Module 14 - Hand & Upper Extremity
advertisement
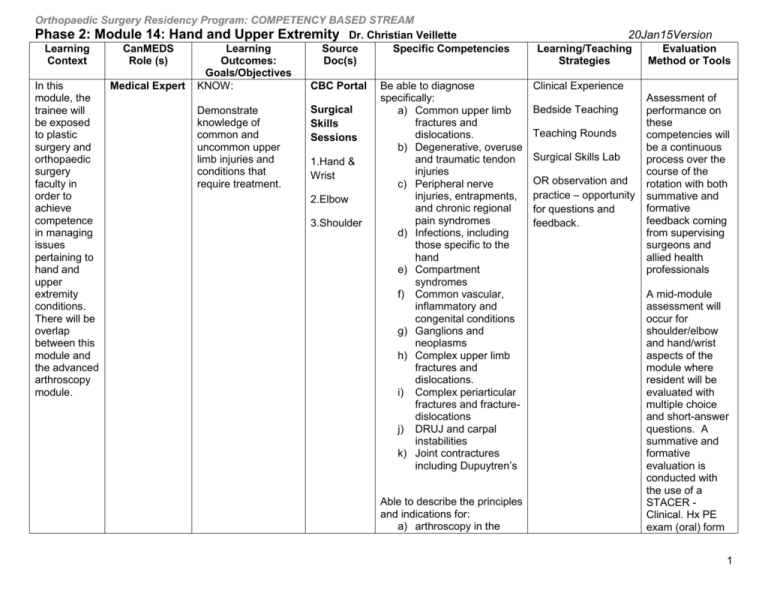
Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives Medical Expert KNOW: CBC Portal Be able to diagnose In this module, the specifically: Surgical trainee will Demonstrate a) Common upper limb be exposed knowledge of fractures and Skills to plastic common and dislocations. Sessions surgery and uncommon upper b) Degenerative, overuse orthopaedic limb injuries and and traumatic tendon 1.Hand & surgery conditions that injuries Wrist faculty in require treatment. c) Peripheral nerve order to injuries, entrapments, 2.Elbow achieve and chronic regional competence pain syndromes 3.Shoulder in managing d) Infections, including issues those specific to the pertaining to hand hand and e) Compartment upper syndromes extremity f) Common vascular, conditions. inflammatory and There will be congenital conditions overlap g) Ganglions and between this neoplasms module and h) Complex upper limb the advanced fractures and arthroscopy dislocations. module. i) Complex periarticular fractures and fracturedislocations j) DRUJ and carpal instabilities k) Joint contractures including Dupuytren’s Able to describe the principles and indications for: a) arthroscopy in the 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies Evaluation Method or Tools Clinical Experience Bedside Teaching Teaching Rounds Surgical Skills Lab OR observation and practice – opportunity for questions and feedback. Assessment of performance on these competencies will be a continuous process over the course of the rotation with both summative and formative feedback coming from supervising surgeons and allied health professionals A mid-module assessment will occur for shoulder/elbow and hand/wrist aspects of the module where resident will be evaluated with multiple choice and short-answer questions. A summative and formative evaluation is conducted with the use of a STACER Clinical. Hx PE exam (oral) form 1 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives shoulder b) arthroscopy in the elbow and wrist c) amputations and arthrodesis d) Brachial plexus and tendon transfers Able to describe the unique principles of treatment of skeletal metastases Able to describe the principles and indications for joint reconstruction of the upper limb Able to describe appropriate splinting and rehabilitation plans 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies Evaluation Method or Tools An end-of-module assessment will occur where resident will be evaluated with an oral examination and multiple choice and shortanswer questions. A summative and formative evaluation will then follow An ITER will be filled out at the end of module at the time of the exit interview During the latter half of the module, the resident will be evaluated via a STACER – Surgical form on the following procedures : 1) carpal tunnel decompression 2) shoulder hemiarthroplasty or arthroscopic 2 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies Evaluation Method or Tools subacromial decompression Medical Expert Able to demonstrate proficient and appropriate use of procedural skills in orthopaedic hand and upper extremity procedures. CBC Portal DO: Specific competencies include performing: Diagnostic and therapeutic injections to the upper limb Closed and open reduction techniques for common upper limb fractures and dislocations Common surgical exposures to the upper limb Tendon rupture repair and reconstruction • Rotator cuff and Distal biceps • Extensor Pollicis Clinical Experience Bedside Teaching Rounds – Medical Topics Surgical Skills Lab OR observation and practice – opportunity for questions and feedback. 