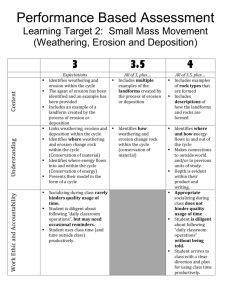
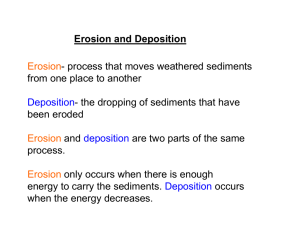
unit xii: erosion, deposition, and landscapes notes packet
advertisement

NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes UNIT XII: EROSION, DEPOSITION, AND LANDSCAPES NOTES PACKET Picture: The Adirondack Mountains in northern New York State. Most rocks found here are metamorphic in origin and over 1 billion years old. The Grenville Orogeny was responsible 1 |for P athe g eobserved changes recorded in the rocks. NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes After UNIT XII you should be able to: o Understand how sediments are transported in a stream, use the Relationship of Transported Particle Size to Water Velocity reference table chart, and recognize the characteristics of sediments that have been weathered in a stream o Understand basic erosional and depositional features of a river o Understand the relationship between particle shape and settling rate o Understand how climate impacts landscapes near rivers o Match topographical features with stream drainage patterns o Recognize differences between glacial and river sediments o Recognize differences between valleys eroded by glaciers and rivers o Recognize common erosional and depositional features of glaciers o Understand how erosion and deposition function within systems driven by wind, shoreline current, and mass movement and recognize common features of these systems o Recognize common landscape features of New York State and how they formed o Be able to use the Generalized Landscape Regions of New York State map UNIT XII vocabulary you should be able to use and understand: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Erosion Sediment Gravity Velocity Particle Transport Boulders Cobbles Sand Silt Clay Dissolved minerals Deposition Diameter Morphology Transect River channel Meander Oxbow lake o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Accumulation Unsorted sediments Angular Continental glacier Ice sheet Valley glacier Alpine glacier Abrasion Striations Polishing Plucking V-shaped valley U-shaped valley Finger lakes Drumlins Erratics Kettle lakes Eskers Kames o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Moraines Outwash plain Cirque Arete Horn Sand dunes Long-shore drift Mass movement Landslide Slump Creep Mudflow Mountains Fault-block mountains Folded mountains Landscape region Plateau Plain Valleys o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Meander scar Rounded Sorted sediments Suspended sediment Settling rate Delta Alluvial fan Downcutting Stream drainage pattern Orientation Resistance Weathering Lowlands Arid Canyons Humid Topography Glacier Escarpment Tying it together… You now have had significant experience learning about the variety of ways rocks form, and some unique formations associated with the study of plate tectonics. You are most familiar with what are known as uplifting forces. For example, the contribution of plate convergence to volcanic mountain ranges. New crust is formed, old crust is recycled back into the Earth. The focus of this unit seeks to broaden your understanding of leveling forces, those which contribute to transport of materials on the Earth’s surface in conjunction with your prior knowledge of weathering. 2|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Our weathering unit taught us that rocks can be broken down by both physical and chemical means based on climate and bedrock type. Understanding how Earth materials erode, becomes the next step in truly understanding the dynamic nature of landscapes. Basic Principles of Erosion ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ There are 5 distinct agents of erosion: _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Erosion in moving water varies greatly within a river, and between rivers. Lighter, less dense sediment is first to be transported by moving water. Transport of Sediments in Streams Sediment transport is dependent on 2 variables: __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Describing Rock Particle Size _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Increasing Size Rock Particles are categorized into 6 types: *Dissolved minerals are also transported, although they are not visible 3|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Sediment Transport Chart _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ If water velocity falls below that level, sediment is deposited on the bottom of the river Using the Chart _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Water Velocity and Stream Morphology Water velocity is not a constant along a river nor is it constant across a transect In other words, the stream is faster in some areas, slower in others Water Velocity and Stream Morphology Water, for the most part, flows in a straight line and will do so until redirected by the stream channel. Water also over time dictates how the channel changes. Because this is true, rivers have different channel shapes at different locations In a straight line path, rivers are fastest in the middle, leaving a channel deepest in the center __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Stream Meanders Over time, erosion at the outside of the bend causes the stream channel to drift. When the old channel is cut off, an oxbow lake is formed. If the oxbow dries up, it becomes what is known as a meander scar 4|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Sorting of Sediments Faster moving water transports smaller sediments Therefore, a stream bottom will have larger particles on the bottom in faster moving water and smaller particles on the bottom in slower moving water _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Shape and Density of Deposited Sediments When water velocity slows, the shape and density of sediment suspended is important when it comes to the rate that the particles are deposited (settling rate) __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Using Principles of Deposition to Find Gold You can pan for gold and find it in New York State streams, however a strange law prohibits you from keeping what you find. Most gold in the state was transported by glaciers and ground down into fine dust and then concentrated in streams, although nuggets are found on occasion. Since gold is high in density, it settles first when water slows. When panning for gold, focus on cracks or joints in bedrock within the stream, and on the inside of meanders. Rivers Entering Lakes and Oceans The deposition of sediments at the mouth of a river results in the formation of a delta or alluvial fan _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Stream Valley Shape ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Drainage Patterns Looking at maps and examining rivers often tells us something about the rock strata beneath. Stream drainage patterns are dictated by: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Differences in Elevation Higher elevations with steep slopes result in deep ‘V’ shaped valleys _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Drainage Topography in Arid Regions Weathering in dry regions is generally a very slow process. The majority of weathering and erosion takes place in the river channel. