Review Activity Answers
advertisement

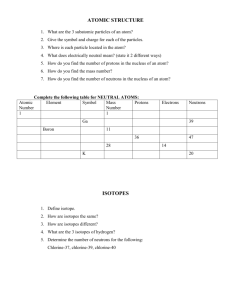
ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1. What are the 3 subatomic particles of an atom? Proton, neutron, electron 2. Give the symbol and charge for each of the particles. p+, e-, n0 3. Where is each particle located in the atom? Protons and neutrons in the nucleus, electrons outside the nucleus 4. What does electrically neutral mean? (state it 2 different ways) # p+ = # e- There is no charge 5. How do you find the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom? Locate the element on the periodic table and look at the atomic number for that element 6. How do you find the mass number? # protos + # Neutrons 7. How do you find the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom? Mass # - atomic # Complete the following table for NEUTRAL ATOMS: Atomic Element Symbol Mass Protons Number Number 1 Hydrogen H 1 1 Electrons Neutrons 1 0 31 Gallium Ga 70 31 31 39 5 Boron B 11 5 5 6 36 Krypton K 83 36 36 47 14 Silicon Si 28 14 14 14 19 Potassium K 39 19 19 20 ISOTOPES 1. Define isotope. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons 2. How are isotopes the same? They have the same atomic # (same # protons) 3. How are isotopes different? They have different mass #’s and different #’s of neutrons 4. What are the 3 isotopes of hydrogen? Protium, deuterium, tritium 5. Determine the number of neutrons for the following: Chlorine-37 (37-17 = 20 n), chlorine-39 (22 n) , chlorine-40 (23 n) WRITING NUCLIDE SYMBOLS 1. 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 # How do you write a nuclide symbol? 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑐 El… “El” represents the element’s chemical symbol # 2. Write the nuclide symbol for the following: Carbon-12 12 C 6 carbon-13 13 𝐶 6 63 copper-63 29 Cu copper-65 65 29 𝐶𝑢 3. How are the isotopes of carbon the same? How are they different? They have the same number of protons…the same atomic # They have different mass #’s and different #’s of neutrons 4. How are the isotopes of copper the same? How are they different? They have the same number of protons…the same atomic # They have different mass #’s and different #’s of neutrons WRITING NUCLIDE NAMES 1. How do you write nuclide names? Name of the element hyphen mass # 2. Write the nuclide name for each of the following: 234 U 92 235 U 92 238 U 92 Uranium-234 Uranium-235 Uranium-238 n=142 n=143 n=146 23 Na+ 11 22 Na 11 Sodium-23 cation n=12 sodium-22 n=11 16 O 8 18 2O 8 Oxygen-16 oxygen-18 anion…b/c of the negative charge..2n=8 n=10 3. How many neutrons does each isotope have?...see under nuclide name BOHR DIAGRAMS 1. Draw Bohr Diagrams for the following: Hydrogen Chlorine…7 valence e- Argon Nitride ion…add 3 more electrons to the outer shell…8 valence e- now Calcium ion…8 valence e- now Boron ion…modify this bohr diagram by removing the 3 electrons in the outer shell, so there are only 2 electrons in the boron ion…2 valence electrons now 2. How many valence electrons does each of the above atoms or ions have? VALENCE ELECTRONS 1. What are valence electrons? e- in the outer most shell of an atom 2. How do you know how many valence electrons an element has? The # of valence electrons are the same as the group # 3. How many valence electrons does each of the following have? 4. Write the ion symbol for each of the elements above. Element name # valence Ion symbol electrons Hydrogen 1 H+ Neon 8 no ion symbol Silicon 4 Si4+ Arsenic 5 Ar3- Calcium 2 Ca2+ Lithium 1 Li+ Phosphorus 5 P3- Aluminum 3 Al3+ IS IT AN ANION OR CATION? 1. What is an anion? A negatively charged particle 2. What is a cation? A positively charged particle 3. Determine whether the following are anions, cations, or neutral: H+ cation…+1 He2 neutral I- anion…-1 Ag+ cation…+1 O2 neutral O2- anion…-2 N3- anion…-3 Mg2+ cation…+2 4. How do you know it is an anion, cation, or neutral? If you see a charge written as a superscript to the right of trhe chemical symbol, then you know it is an ion 5. What is the charge of each of the above ions or atoms?...see above WRITING NAMES OF IONS 1. How do you write the name for cations? Name of the element + the word “ion” 2. How do you write the name for anions? Root name of the element with an “-ide” ending 3. Write the name for each of the following: H+ hydrogen ion Al3+ aluminum ion B3+ boron ion I- iodide Ag+ silver ion As3- arsenide S2- sulfide O2- oxide Na+ sodium ion F- fluoride N3- nitride Mg2+ magnesium ion DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1. Joanie skateboards 3.2 miles across town to get to her friend’s house. How many inches is this? 3.2 mi x 5280 ft x 12 in = 202752 in = 2.0 x 105 inches 1 mi 1 ft 2. A thirsty antelope drinks 2.15 gallons a day. How many liters is this? 2.15 gal x 4 qts x 1 L = 8.13623L = 8.14 L 1 gal 1.057 qts 3. Johhny rollerblades on the boardwalk at 12 mph. How many meters per second is this? 12 mi x 5280 ft x 12 in x 2.54 cm x _ 1 m_ x 1 hr x 1 min = 5.36 m/s= 5.4 m/s 1 hr 1 mi 1 ft 1 in. 100 cm 60 min. 60 sec CALCULATING ATOMIC MASS 1. Look at the table of values of the isotopes of argon. Which value do you think the average atomic mass of argon will be closest to? Why? Argon-40 because it has the largest percent abundance, therefore it contributes the most to the average mass 2. There are 3 isotopes of argon with the following isotopic masses. Calculate the average atomic mass of Argon? Isotope Argon-36 Argon-38 Argon-40 Mass of Isotope 35.97 amu 37.96 amu 39.96 amu % Abundance 0.337% 0.063% 99.60% (35.97) (0.003370) + (37.96) (0.00063) + (39.96) (.9960) = 39.945 = 40 amu *note: percents are expressed in decimal form CALCULATING PERCENT ABUNDANCE Calculate the % abundance for each of the isotopes of copper; the average atomic mass of Copper is 63.55 amu. Isotope Copper-63 Copper-65 Mass of Isotope 62.93 amu 64.93 amu (62.93) (x) + (64.93) (1.00 – x) = 63.55 62.93 x + 64.93 -64.93x = 63.55 -2 x = -1.38 x= 0.69→69% Cu-63 1.00- 0.69 = 0.31 → 31% Cu-65 % Abundance x 1.00 - x