3 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives Longus DO DO Joint Instabilities Open/Arthroscopic Shoulder Stabilization AC Instability – acute and chronic Stabilization techniques for elbow or carpal dissociations 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies Evaluation Method or Tools DO Arthroplasty Primary shoulder hemiarthroplasty Radial head arthroplasty DO: DO: DO: Arthroscopy of the upper limb Loose body removal Arthrodeses of the: Shoulder Wrist Digits DO: 4 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives Treatment of joint contractures: Adhesive capsulitis Elbow Dupuytren’s disease DO: Medical Expert Able to manage a pre and post-operative scenario and take the lead where necessary in various procedural circumstances. CBC Portal 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies Evaluation Method or Tools Amputations – traumatic and elective Demonstrate skill in the surgical management of: • Compartment syndromes • Nerve entrapment syndromes • Ganglions • Infections • Diagnostic arthroscopy of the shoulder Demonstrate skill in the management of intra-articular and periprosthetic fractures of the upper limb Clinical Experience Bedside Teaching Rounds – Medical Topics Surgical Skills Lab OR observation and practice – opportunity for questions and feedback. Demonstrate skill in the management of scaphoid 5 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives non-union Communicator Communicator Communicator Communicator Manager KNOW: Able to obtain an informed consent for common upper limb procedures. Obtain an appropriate informed consent for patients undergoing interventions. Demonstrate an understanding of the consent requirements for communication with third party agents Be capable of effective oral and written communication with third party agents such as Workers’ Compensation Insurance and disability insurers Utilize time and resources effectively in order to balance patient care, outside activities and personal lifestyle WSIB – Ask Herb von Schroeder, Director Hand & Surgical DO Able to carry out a corrective osteotomy of the distal radius Effectively complete all necessary forms for WSIB patients Resident to spend time in clinic shadowing supervisor Evaluation Method or Tools Direct Observation Review and assessment of resident forms from clinic 360 of resident in clinic –ITER Resident will review of source documents Powerpoint presentatio n – How to fill out WSIB forms properly EMR – Use of an Learning/Teaching Strategies Supervisor will review form completion by resident and provide time for feedback and questions Sample form – clinical rotator cuff Health Informatics Book/ Ch’s 20Jan15Version Orientation with workers compensation through educational lecture. Prioritize emergent and elective care based on evidence for the benefit of individual patients, populations served and resource availability Resident will meet with supervisor to have one-on-one session to describe an observed inefficiency and be Presentation of how efficiencies in healthcare system can be improved 6 Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 2: Module 14: Hand and Upper Extremity Dr. Christian Veillette Learning CanMEDS Learning Source Specific Competencies Context Role (s) Outcomes: Doc(s) Goals/Objectives considerations. electronic medical Demonstrate leadership when record allocating finite health care resources Manager Establish an Determine inefficiencies in the understanding of healthcare environment and health care resource describe to supervisor and allocation and peers. educational resources Manager Effectively utilize Determine a solution for information inefficiency through the use of technology to a technology. optimize patient care and for continued Recognize the financial self-directed learning. impact of implementing new technologies into clinical practice Manager KNOW: Apply evidence and Demonstrate an management processes for understanding of the cost-appropriate care importance of the allocation of health care resources and how that effects wait list management 20Jan15Version Learning/Teaching Strategies able to provide explanation of possible solutions to inefficiency. Evaluation Method or Tools Lead teaching rounds at the end of rotation 7