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Drainage Topography in Humid Regions _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Common occurrence in NYS Drainage Topography _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Mate these with an overhead pattern Glaciers New York State owes its many unique landforms to the presence of glaciers in the past. Evidence of repeated glacial events surrounds us in western New York. Glaciers are responsible for both erosional and depositional features. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 6|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Types of Glaciers For our purposes, there are 2 types of glaciers that we are concerned with: _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Glacial Presence in NYS A massive glacier covered New York (most recently around 10,000 years ago), and it is important to understand how it shaped landforms in the area The glacial movement map (with gray arrows) shows directional flow of the recent surges of ice Glacial Weathering Abrasion is the dominant form of weathering underneath a glacier _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ This sediment may also result in the polishing of bedrock Glaciers also pluck rock masses in their base and carry them along Glacial Erosion As glaciers erode a valley, they leave evidence of having been there ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Finger Lakes Glacial erosion can leave behind a variety of observable features _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Satellite image (right) of the Finger Lakes region of New York State and the inferred glacial movement that produced them (left) 7|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Drumlins Elongated hills called drumlins are also found in areas that have undergone glaciation. The steeper end is on the side where the glacier approached, the tapered end is the side the glacier was moving. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Our Chimney Bluffs field trip was to one of the thousands of drumlins found in central and western New York (image shows high lake level after glacial melt) Erratics Very large boulders that do not match local bedrock type (transported) or are found in awkward elevations or places were likely transported there by a glacier. This erratic is in Central Park sitting on top of striated bedrock, another piece of evidence for glaciation. Kettle Lakes _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Devil’s Bathtub in Mendon Ponds Park is a kettle lake, one of a few that can be found there Eskers Long, winding hills of sediment deposited by streams beneath a glacier _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 8|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Kames Rocky debris that is deposited in crevasses within a glacier to form a hill. A kame in Mendon Ponds Park is the highest point in Monroe County. Kames, eskers, and kettles can all be found in Mendon Ponds Park. Moraines Moraines are long hills that are composed of material that a glacier has pushed or pulled along _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ The Valley Heads Moraine in the Finger Lakes Region represents the extent of the last glacial advance and prevents southward drainage of the lakes The Pinnacle Hills Range in Rochester – A series of hills caused by a sudden resurgence of ice depositing sediment and home to many radio and telecommunication towers Outwash Plain An outwash plain is where streams flow out of the glacier as it melts. The plain is relatively flat with sorted and rounded sediments due to abrasion in the streams. Cirques, Aretes, Horns All features found in mountainous areas (such as the Adirondack region) once covered by glaciers Horn: Sharp point at mountain peak Cirque: Bowl-shaped depression caused by abrasion Arete: Sharp ridge carved out of the mountainside Wind Erosion and Weathering ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 9|Page NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Wind Deposition _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Wave Erosion and Weathering Abrasion is the dominant form of weathering along beaches _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Long Shore Current Long shore currents flow parallel to the beach. This flow steadily drags sediments along the shore in what is called long shore drift. Mass Movement The final, though less substantial type of erosion is called mass movement. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Landslide Landslide is a commonly used term for the movement of a mass of bedrock or loose soil and rock down the slope of a hill, mountain or cliff. Creep _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Slump Blocks of land that have tilted and moved downhill along a surface that curves into the slope Mudslides/Flows _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 10 | P a g e NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Weathering, erosion, deposition, plate tectonics, folding and faulting all contribute to the beautiful landscapes around us, many of which can be found in New York. Landscapes Features of NYS _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Mountains ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ NYS Example: Mount Marcy (Adirondack Mountains) The Adirondack Mountains are part of an area which has been uplifted and domed upward and continues to do so. They are not volcanic in origin and are comprised mostly of metamorphic and intrusive igneous rocks. Other Types of Mountains Folded Mountains form when compression occurs typically during a tectonic collision Fault Block Mountains occur when faults (lines of breakage) allow rock on either side to move up or down relative to the opposite side Plateau _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ NYS Example: Allegheny Plateau 11 | P a g e NYS Regents Earth Science UNIT XII: Erosion, Deposition, and Landscapes Plains _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Example: Erie-Ontario Lowlands, City of Rochester Valleys Valleys can be formed from erosion by rivers, glaciers, in between folds in bedrock, or where a fault block has fallen down. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Ridges A chain of mountains or hills that form a crest for some distance Folded bedrock in Pennsylvania has formed ridges along the folds Ridges are sometimes lines of resistant bedrock Escarpments Escarpments are long cliffs formed by erosion or faulting Land is relatively flat on either side __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ NYS Landscape Map Use this map to identify major landscape regions in NYS For example: Which landscape region is Rochester located in? Answer:__________________________ 12 | P a g e