File - Information on Syrian hamsters
advertisement

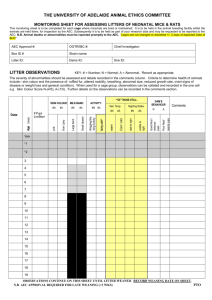
“Information about (Syrian) hamsters” presents ‘Reproduction Continued’ Workbook Level 3 What? This workbook includes a total of 11 questions on reproduction and genetics. The information needed to answer the questions can be found on the corresponding section of the website. Try to answer the questions without looking. How? Some questions have words intentionally missing, add the missing word in capital letters to answer the question. The amount of blank spaces indicates how many letters the word has. Sometimes, a letter or two is also provided as a hint. A single gap _ indicates a number is required to answer the question. When multiple answers are provided, delete the incorrect answers as prompted. For example: Questions: 1) This workbook is based on ‘H _ _ _ _ _ _ S’. 2) Syrian hamsters were first discovered in ‘_’. 3) Syrian hamsters must ‘live in pairs’/’live alone’. (Delete the incorrect answers). Answers: 1) This workbook is based on ‘HAMSTERS’. 2) Syrian hamsters were first discovered in ‘1930’. 3) Syrian hamsters must ‘live alone’. If you would like your answers marked for the opportunity of earning a certificate, email the workbook with your answers to workbooks@hamster-information.com. Please also provide the email address you would like us to reply to, and the name (or pseudonym) to be put on the certificate. This may take up to 7 days. Page 1 – http://www.hamster-information.com/ Questions: 1) Cinnamon fur is represented by ‘p’ - this indicates it is ‘RECESSIVE/DOMINANT. (Delete the incorrect answer). 2) ‘PP’ might be found written on a hamster’s pedigree certificate, this indicates that the hamster has two, one or no ‘cinnamon fur’ alleles? (Delete the incorrect answers). 3) Complete the punnet square below. p P P __ __ p __ __ 4) If two parents both carry one mutant allele at the P locus (Pp) and the mother conceives 16 pups, you would statistically expect _ of the pups to be display Cinnamon in their phenotype. (Use the punnet square from question 3). 5) Using the same scenario detailed in question 5, you would statistically expect _ out of the 16 pups to be heterozygous at the cinnamon locus. 6) Complete the punnet square below for the following pairing: One parent is homozygous for black fur (aa) while the other parent is heterozygous at the black fur locus (Aa) _ _ _ __ __ _ __ __ (Continued on next page) Page 2 – http://www.hamster-information.com/ 7) When considering a dihybrid cross, it is important to carefully calculate the potential allele combinations in a hamsters gametes. If a male hamster (named Shadow) is ‘AaPp’ at the black and cinnamon fur loci, what are the four potential allele combinations in his sperm? AaPp (Sperm) __ __ __ __ 8) If a female hamster (named Sunshine) is ‘AaPp’ at the black and cinnamon fur loci, what are the four potential allele combinations in her ova? AaPp (Ova) __ __ __ __ 9) You mate ‘Shadow’ with ‘Sunshine’; using your gamete tables above, complete the punnet square below. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ (Continued on next page) Page 3 – http://www.hamster-information.com/ 10) If Shadow and Sunshine produced 16 pups, use the punnet square above to determine the following: - Statistically there should be _ Golden coloured pups. - Statistically there should be _ Black coloured pups. - Statistically there should be _ Cinnamon coloured pups. - The colour dove appears when a hamster is homozygous for the black and cinnamon mutations. Statistically there should be _ Dove coloured pups. 11) In your own words, describe why we can only theoretically predict the pup’s phenotypes. That is to say, why could (despite the odds) there be 3 dove pups for example. Answer: Page 4 – http://www.hamster-information.com/