File - EnjoyPhonetics
advertisement

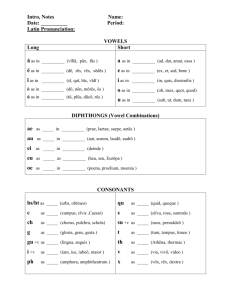
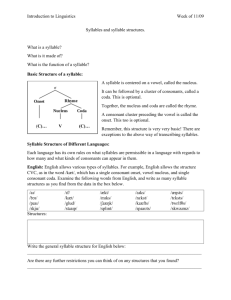
Some phonotactic rules in English /ŋ/ never occurs at the beginning of a syllable and can’t occur after long vowels and diphthongs /w,r,l, j/ occur in second position in consonant sequences at the beginning of words. e.g. "sweep, train, play, music“ when /j/ occurs in an initial consonant cluster the following vowel must be /u/, “pew”, “beautiful” or schwa, “junior” (in some speakers /ɔ/ is allowed as in “cure, pure” /h,w, j/ never occur in syllable final position Syllables 1. A syllable is an organisational unit in phonology. It must always contain a vowel (or a consonant that can function as a vowel such as /m, n, l/) 2. The consonants before the vowel are called the onset of the syllable. 3. The vowel + following consonants are called the rhyme. “scratch” -/skræʧ/ onset = /skr/ rhyme = /æʧ/ English Syllables In English, syllables can contain up to three consonant before the vowel but there is a strict order. The sequence /fricative, stop, approximant/ is the maximum that can occur in a syllable initial consonant cluster e.g. string, square, screech English syllables can contain up to four consonants after the vowel but again there are restrictions on their sequencing. “twelfths” /-lfθs/ “texts” /teksts/ Syllabic structure of English words Speech can be divided into the minimal pronounceable units – syllables There exist two points of view about the syllable: 1) some linguists think that a syllable doesn’t have any functional value; 2) some linguists think that a syllable has a certain linguistic function. The definition of the syllable includes the following points: 1) a syllable is a chain of phonemes 2) a syllable consists of opposites: (vowel-consonants) 3) the nuclear of the syllable is a vowel, the presents of consonants is optional 4) the position of phonemes in the syllable follows specific rules. Syllables in English consist of oppositions: v-c. Vowels are usually syllabic while consonants are not except l,m,n. They become syllabic if they are in an unstressed position, in the end of the word, after a noise consonant, e.g. little, blossom, garden The structure of the syllable can be different because of the number and position of consonants. In English there are 4 types of syllables: 1. open с+v no 2. closed v+с it 3. covered c+v+c note 4. uncovered v oh In Russian the basic type of syllable is open. In English it is closed, the varieties of syllables are 23 and the number of syllables in one English word can be from 1 to 8: come [kʌm] city [sɪtɪ] family [fæməlɪ] simplicity [sɪmplɪsətɪ] incomparability [ɪnkɔmpərəbɪlətɪ] intelligibility [ɪntəlɪʤɪbɪlɪtɪ] A syllable has 2 main function: 1. constitutive – from syllable words and so on are made 2. distinctive – syllables differentiate words.