Ch 17 Biological Communities Study Guide
advertisement

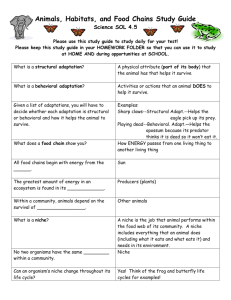
Ch.17 Biological Communities Study Guide Vocabulary Words Climate: prevailing weather conditions in a given area Latitude: reduces the temperature and moisture conditions in a area as it increases Temperature: decrease as elevation increases Savanna: exist in tropical areas, but experience low rainfall Desert: overriding characteristic is scarcity of water Tropical forest: experiences very little differences in seasons Temperate forest: consists of two types - evergreen and deciduous Essay Describe the similarities and differences between the limnetic freshwater zone and the surface of the open sea. Both the limnetic zone and the surface of the open sea are the waters closest to the surface. Both contain algae, plankton, and fish. The limnetic zone is only the freshwater habitats and is far from shore. The surface waters of the open sea can be close to or far from shore and are part of the marine environment. How are freshwater habitats connected to terrestrial habitats? Marshes and wetlands are intermediate habitats between the open water and the land. Can two occupy the same realized niche? Explain – No two species can have the same niche. The principle of competitive exclusion states that if two species are competing for the same resources, the species that uses the resources more efficiently will eventually eliminate the other. Concepts to Know Parasitism is considered a special case of predation. Some interactions among species are the result of a long evolutionary history in which many of the participants evolve with one another over time. A long-term relationship in which both participating species benefit is known as mutualism. Thorns, spines, and secondary compounds are examples of plant defenses. An example of an internal human parasite is a hookworm. Some ants and aphids are mutualistic. All the ways in which a jaguar interacts with its environment make up its niche. Resources for which species compete include living space, light, and food. A niche is an organism’s functional role in an ecosystem. The total niche an organism is potentially able to occupy within an ecosystem is its fundamental niche. When two protest species that use different resources were placed in the same culture tube, both of the species were able to coexist. The principle of competitive exclusion states that if two species are competing, the species that use the resource more efficiently will eventually eliminate the other species locally. Areas that have a high degree of biodiversity experience greater stability in adverse conditions. Predation can increase biodiversity by reducing the numbers of overcrowding prey species. A biome’s characteristics over time are NOT affected by localized disasters.