UDL and Science Lessons
advertisement

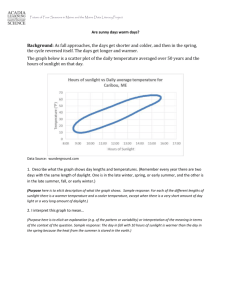
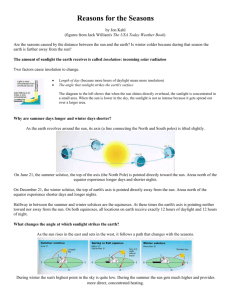
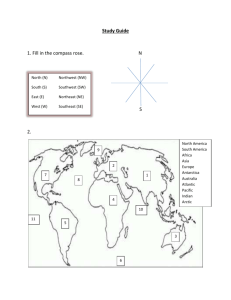
Lessons without Technology Goal: To have students understand that the seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth and the effects of Sunlight on the Earth. Learning Objective: Explain that it is warmer in summer and colder in winter for people in New Jersey because the intensity of sunlight is greater and the days are longer in summer than in winter. Connect these seasonal changes in sunlight to the tilt of Earth’s axis with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. Students will identify relationships between latitude, sunlight, and seasonal change by examining patterns in their research. Formulate a general description of the daily motion of the Sun across the sky based on shadow observations. Explain how shadows can be used to tell the time of day. Gather, evaluate, and represent evidence using scientific tools, technologies, and computational strategies. Present evidence to interpret and/or predict cause-and-effect outcomes of investigations. The Learning Engagement: Identify at local sunrise and sunset times Graph sunlight changes in New Jersey Analyze sunrise/sunset times from locations around the globe Estimate longitude locations using Universal Time Lessons without Technology: Read Chapter 4 Section 1 about longitude/latitude and Universal time from Prentice Hall Book Complete worksheet which identifies various locations and students have to predict the time. Read Chapter 4 Section 2 about the Earth’s axis and northern/southern hemisphere Draw Earth (two times) tilted on its axis in summer and winter. Color to show the summer months and the winter months. Graph sunlight changes in New Jersey given a worksheet with sunrise and sunset times. Evaluation: Answers on worksheets about longitude/latitude Poster activity rubric Graphing worksheet Lessons with Technology Goal: To have students understand that the seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth and the effects of Sunlight on the Earth. Learning Objective: Explain that it is warmer in summer and colder in winter for people in New Jersey because the intensity of sunlight is greater and the days are longer in summer than in winter. Connect these seasonal changes in sunlight to the tilt of Earth’s axis with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. Students will identify relationships between latitude, sunlight, and seasonal change by examining patterns in their research. Formulate a general description of the daily motion of the Sun across the sky based on shadow observations. Explain how shadows can be used to tell the time of day. Gather, evaluate, and represent evidence using scientific tools, technologies, and computational strategies. Present evidence to interpret and/or predict cause-and-effect outcomes of investigations. The Learning Engagement: Use technology to record and analyze local sunrise and sunset times Calculate, graph, and analyze sunlight changes in New Jersey Record, graph, and analyze sunrise/sunset times from locations around the globe Use Universal Time to estimate longitude of locations Interpret and compare data to make predictions Utilize technology and reference materials to research and decipher continent-countrycity clues to pinpoint locations Use technology to create a Prezi presentation Lessons with Technology: Teacher will create an interactive SmartBoard lesson about Universal Time and longitude/latitude Students will use interactive activity to find information about longitude/latitude on two websites: http://geographyworldonline.com/tutorial/lesson1.html http://www.eduplace.com/kids/socsci/books/applications/imaps/maps/g3_u6/index.html Students will use interactive activity to find information about north and southern hemisphere and locations of various countries on two websites: http://www.marcsobservatory.com/mo_whatsit_hemispheres.html http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/encyclopedia/hemisphere/?ar_a=1 Take quiz on mapping skills http://www.teachersfirst.com/globetracker/gt_review/mapskills/mapskills1.cfm Students will use interactive activity to find information about seasons http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/007299181x/student_view0/chapter2/seasons_interactive. html http://www.learner.org/jnorth/tm/mclass/season_simulator.html Create a graph using data about sunrise and sunset times in New Jersey. Each student must log onto website to calculate information. http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/RS_OneDay.php Students will type their findings/information in a journal found in MOODLE Students will create a Prezi presentation UDL Guidelines: Principle I: Provide Multiple Means of Representation Teacher presents information by customizing and differentiating instruction by mixing and matching features to each student's individual needs. In this lesson, the teacher provides multiple representations of the same information by using SmartBoard interactive presentations, websites, apps, gamming, MOODLE, and interactive activities. Principle II: Provide Multiple Means of Action and Expression The teacher provides assistive technology tools for students who require diverse means of expression. The students have choices for how they engage with and demonstrate their understanding of information, or skills. In this lesson, the student uses multiple representations of their knowledge by creating interactive presentations on SmartBoard, Podcast, screen casting, or Prezi. They can create webpage, and use various applications to present their knowledge. Principle III: Provide Multiple Means of Engagement In a classroom there are many students with many different interests and environmental knowledge therefore, there is not one means of engagement that will be optimal for all learners in all contexts. In this lesson, the teacher provides multiple options for student engagement. The teacher has the opportunity to hold the students’ attention because the task emphasizes the individual interests of the student into the lesson. In this lesson, students are able to apply the learned science content and present their knowledge through any medium. This could include, creating interactive presentations on a SmartBoard, using Podcast, screen casting, or Prezi. They can create a webpage, and use various applications to present their knowledge based on their personal interests. Evaluation: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships among fundamental concepts in Earth systems by: Measuring, gathering, evaluating, and sharing evidence with other students. Using basic tools and technology to extend exploration in conjunction with science investigation. Observing, journaling, and predicting during long-term investigation. Using a rubric to evaluate the content knowledge of their presentations (see below) Technology-Based Scoring Rubric for Science Presentations Poor PRESENTATION SKILLS Excellent 1 2 3 4 5 Were the main ideas presented in an orderly and clear manner? ......................................................... Did the presentation fill the time allotted? ........................................................................................... Were the overheads/handouts appropriate and helpful to the audience? .......................................... Did the talk maintain the interest of the audience? .............................................................................. Was there a theme or take-home message to the presentation? ........................................................ Was the presenter responsive to audience questions? ........................................................................ Was proper background information on the topic given? .................................................................... Was the material selected for presentation appropriate to the topic? ................................................ Was enough essential information given to allow the audience to effectively .................................... Was irrelevant or filler information excluded? ..................................................................................... Did the presenter have a clear understanding of the material presented? .......................................... Were the main issues in this area clearly identified? ............................................................................ Were both theoretical positions and empirical evidence presented? .................................... KNOWLEDGE BASE evaluate the topic? CRITICL THINKING Were the strengths and weaknesses of these theories, and the methods used to ............................... Did the presenter make recommendations for further work in this area? ........................................... Did the main conclusions of the presentation follow from the material presented? ........................... Were competing explanations or theories considered and dealt with properly? ................................. gather this evidence adequately explained? OVERALL IMPRESSION .................................................................................................................................................. _______ / 15 COMMENTS TOTAL SCORE _______ / 100