound were revealed. Auscultation revealed bronchial respiration. Blood count: WBCs – 14109/l, ESR - 35 mm/h. What is the provisional diagnosis? Exudative pleuritis Cavernous tuberculosis of the right lung Right-sided croupous pneumonia Lung cancer Focal right-sided pneumonia 65. X-ray picture of chest shows a density and an abrupt decrease in the upper lobe of the right lung. The middle and lower lobe of the right lung exhibit significant pneumatization. The right pulmonary hilum comes up to the dense lobe. In the upper and middle parts of the left pulmonary field there are multiple focal shadows. In the basal region of the left pulmonary field there are clear outlines of two annular shadows with quite thick and irregular walls. What disease is this X-ray pattern typical for? Atelectasis of the right upper lobe Peripheral cancer Abscessing pneumonia Pancoast tumour Fibro-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis 66. A 48-year-old patient complains of weakness, subfebrile temperature, aching pain in the kidney region. These presentations turned up three months ago after hypothermia. Objectively: kidneys are painful on palpation, there is bilaterally positive Pasternatskys symptom. Urine test res: acid reaction, pronounced leukocyturia, microhematuria, minor proteinuria - 0,165-0,33 g/l. After the urine sample had been inoculated on conventional media, bacteriuria were not found. What research is most required in this case? Zimnitsky urine test Daily proteinuria Nechiporenko urine test Isotope renography Urine test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis 67. X-ray picture of chest shows a density and an abrupt decrease in the upper lobe of the right lung. The middle and lower lobe of the right lung exhibit significant pneumatization. The right pulmonary hilum comes up to the dense lobe. In the upper and middle parts of the left pulmonary field there are multiple focal shadows. In the basal region of the left pulmonary field there are clear outlines of two annular shadows with quite thick and irregular walls. What disease is this X-ray pattern typical for? Fibro-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis Atelectasis of the right upper lobe Abscessing pneumonia Peripheral cancer Pancoast tumour 68. A 15-year-old child presents with puffiness in the region of the mandible branch; enlarged, dense and painless lymph nodes adhering to the surrounding tissues. X-ray picture of mandible branch shows a well-defined bone resorption area containing small sequestra. After Mantoux test a 12 mm papule was noted. What is the most likely diagnosis? Tuberculosis of mandible branch Mandibular actinomycosis Chronic osteomyelitis of mandible branch Acute mandibular osteomyelitis Ewings sarcoma 69. A 39-year-old patient complains of some soft ulcers and tubercles on the oral mucosa, gingival haemorrhage, pain and loosening of teeth. Objectively: mucous membrane of tongue and gums presents single ulcers with soft, swollen, slightly painful edges, covered with a yellow film. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged, soft, painless, not adherent to the surrounding tissues. What is your provisional diagnosis? Lupus tuberculosis Lepra Tertiary syphilis Scrofuloderma Suttons aphthae 70. A 42-year-old patient complains of a painful ulcer in the mouth that is getting bigger and does not heal over 1,5 months. Objectively: on the buccal mucosa there is a shallow soft ulcer 2 cm in diameter with irregular undermined edges. The ulcer floor is uneven and covered with yellow-gray coating. The ulcer is surrounded by many small yellowish tubercles. Regional lymph nodes are elastic, painful, matted together. Which disease is characterized by such symptoms? Tuberculosis Syphilis Lichen planus Cancer Ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis