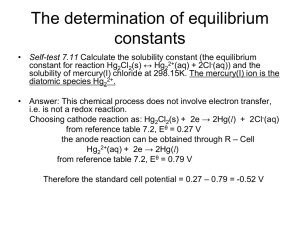
e* + ____ H+ * ____ Cr3+ + ____ H2O
advertisement

AP Chemistry Quarter 3 Exam 1 – Practice February 10, 2012 This exam consists of two sections. You will have 55 minutes to complete it. When you finish the multiple-choice section and turn in your scantron sheet, you may take out your calculator. Name: _______________________________________________ Block: ______ Multiple-Choice Section – Write “1A” on the Test Name line of the scantron sheet. You may use your periodic table only. You may NOT use a calculator. Please record all answers on the scantron sheet. You may use a MAXIMUM of 25 minutes on this section. 1. A chemist is conducting an experimental study of a particular reaction. She finds that the value of the equilibrium constant, K, decreases as the temperature increases. Based on this information, which of the following can she conclude? I. The activation energy for the reaction is negative. II. The standard entropy change for the reaction, ΔS˚, is negative. III. The standard enthalpy change for the reaction, ΔH˚, is negative. (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III W(g) + 2 X(g) Y(g) + Z(g) ΔH˚ = +122 kJ/mol 2. What conditions of temperature and pressure would allow a chemist to maximize the yield of the products in the hypothetical reaction shown above? (A) Low T, Low P (B) Low T, High P (C) High T, Low P (D) High T, High P (E) Low T, but pressure makes no difference. 3. 2 PbS(s) + 2 CO(g) + 3 O2(g) 2 Pb(l) + 2 SO2(g) + 2 CO2(g) For the reaction shown above, which change would cause an increase in the amount of Pb(l) produced? I. Adding PbS(s) II. Removing SO2(g) III. Increasing the volume of the container (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) II and III only 4. For which of these reactions is the value of ΔS˚ positive? (A) CaCO3(s) CO2(g) + CaO(s) (B) Hg(l) Hg(s) (C) Pb2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) PbI2(s) (D) H2O(l) + CO2(g) H2CO3(aq) (E) 2 Ag+(aq) + Cu(s) 2 Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) 5. Which of these reactions will be spontaneous under standard conditions at any temperature? (A) None of these will be spontaneous at any temperature. (B) Reaction B: ΔH˚ = -100 kJ mol-1, ΔS˚ = + 32 J mol-1 K-1 (C) Reaction C: ΔH˚ = +27 kJ mol-1, ΔS˚ = + 85 J mol-1 K-1 (D) Reaction D: ΔH˚ = -1330 kJ mol-1, ΔS˚ = -18 J mol-1 K-1 (E) Reaction E: ΔH˚ = +450 kJ mol-1, ΔS˚ = - 102 J mol-1 K-1 HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(l) + CO32-(aq) ΔH = -41.4 kJ [CO3 2 ] 6. When the reaction represented by the equation above is at equilibrium at 1 atm and 25 C, the ratio [HCO3 ] can be increased by doing which of the following? (A) Adding H+ to react with the OH− (B) Adding a catalyst (C) Diluting the solution with distilled water (D) Bubbling neon gas through the solution (E) Decreasing the temperature o 7. Which of the following must be true for a reaction for which the activation energy is the same for both the forward and reverse reactions? (A) A catalyst is present. (B) The reaction order can be obtained directly from the balanced equation. (C) The reaction order is zero. (D) ΔS° for the reaction is zero. (E) ΔH° for the reaction is zero. 8. When solid NH4SCN is mixed with solid Ba(OH)2 in a closed container, the temperature drops and a gas is produced. Which of the following indicates the correct signs for ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS for this process? ΔG ΔH ΔS (A) – – – (B) – + – (C) – + + (D) + – + (E) + – – 9. Which of the equilibrium systems shown below will exhibit a shift to the right (toward the products) when the pressure is increased by lowering the volume of the system? I. C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) II. Br2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 BrCl(g) III. Na2CO3(s) Na2O(s) + CO2(g) (A) I only III (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and HF(aq) H+(aq) + F−(aq) ΔS˚ < 0 10. When hydrofluoric acid, HF, dissociates in water, the entropy of the system is decreased, despite an increase in the number of dissolved particles. Which of the following best helps account for this phenomenon? (A) H+ ions are smaller than F− ions. (B) The bonds in HF are weaker than the bonds in H2O. (C) Water molecules surrounding the dissolved ions are more ordered than molecules in pure water. (D) The H+ an F− ions are more free to move around when dissociated than when together. (E) In solution, the average distance between particles is greater when the particles are dissociated. 11. For which of the following processes does the entropy of the system increase? I. 2 Mg(s) + O2(g) 2 MgO(s) II. Mixing of liquid ethanol and liquid water III. Crystallization of solid iodine from an iodine solution (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III 12. A reaction system is at equilibrium. Which of the following changes would cause a change in the value of the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the system? (A) Adding more products to the system (B) Removing reactants from the system (C) Adding a catalyst to the system (D) Reducing the volume of the system (E) Cooling the system in an ice bath 13. Which of the following is true for any system at equilibrium? (A) ΔG° < 0 (B) ΔH = TΔS (C) ΔS = 0 (D)ΔG = TΔS (E) ΔH° > 0 14. A certain reaction is spontaneous at temperatures below 300 K and non-spontaneous at temperatures above 300 K. The value of ΔS˚ for the reaction is known to be -50 J mol-1 K-1. Assuming that ΔH˚ and ΔS˚ do not change appreciably with temperature, determine the value of ΔH˚ for this reaction. (A) -15 kJ mol-1 (B) – 1.5 kJ mol-1 (C) 1.5 kJ mol-1 (D) 15 kJ mol-1 (E) 30 kJ mol-1 C2H4(g) + Cl2(g) C2H4Cl2(g) ΔH° = -201 kJ mol-1 15. The equilibrium system represented above is contained in a sealed, rigid vessel. Which of the following will increase if the temperature of the mixture is raised? I. The rate of the forward reaction II. The rate of the reverse reaction III. The total number of moles of gas in the vessel (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III C2H4(g) + Cl2(g) C2H4Cl2(g) ΔH° = -201 kJ mol-1 16. Which of the steps in the reaction shown above is/are exothermic? I. Breaking the bonds in C2H4 II. Breaking the bonds in Cl2 III. Forming the bonds in C2H4Cl2 (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III 17. The chemical equation for the dissociation of hypochlorous acid is shown below HOCl(aq) + H2O (l) H3O+(aq) + OCl-(aq) K = 3.5 x 10-8 at 25oC If the initial concentration of HOCl at 25oC is 0.7 M, what is the concentration of HOCl at equilibrium? (A) 0.35 M (B) 2.0x107 M (C) 4.95x10-4 M (D) 2.45x10-7 M (E) 0.7 M 18. For the combustion of hydrocarbons like methane, the value of ΔG° is a large negative number. Which of the following best accounts for the fact that these compounds don’t combust on their own without a spark being provided? (A) ΔS° for the combustion is positive. (B) ΔH° for the reaction is negative. (C) The pressure of the reactants is normally too high for the reaction to occur. (D) The hydrocarbons have stronger bonds than the products do. (E) The activation energy for combustion is very large. C2H4(g) + Cl2(g) C2H4Cl2(g) ΔH° = -201 kJ mol-1 19. Given the bond energy values in the table below, determine the bond energy for the pi bond in C2H4. Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1) Cl-Cl 199 C-Cl 330 (B) -459 kJ mol-1 (B) -70 kJ mol-1 (C) 70 kJ mol-1 (D) 260 kJ mol-1 (E) 459 kJ mol-1 2 HBr(g) H2(g) + Br2(g) 20. At a certain temperature, the value of the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the reaction above is 4.0 x 10-6. What is the value of Keq for the reverse reaction at the same temperature? (A) −4.0 × 10-6 (B) 4.0 × 10-6 (C) 4.0 × 106 (D) 2.5 × 105 (E) 2.5 × 106 Open Response Section You may use your periodic table, formula sheet, and calculator. Please write all answers in the space provided. Name: _______________________________________________ Block: ______ Question Score 21 _____/12 22a-d _____/10 22e-g _____/12 23 _____/16 Total _____/50 21. Before answering, please fill in your name and block above. Consider the reaction shown below. C2H5NH2(aq) + H2O(l) C2H5NH3+(aq) + OH-(aq) K = 9.3 x 10-5 (a) Write the equilibrium expression for this reaction. (2 pt) (b) A scientist dissolves 20.0 g of C2H5NH2 in enough water to make 100.0 mL of solution. Find the concentration of OH- in the solution at equilibrium. (10 pt) 2 IF(g) I2(g) + F2(g) ΔH˚ > 0 22. After a 3.2 mole sample of IF(g) is placed in an evacuated 2.0 L container at 1700. K, the reaction represented above occurs. The concentration of IF(g) as a function of time is shown below. Concentration (mol/L) 2 1 [IF] 0 Time (a) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction. (2 pt) (b) What is [IF] at equilibrium? (2 pt) (c) Determine the equilibrium concentrations of F2(g) and I2(g). (4 pt) (d) On the graph above, make a sketch that shows how the concentration of I2(g) changes as a function of time. (2 pt) 22 (cont’d) (e) Calculate the value of the following equilibrium constants at 1700. K. (i) Kc (4 pt) (ii) Kp (f) At a different temperature, the value of Kc for the reaction is 1.2. In an experiment, 0.25 mole of IF(g), 0.10 mole of F2(g), and 0.40 mole of I2(g) are placed in a 1.0 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium at this temperature. Determine whether the equilibrium concentration of IF(g) will be greater than, equal to, or less than the initial concentration of IF(g). Justify your answer. (4 pt) (g) Would each of the following stresses tend to make the amount of I2 increase, decrease, or remain the same? (Circle one.) (1 pt each) Adding F2 increase decrease remain same Adding IF increase decrease remain same Heating the mixture increase decrease remain same Adding Ar increase decrease remain same 6. Use the principles of thermodynamics to answer the following questions. The gas N2O4 decomposes to form NO2 gas according to the equation below. (a) Predict the sign of ΔH˚ for this reaction. Justify your answer. (4 pt) (b) Predict the sign of ΔS˚ for this reaction. Justify your answer. (4 pt) (c) The value of the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction at 25˚C is 0.0050. Will the value of K at 100˚C be greater than, less than, or equal to 0.0050? Explain. (4 pt) Greater Less Equal (d) Given the K value in part (d), which has a greater magnitude at 25˚C, ΔH˚ or TΔS˚? Explain. (4 pt) ΔH˚ is greater TΔS˚ is greater They are equal